Security Policy Administrators, Auditors, and Application Auditors can run an entitlement report.
To export the data from an Entitlement report
-
Navigate to Reports > Entitlements.
-
From the top of the Entitlements page, select the tab for User, Asset, or Account.
NOTE: The number indicated in the tab title shows the number of unique users, assets, or accounts. When you enter search criteria for the report, the number displayed on the tab will adjust accordingly.
-
(Optional) Apply any desired filters to the table.
-
You can then select to either export the data for all listed items or the data for a single item:
-
To export data for all items, select 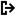 Export on the toolbar.
Export on the toolbar.
-
To export data for a single item, select an item and click  View Details. From the details dialog, select
View Details. From the details dialog, select 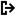 Export.
Export.
-
From the Export dialog, select to export the data as either a JSON or CSV file. For more information, see Exporting data. The time is set according to the user time zone.
-
Click Export to generate the report file.
Security Policy Administrators, Auditors, and Application Auditors can export a user entitlement report that also includes detailed information on each of the associated accounts.
To export a detailed user entitlement report
-
Navigate to Reports > Entitlements.
-
From the top of the Entitlements page, select the User tab.
NOTE: The number indicated in the tab title shows the number of unique users. When you enter search criteria for the report, the number displayed on the tab will adjust accordingly.
-
(Optional) Apply any desired filters to the table.
-
Click the  button to export a CSV file containing the data.
button to export a CSV file containing the data.
Asset Administrators, Auditors, and Application Auditors can run an ownership report.
To export the data from an Ownership report
-
Navigate to Reports > Ownership.
-
From the top of the Entitlements page, select the tab for User, Asset, Account, Partition, or Tag.
NOTE: The number indicated in the tab title shows the number of unique users, partitions, assets, accounts, or tags. When you enter search criteria for the report, the number displayed on the tab will adjust accordingly.
-
(Optional) Apply any desired filters to the table.
-
You can then select to either export the data for all listed items or the data for a single item:
-
To export data for all items, select 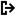 Export on the toolbar.
Export on the toolbar.
-
To export data for a single item, select a listed item and click  View Details. From the details dialog, select
View Details. From the details dialog, select 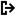 Export.
Export.
-
From the Export dialog, select to export the data as either a JSON or CSV file. For more information, see Exporting data. The time is set according to the user time zone.
-
Click Export to generate the report file.
Safeguard for Privileged PasswordsAppliances can be clustered to ensure high availability. Clustering enables the recovery or continuation of vital technology infrastructure and systems following a natural or human-induced disaster. This reduces down time and data loss.
Another benefit of clustering is load distribution. Clustering in a managed network ensures the load is distributed to ensure minimal cluster traffic and to ensure appliances that are closest to the target asset are used to perform the task. The Appliance Administrator defines managed networks (network segments) to effectively manage assets, account, and service access requests in a clustered environment to distribute the task load.
Primary and replica appliances
A Safeguard for Privileged Passwords cluster consists of three or five appliances. An appliance can only belong to a single cluster. One appliance in the cluster is designated as the primary. Non-primary appliances are referred to as replicas. All vital data stored on the primary appliance is also stored on the replicas. In the event of a disaster, where the primary appliance is no longer functioning, you can promote a replica to be the new primary appliance. Network configuration is done on each unique appliance, whether it is the primary or a replica.
The replicas provide a read-only view of the security policy configuration. You cannot add, delete, or modify the objects or security policy configuration on a replica appliance. On the replica; you can perform check and change operations for passwords and ssh keys, set password, and set ssh key (both imported and generated). Users can log in to replicas to request access, generate reports, or audit the data. Also, passwords, SSH keys, and sessions can be requested from any appliance in a Safeguard cluster.
Supported cluster configurations
Current supported cluster configurations follow.
- 3 Node Cluster (1 Primary, 2 Replicas): Consensus is achieved when two of the three appliances are online and able to communicate. Valid states are: Online or ReplicaWithQuorum. For more information, see Appliance states.
- 5 Node Cluster (1 Primary, 4 Replicas): Consensus is achieved when three of the five appliances are online and able to communicate. Valid states are: Online or ReplicaWithQuorum. For more information, see Appliance states.
Consensus and quorum failure
Some maintenance tasks require that the cluster has consensus (quorum). Consensus means that the majority of the members (primary or replica appliances) are online and able to communicate. Valid states are: Online or ReplicaWithQuorum. For more information, see Appliance states.
Supported clusters have an odd number of appliances so the cluster has a consensus equal to or greater than 50% of the appliances are online and able to communicate.
If a cluster loses consensus (also known as a quorum failure), the following automatically happens:
- The primary appliance goes into Read-only mode.
- Password and SSH key check and change is disabled.
When connectivity is restored between a majority of members in a cluster, consensus is automatically regained. If the consensus members include the primary appliance, it automatically converts to read-write mode and enables password and SSH key check and change.
Health checks and diagnostics
The following tools are available to perform health checks and diagnose the cluster and appliances.
- Perform a health check to monitor cluster health and appliance states. For more information, see Maintaining and diagnosing cluster members.
- Diagnose the cluster and appliance. You can view appliance information, run diagnostic tests, view and edit network settings, and generate a support bundle. For more information, see Diagnosing a cluster member.
- If you need to upload a diagnostic package but can't access the UI or API, connect to the Management web kiosk (MGMT). The MGMT connection gives access to functions without authentication, such as pulling a support bundle or rebooting the appliance, so access should be restricted to as few users as possible.
Shut down and restart an appliance
You can shut down and restart an appliance.
Run access request workflow on an isolated appliance in Offline Workflow Mode
You can enable Offline Workflow Mode either automatically or manually to force an appliance that no longer has quorum to process access requests using cached policy data in isolation from the remainder of the cluster. The appliance will be in Offline Workflow Mode.
Primary appliance failure: failover and backup restore
If a primary is not communicating, perform a manual failover. If that is not possible, you can use a backup to restore an appliance.
Unjoin and activate
If the cluster appliances are able to communicate, you can unjoin the replica, then activate the primary so replicas can be joined.
Cluster reset
If the appliance is offline or the cluster members are unable to communicate, you must use Cluster Reset to rebuild the cluster. If there are appliances that must be removed from the cluster but there is no quorum to safely unjoin, a cluster reset force-removes nodes from the cluster. For more information, see Resetting a cluster that has lost consensus.
Factory reset
Perform a factory reset to recover from major problems or to clear the data and configuration settings on a hardware appliance. All data and audit history is lost and the hardware appliance goes into maintenance mode.
You can perform a factory reset from:
Export on the toolbar.
View Details. From the details dialog, select
Export.

 button to export a CSV file containing the data.
button to export a CSV file containing the data.