Configuring a front-end authentication method
Topics:
Microsoft Active Directory authentication
Configuring smart card authentication
Microsoft Active Directory LDS
Windows Azure Active Directory authentication
Before users and administrators can log in to Cloud Access Manager you will need to configure a Front-end Authentication method. Typically this will involve configuring the Microsoft Active Directory authenticator to authenticate users to your domain, but equally you can configure the SAML or WS-Federated authenticator to authenticate users to a different security authority.
Figure 1: Cloud Access Manager
Microsoft Active Directory authentication
To configure Microsoft Active Directory front-end authentication
- Log in to the Administration Console and select Add New from the Front-end Authentication section on the home page.
- Select Microsoft Active Directory, then click Next.
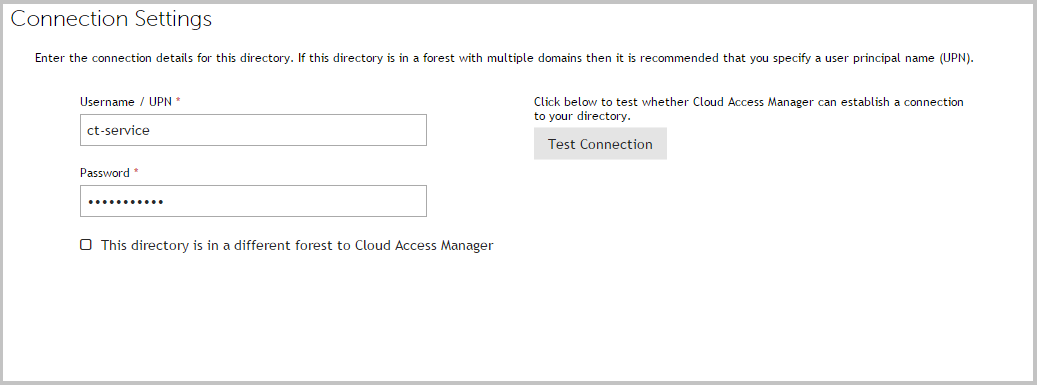
- Enter the full user principal name (UPN), for example johndoe@domain.org, and password of a Windows domain account that has read access to all user and group objects in the forest (usually a regular user account belonging to the Domain Users group is sufficient).
-
Click Test Connection. This will test that Cloud Access Manager can connect to the domain using the credentials provided. When successful, click Next.
-
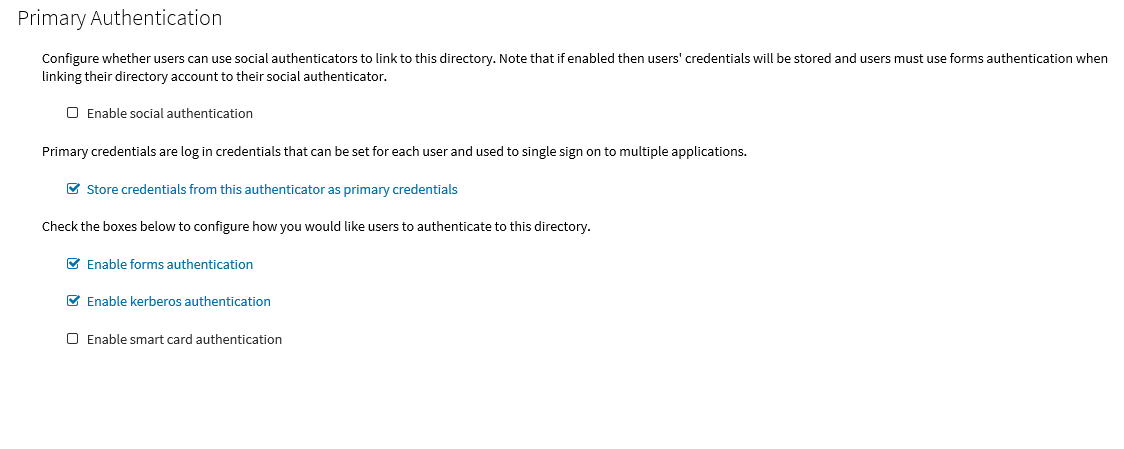
The settings on the Primary Authentication screen are split into three sections. When complete, click Next.
The first section is used to determine whether or not users are allowed to use social authenticators, for example Facebook or Google, and link to the selected authenticator when authenticating to Cloud Access Manager.
The second section determines whether users’ credentials are stored for accessing other applications. If selected, the credentials used to authenticate to Cloud Access Manager are stored as the Primary Credentials in the user’s Password Wallet. Please refer to Primary credentials for details.
The third section is used to determine how users are challenged for their Windows credentials, you must choose at least one option. Cloud Access Manager checks for credentials presented in the following order of precedence:
-
Enable kerberos authentication — Cloud Access Manager will check for a Kerberos ticket generated during Windows domain login and supplied by the browser. If the Kerberos ticket is present and valid, then the user will be successfully logged in.
Successful Kerberos authentication requires correct configuration of the user's browser. Please refer to Integrated Windows Authentication for details. In addition some browsers do not support Kerberos authentication. Please refer to the One Identity Cloud Access Manager Installation Guide for browsers that support Integrated Windows Authentication.
- Enable smart card authentication — Users are given the opportunity to present an X.509 certificate in order to log in to Cloud Access Manager. The X.509 certificate may be located on a smart card or in the client computer's certificate store. If the certificate is invalid or expired the login attempt will be rejected. Please refer to the section Configuring smart card authentication for details.
- Enable forms authentication — Users are prompted for their Active Directory username and password using a login form.
NOTE: If you enable social authentication, storing credentials from the authenticator is required, this in turn requires that forms authentication is the only enabled authentication method. Storing credentials is required as Cloud Access Manager needs to verify if the linked account used for primary authentication is still valid, for example the account is not disabled, or the password has not expired when authenticating using a social authenticator. If a user attempts to authenticate with a social authenticator and the linked account is not valid, the user will be prompted to enter the correct credentials for the primary authenticator.
NOTE: If you enable social authentication, we recommend that you set linked accounts to have a long password expiry, this allows seamless authentication using the social authenticator.
-
-
If you require two factor authentication each time users authenticate to Cloud Access Manager, select Use two factor authentication for all applications from the Two factor authentication mode list. Select the method of authentication from the Type of two factor authentication list.
For information on how to configure the various authentication types or how to configure two factor authentication only for specific users or applications, refer to Configuring step-up authentication. When complete, click Next
-
In the Authenticator Name field, enter the name that will be used to identify the authenticator within Cloud Access Manager, then click Finish.
NOTE: This name will be seen by Cloud Access Manager users during authentication if multiple authentication methods have been configured.
-
You have now created the front-end authentication method. Click Edit Roles.
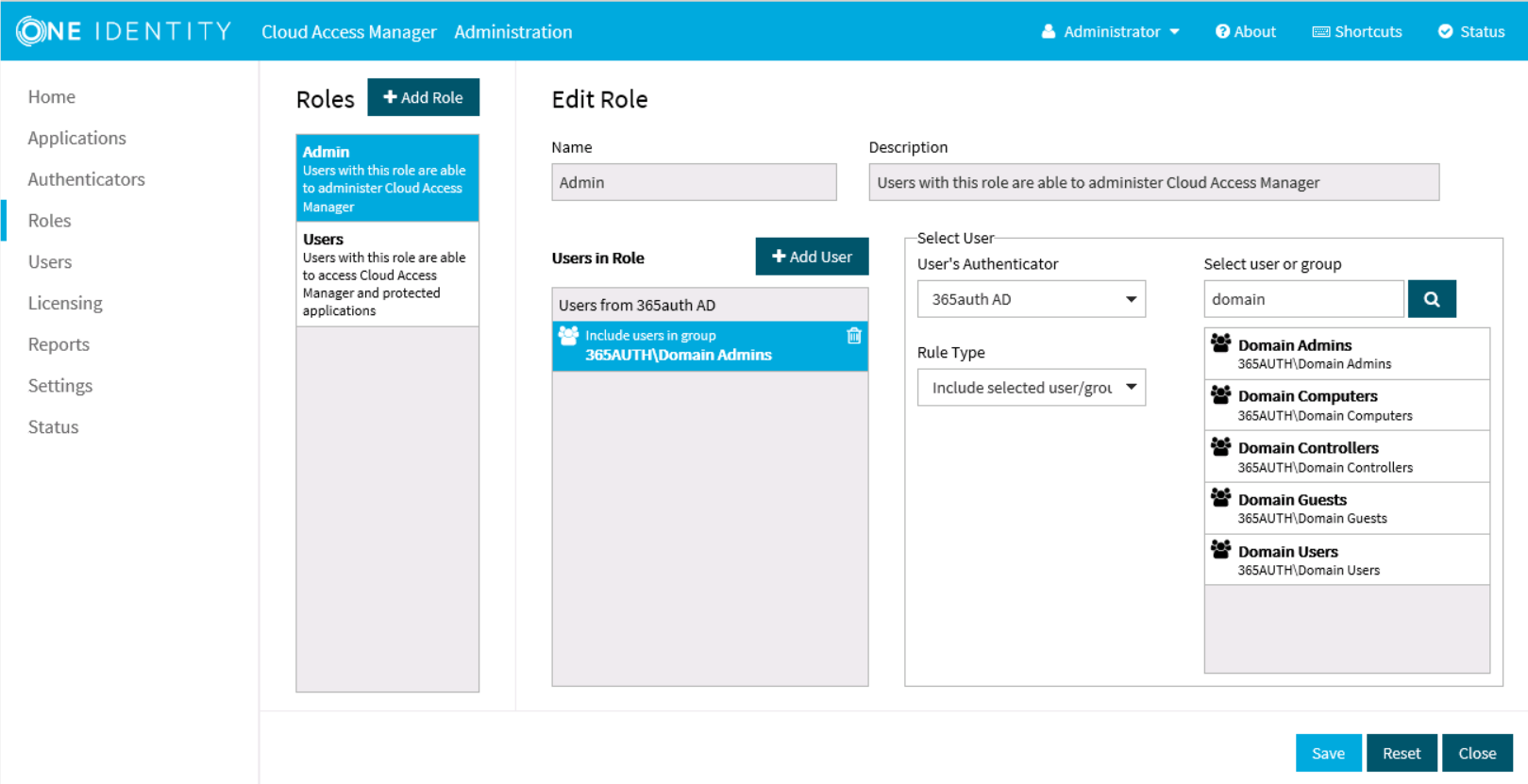
Before Cloud Access Manager administrators and users can log in to Cloud Access Manager using their Active Directory credentials, you must tell Cloud Access Manager how to identify administrators and users based on their Active Directory group membership. For example, the Domain Admins group for Cloud Access Manager administrators and the Domain Users group for regular Cloud Access Manager users.
- Click Admin.
-
Click +Add User.
- Select the new Active Directory authentication method from the list.
- Use the search box to locate the group whose members are to be granted access to the Cloud Access Manager Administration application, then select the group from the list.
- Click Save.
- Now repeat the process for the Cloud Access Manager users. Click Users.
- Click +Add User.
- Select the new Active Directory authentication method from the list.
- Select a group from the list whose members are to be granted access to the Cloud Access Manager application portal.
- Click Save.
-
Click Close to return to the Cloud Access Manager Administration Console. The configuration is now complete. Cloud Access Manager administrators and users can now log in to Cloud Access Manager using their Active Directory credentials.
NOTE: The Active Directory authentication method supports single sign-on (SSO) using Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA) to the Cloud Access Manager application portal for users signed into a domain connected workstation. The next section describes how to configure Cloud Access Manager for Integrated Windows Authentication.
Configuring Cloud Access Manager for Integrated Windows Authentication
The Active Directory front-end authentication method supports Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA) to provide single sign-on (SSO). This allows users signed into a domain connected workstation using their Active Directory account access to their Cloud Access Manager portal without re-entering their credentials.
To enable users to access the Cloud Access Manager portal without entering their Active Directory credentials, the following additional steps are required.
Configuring the Cloud Access Manager service account for SSO
|
|
NOTE: This step is not required when using the Proof Of Concept (POC) installation type. This uses the built-in system account rather than a dedicated service account. |
- To enable the user's web browser to authenticate the user with Cloud Access Manager using Kerberos, the browser must first identify the service account used to run Cloud Access Manager. The user’s browser must authenticate with the Cloud Access Manager service account. This is achieved by configuring a Service Principal Name (SPN) for the service account that maps the Cloud Access Manager Proxy hostname to the Cloud Access Manager service account name.
- To create an SPN, you need the name of the service account specified during the Cloud Access Manager installation and the hostname assigned to the proxy for the Cloud Access Manager portal. This is the account name and the hostname entered in the section Installing Cloud Access Manager, in the One Identity Cloud Access Manager Installation Guide.
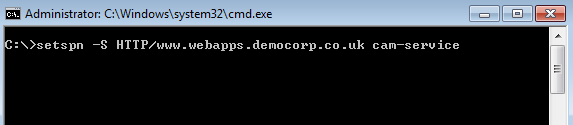
- On the Cloud Access Manager STS host, open a command prompt window and run the following command:
setspn -S HTTP/<hostname> <account>
Where <hostname> is the hostname assigned to the proxy for the Cloud Access Manager portal and <account> is the name of the service account specified during the Cloud Access Manager installation.
For example:
Configuring Microsoft Internet Explorer to single sign-on to the Cloud Access Manager portal
- Open the Cloud Access Manager application portal using Internet Explorer.
- Make a note of the Cloud Access Manager application portal hostname displayed in the address bar.
-
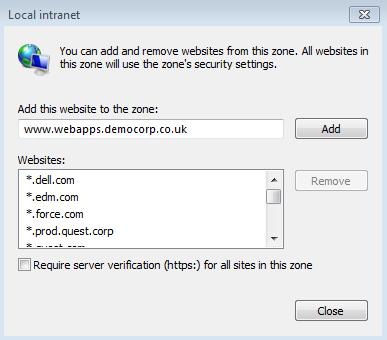
Add Cloud Access Manager to Internet Explorer's Local intranet zone. To do this, click Tools |Internetoptions | Security | Local Intranet | Sites | Advanced. Verify that the website address displayed matches the Cloud Access Manager application portal address noted in Step 2, then click Add.
-
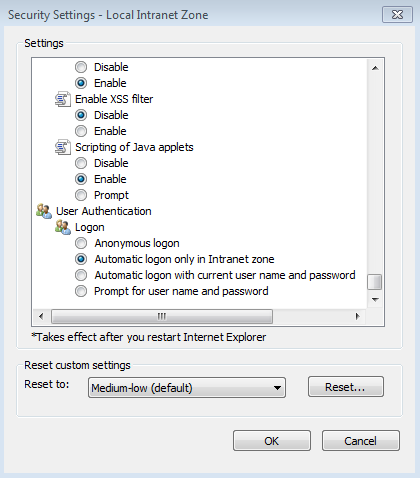
Next, click Tools | Internet options | Security | Local Intranet | Custom level to verify that the local Intranet zone has the default logon option of Automatic logon only in Intranet zone selected.
-
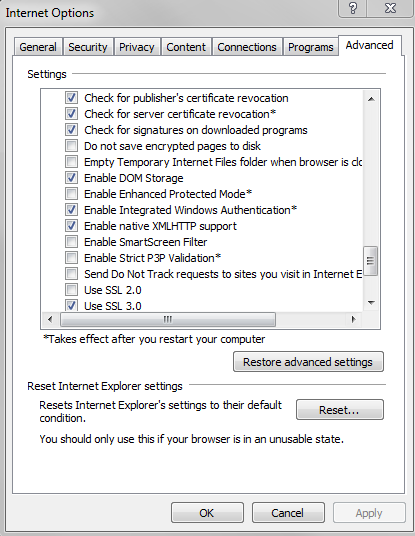
Check that Enable Integrated Windows Authentication is selected in the Internet Explorer Advanced panel.
- Close Internet Explorer.
- You should now be able to access Cloud Access Manager without providing a username and password in Internet Explorer.
Configuring Google Chrome to single sign-on to the Cloud Access Manager portal
- Open the Cloud Access Manager application portal using Google Chrome.
- Make a note of the Cloud Access Manager application portal hostname displayed in the address bar.
-
Add Cloud Access Manager to the Google Chrome local intranet zone. To do this, click the Chrome menu Customize and control Google Chrome | Settings | Show Advanced Settings... | Network | Change proxy settings... This will open Internet Explorer's Tools |Internet options | Connections.
NOTE: Google Chrome uses Internet Explorer’s Integrated Windows Authentication settings for Kerberos configuration.
- Next, click Security | Local Intranet | Sites | Advanced. Verify that the website address displayed matches the Cloud Access Manager application portal address noted in Step 2, then click Add.
- Next, follow from Step 4 in the section Configuring Microsoft Internet Explorer to single sign-on to the Cloud Access Manager portal.
- Close Google Chrome.
- You should now be able to access Cloud Access Manager without providing a username and password in Google Chrome.
Configuring Mozilla Firefox for Integrated Windows Authentication
- Open the Cloud Access Manager application portal using Firefox.
- Make a note of the hostname displayed in the address bar.
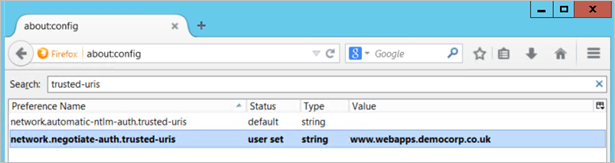
- Type about:config into the address bar and press enter.
- Search for the setting network.negotiate-auth.trusted-uris
-
Double click the network.negotiate-auth.trusted-uris setting and edit it by entering the hostname of the Cloud Access Manager application portal noted in Step 2. If the setting already contains a value, separate the existing and new values with a comma. The value entered into this setting should contain only the hostname of the application portal and should not contain the https:// protocol prefix or the portal path.
- Close Firefox.
- You should now be able to access Cloud Access Manager without providing a username and password in Firefox.
Configuring smart card authentication
Cloud Access Manager can be configured to require your Microsoft Active Directory users to present an X.509 Certificate as a means of authentication. The certificate can be stored on a standards-based smart card or in the user’s local certificate store.
|
|
NOTE: You must be logged in to Cloud Access Manager using the fallback admin login if you wish to enable smart card authentication. |
To configure smart card authentication
-
On the Primary Authentication page ensure that Enable smart card authentication is selected. In this example we will not allow other authentication methods.
NOTE: If smart card authentication is enabled, users primary credentials will not be populated on user login. Users will need to populate their primary credentials manually in a one time task, either in the Cloud Access Manager Password Wallet, or when they first access an application that requires their primary credentials. This applies to other Front-end Authenticators that do not provide a user password on login, for example Kerberos authentication or SAML federation.
-
Select the Enable certificate revocation list checking box to cause Cloud Access Manager to check the Certificate Authority's Certificate Revocation List (CRL) to ensure the user’s certificate has not been revoked. If the user's certificate has been revoked, the login request will be denied.
NOTE: Cloud Access Manager will use the CRL location defined within the user’s certificate to check whether it has been revoked. The location can be found in the certificate field “CRL Distribution Points”. The STS host must have network connectivity to the host specified in this field in order to perform a CRL check. If the host is not contactable then all X.509 certificate authentications will fail if this option is switched on.
NOTE: If certificate revocation list checking is enabled then the root CA certificate must be installed in the Local Computer\Trusted Root Certification Authorities folder in the Windows certificate store of all Cloud Access Manager STS hosts. Refer to Microsoft documentation on how to use the Certificates.msc snap-in to import certificates into the Windows certificate store. If you are using the Microsoft Certificate Authority the root CA certificate will be installed automatically on all hosts within the domain.
Cloud Access Manager must redirect the user's browser to another port in order to perform an X.509 certificate authentication, the default port used is 8443. You can change this if 8443 is being used by another service on the Cloud Access Manager host. Your firewall(s) will also need to be updated to allow users to access the proxy hosts using 8443 in addition to the standard ports 80 and 443.
- Export the certificate from your Certificate Authority in .pem or base-64 encoded format, copy it to the Cloud Access Manager STS host and upload it using the Choose File control on this page. In order to perform X.509 certification authentication, the public signing certificate of the root Certificate Authority must be uploaded into Cloud Access Manager.
- Follow the front-end authentication wizard to completion.
Configuration of smart card authentication for Microsoft Active Directory front-end authentication is now complete.
To test your smart card authentication setup
- Follow Microsoft documentation to enroll a certificate for a user in your Active Directory forest.
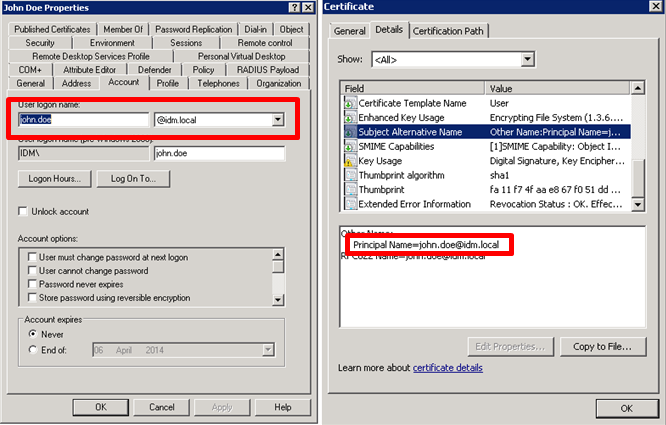
- Open the certificate and verify that the Subject Alternative Name contains a Principal Name value that matches the user’s User Principal Name (UPN) defined in Active Directory. This certificate value is used to locate the user in Active Directory.
- To determine the User Principal Name, open the user object in Active Directory Users and Computers.
-
Click the Account tab and concatenate the User logon name with the domain name that follows it, as shown below. Click Next.
LDAP authentication
To configure LDAP front-end authentication
- Log in to the Administration Console and select Add New from the front-end Authentication section on the home page.
-
Select LDAP, then click Next. The Connection Settings page is displayed.
- In the Comma separated list with optional ports field, enter either a single host or a comma separated list of hosts, including the port. The default port is 389 (or 636 if the Use secure LDAP? box is selected). If you want to use a different port, it should be explicitly specified on a per host basis.
-
In the DN of User to Bind With field, enter a user account to use to connect to the directory, for example,
cn=administrator,cn=users,dc=company,dc=com
The account must have the appropriate privileges to allow it to read user and group information from the directory.
- In the Object Class of Users field and Object Class of Groups field, enter appropriate object classes to distinguish users and groups.
-
In the Attribute Mappings section, complete the attributes as required. The User’s Unique ID Attribute field and Group’s Unique ID Attribute field are usually left empty. They will default to the object’s distinguished name.
NOTE: The User’s Unique ID Attribute is used to link to the Group’s Members Attribute, so it is important that they are in the same format.
- When you have entered the required configuration information, click Test Connection to verify the configuration. Click Next.
-
The settings on the Primary Authentication screen are split into two sections. When complete, click Next.
- Store credentials from this authenticator as primary credentials — Determines whether the user's credentials are stored for accessing other applications. If the box is selected, the credentials used to authenticate to Cloud Access Manager are stored as the Primary Credentials in the user's Password Wallet. Please refer to Primary credentials for details.
- Enable social authentication — Determines whether users are allowed to use social authenticators, for example Facebook or Google, and link to the selected authenticator when authenticating to Cloud Access Manager.
NOTE: If you enable social authentication, it may be beneficial to set linked accounts to have a long password expiry, this allows seamless authentication using the social authenticator.
NOTE: If you enable social authentication, storing credentials from the authenticator is required, this in turn requires that forms authentication is the only enabled authentication method. Storing credentials is required as Cloud Access Manager needs to verify if the linked account used for primary authentication is still valid, for example the account is not disabled, or the password has not expired when authenticating using a social authenticator. If a user attempts to authenticate with a social authenticator and the linked account is not valid, the user will be prompted to enter the correct credentials for the primary authenticator.
- Click Next.
- If you require two factor authentication each time users authenticate to Cloud Access Manager, select Use two factor authentication for all applications from the Two factor authentication mode list. Select the method of authentication from the Type of two factor authentication list.
For information on how to configure the various authentication types or how to configure two factor authentication only for specific users or applications, refer to the Configuring step-up authentication section. When compete, click Next. -
In the Authenticator Name field, enter the name that will be used to identify the authenticator within Cloud Access Manager, then click Finish.
NOTE: This name will be seen by Cloud Access Manager users during authentication if multiple authentication methods have been configured.
-
You have now created the front-end authentication method. Click Edit Roles.
Before Cloud Access Manager administrators and users can log in to Cloud Access Manager using their directory credentials, you must tell Cloud Access Manager how to identify administrators and users based on their directory group membership. For example the admins group for Cloud Access Manager administrators and the users group for regular Cloud Access Manager users.
- Click Admin.
-
Click +Add User.
- Select the new Active Directory authentication method from the list.
- Use the search box to locate the group whose members are to be granted access to the Cloud Access Manager Administration application, then select the group from the list.
- Click Save.
- Click Users, now repeat Step 9 through Step 12 for Cloud Access Manager users.
- Click Close to return to the Cloud Access Manager Administration Console. The configuration is now complete. Cloud Access Manager administrators and users can now log in to Cloud Access Manager using their directory credentials.