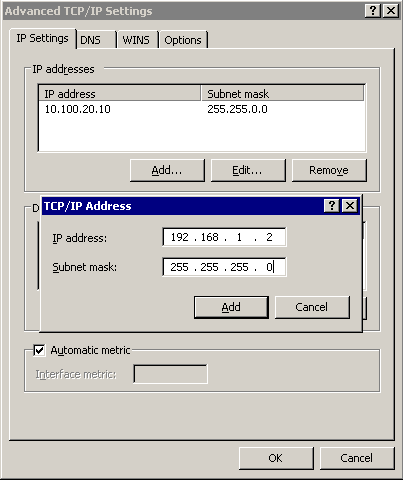
This procedure describes how to assign an alias IP address to a network interface on Microsoft Windows platforms.
To assign an alias IP address to a network interface on Microsoft Windows platforms
-
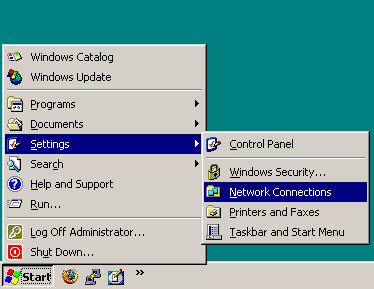
Navigate to Start menu > Settings > Network Connections.
-
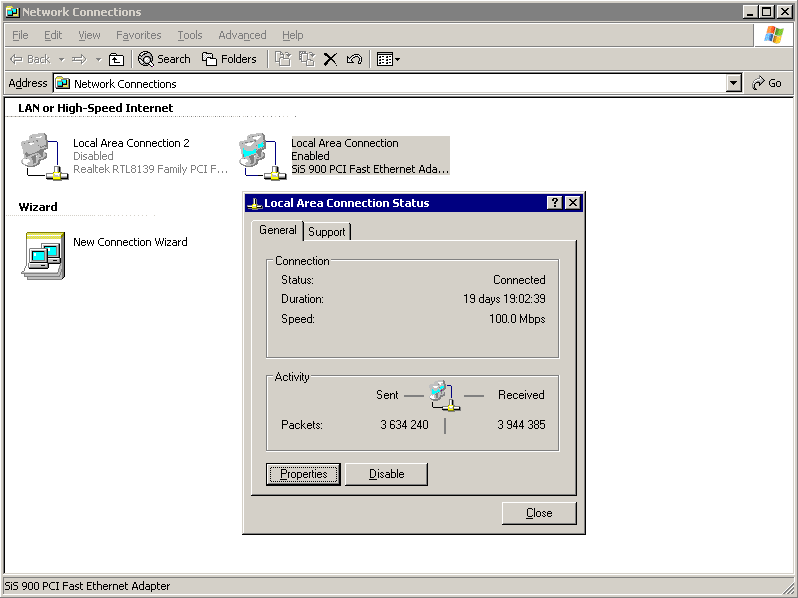
Double-click the Local Area Connection, then click Properties.
-
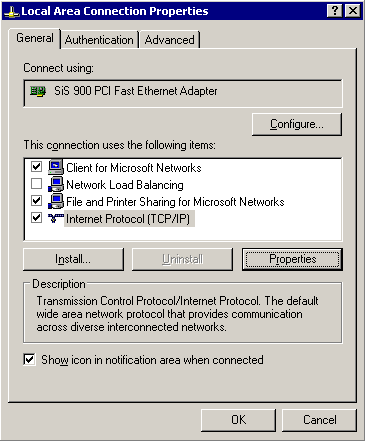
Select the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) component in the list and click Properties.
-
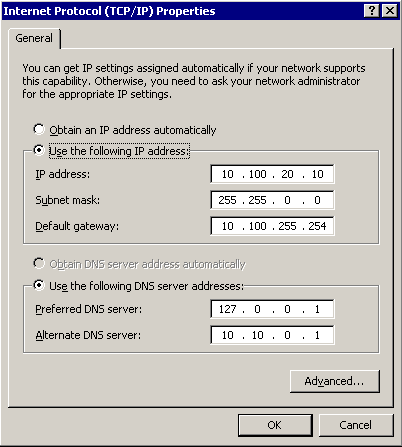
To display the Advanced TCP/IP Settings window, click Advanced.
-
Select the IP Settings tab and in the IP Addresses section, click Add.
-
In the IP Address field, enter 192.168.1.2. In the Netmask field, enter 255.255.255.0.
Caution: If your internal network uses the 192.168.1.0/24 IP range, the 192.168.1.1 and 192.168.1.2 addresses might already be in use. In this case, disconnect syslog-ng Store Box (SSB) from the network, and connect directly a computer to its external interface using a standard cross-link cable.
-
To complete the procedure, click Add.