In the wizard for creating user accounts, whether in the Active Roles console or Web Interface, the Create an Exchange mailbox option is selected by default, causing the user mailbox to be created upon creation of a user account. This behavior can be changed by applying an appropriately crafted policy of the Exchange Mailbox AutoProvisioning category.
A policy can be configured so that the Create an Exchange mailbox option is not selected by default but the administrator who uses the wizard to create a user account can select that option if necessary. It is also possible to configure a policy that forces the Create an Exchange mailbox option to be selected.
To set default creation options for Exchange mailbox
- Create a Policy Object containing an Exchange Mailbox AutoProvisioning policy.
- Open the Properties dialog box for the Policy Object you created.
- On the Policies tab in the Properties dialog box, double-click the Exchange Mailbox AutoProvisioning policy entry.
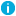
- On the Mailbox Creation tab in the Exchange Mailbox AutoProvisioning Policy Properties dialog box, set policy options as appropriate for your situation:
- Create the user mailbox by default. Determines whether the Create an Exchange mailbox option is selected by default in the wizard for creating user accounts. If you want user mailboxes not to be created by default, unselect this policy option.
- Enforce creation of the mailbox. Causes the Create an Exchange mailbox option to be selected and unavailable so that the administrator who creates a user account cannot unselect that option.
- Click OK to close the dialog boxes you opened.
- Apply the Policy Object to the scope (domains, containers, or Managed Units) where you want this policy to be in effect.