This section describes the prerequisites for forwarding messages from syslog-ng Store Box (SSB) to Splunk.
This section describes the limitations for forwarding messages from syslog-ng Store Box (SSB) to Splunk.
-
Messages with HTTP 400 response code will be dropped
If the message sent to Splunk is invalid, Splunk will reply with an HTTP 400 response code.
The message can be invalid for either of these reasons:
-
A required argument is missing from the message.
-
The message size exceeds limits.
-
The message itself has an invalid format.
In these cases, SSB cannot successfully send the messages to Splunk. These messages would prevent SSB from sending further messages to the messaging service, therefore SSB must drop them.
-
IP address limitation
IPv6 addresses are not supported as HTTP Event Collector (HEC) URLs.
-
Proxy type limitations
Only HTTP proxy types are supported.
-
Authenticated proxy types are not supported.
-
Batch-bytes unit of measurement limitation
When configuring performance-related settings, you must enter the value of Batch-bytes in bytes.
This section describes how you can configure the transport settings (HTTP or HTTPS transport) for your Splunk destination.
To configure the transport settings for your Splunk destination
-
Navigate to Log > Destinations and select 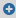 to create a new destination.
to create a new destination.
-
Select Splunk destination.
Figure 182: Log > Destinations > <your-splunk-destination> - Creating your new Splunk destination
-
Select the transport type (HTTP connection settings or HTTPS connection settings) that you want to use for your Splunk destination, then continue configuring the respective connection type settings.
This section describes the HTTP connection settings for your Splunk destination.
After you have set the transport settings for the Splunk destination, and selected the HTTP transport type, you can configure the following:
Figure 183: Log > Destinations > <your-splunk-destination> Transport > HTTP > HTTP connection settings - Configuring the HTTP connection settings for your new Splunk destination
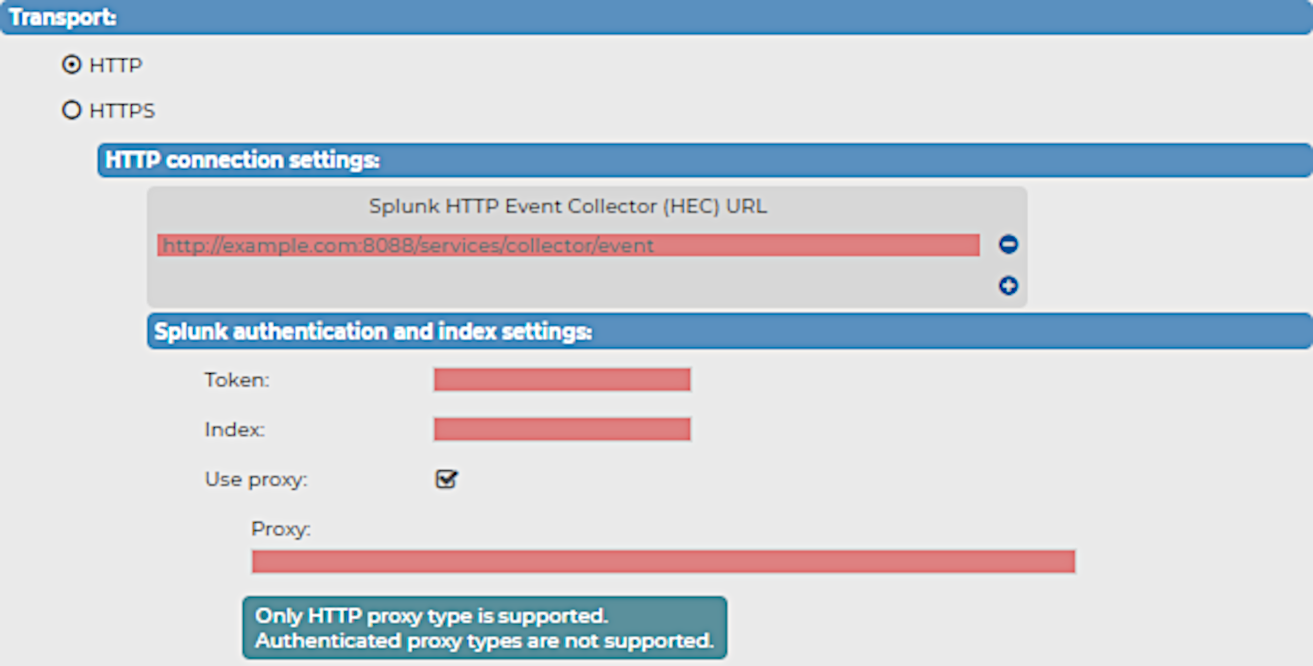
The Splunk HTTP Event Collector (HEC) URL
When configuring the HTTP or HTTPS connection settings for your Splunk destination for syslog-ng Store Box (SSB), you have to configure the HTTP Event Collector (HEC) URL first.
To configure the Splunk HEC URL for your Splunk destination
-
Navigate to Log > Destinations > <your-splunk-destination>.
-
Select the Transport type you want to use (HTTP or HTTPS).
-
Under HTTP connection settings or HTTPS connection settings (depending on your Transport type), enter the Splunk HTTP Event Collector (HEC) URL of your choice.
NOTE: IPv6 addresses are not supported.
Splunk authentication and index settings
After setting the transport settings, and then configuring the Splunk HEC URL for your Splunk destination, you have to configure your Splunk authentication and index settings.
To configure your Splunk authentication and index settings
-
Copy the Splunk HTTP Event Collector token provided by your Splunk deployment into the Token field.
Because the Splunk HTTP Event Collector token permits SSB to send messages to Splunk, configuring the Token field is required for the Splunk destination.
For details about setting up and using the Splunk HTTP Event Collector token on your Splunk deployment, see Set up and use HTTP Event Collector in Splunk Web.
-
Enter the name of the Splunk index where Splunk will store the messages received from SSB into the Index field.
Configuring the Index field is required for the Splunk destination.
-
(Optional) Enable Use proxy to use a proxy address while forwarding messages to your Splunk deployment.
NOTE: When configuring your proxy address, consider the following:

 to create a new destination.
to create a new destination.
