To view the Change History and User Activity for a cloud-only Azure user, you can use the Active Roles Web Interface.
To view the Change History and User Activity of a cloud-only Azure user
- On the Active Roles Web Interface navigation bar, click Directory Management.
-
On the Views tab in the Browse pane, click Azure > <Azure tenant> > Azure Users.
The Azure Users page is displayed and lists the Azure users that are available in Azure.
-
To view the history, select the Azure user.
-
In the Command pane, click Change History or User Activity.
Selecting Change History displays the information on changes that were made to the user through Active Roles.
To delete an Azure user , you can use the Active Roles Web Interface.
To delete an Azure user account
- On the Active Roles Web Interface navigation bar, click Directory Management.
-
On the Views tab in the Browse pane, click Azure > <Azure tenant> > Azure Users.
The Azure Users page is displayed and lists the Azure users that are available in Azure.
-
Select the Azure user that you want to delete.
-
In the Command pane, click Delete.
A message prompts you to confirm the action.
-
Click Yes to continue.
The Azure user that are selected are deleted.
You can invite (or re-invite), modify and remove cloud-only Azure guest users in the Azure AD of your organization with the Active Roles Web Interface.
An Azure guest user is a type of cloud-only Azure user that is not part of the organization domain for which you configure it.
When you create a new cloud-only Azure user for your organization, you must:
-
Specify a User Principal Name (UPN) and password for the Azure user.
-
Select the organization domain where the Azure user will be located within the Azure tenant.
However, when you create an Azure guest user, no domains are assigned to the user within the Azure tenant. Instead, the procedure has the following main steps:
-
You specify the basic permissions of the guest user, along with an email address to which Active Roles will send an invitation.
-
Using the link in the invitation email, the guest user can gain the configured access with their account upon joining the organization.
-
Once the guest accepted the invitation, you can assign additional permissions (like roles, licenses, storage space, and so on) to the user, similarly to a regular cloud-only Azure user.
NOTE: Active Roles does not restrict the type of permissions that you can assign to Azure guest users. However, for security reasons, One Identity recommends that you assign only the rights and resources to guest users that external contractors typically receive in your organization.
If an external user (such as a contractor, or other non-employee resource with limited permissions) must be added to the organization, invite them as Azure guest users to the Azure tenant of the organization using the Active Roles Web Interface.
To invite an Azure guest user
-
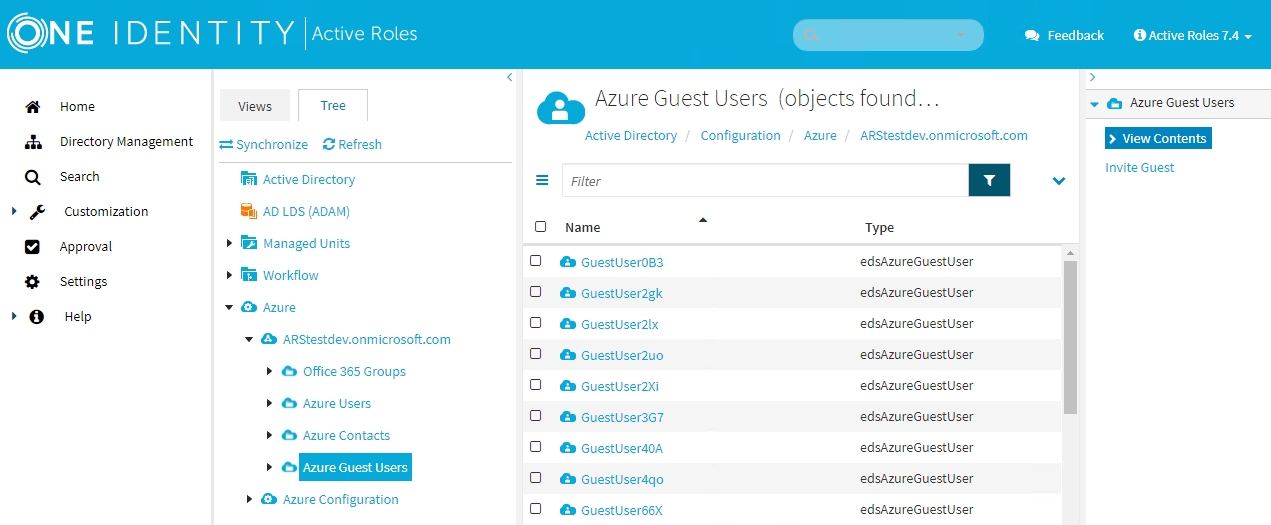
Navigate to Directory Management > Tree > Azure > <azure-tenant-name> > Azure Guest Users.
The list of Azure guest users of the selected tenant is displayed.
Figure 220: Directory Management > Tree View > Azure > <azure-tenant-name> > Azure Guest Users — Listing the Azure guest users in the tenant
-
In the right-side pane, click Invite Guest.
You will invite a new guest user, and set up their account, application licenses and various admin roles, too.
-
Identity
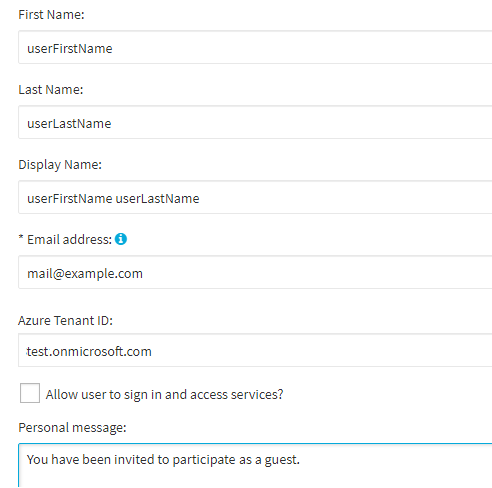
Configure the settings required by your organization for setting up the identity of the guest user.
Figure 221: Azure Guest Users > Invite Guest > Identity – Configuring basic user account settings for the Azure guest user
-
(Optional) Enter the First Name of the Azure guest user.
NOTE: If you do not enter a First Name, Active Roles will fill this field with the local part of the specified Email address.
-
(Optional) Enter the Last Name of the Azure guest user.
-
(Optional) Enter the Display Name of the Azure guest user.
TIP: By default, the Display Name is automatically generated from the specified First Name and Last Name, but you can modify it to something else (such as a nickname).
|
|
CAUTION: Hazard of data loss!
The Display Name field supports special characters. However, to avoid any potential problems in Active Roles when managing the Azure object, do not use any semicolons (;) in the specified display name. |
-
Enter the Email address where Active Roles will send out the invitation. This field is mandatory and must be unique.
-
(Optional) Enter the Azure Tenant ID of the Azure tenant that will contain the guest user.
-
To grant the Azure guest user access to the configured licenses and admin roles, select Allow user to sign in and access services.
-
If this setting is selected during this step, the guest user will receive access as soon as they accept the invitation.
-
If left clear, you must manually grant access later by enabling this setting in the Azure Properties page of the guest user. For more information, see Viewing and updating the properties of an Azure guest user.
TIP: Leaving this setting clear is useful if the account of the Azure guest user is created in advance, and they require access to the assigned resources only later (for example, because their contract project starts only at a later date).
-
(Optional) Enter a unique Personal message that the invitation email will contain.
-
Licenses
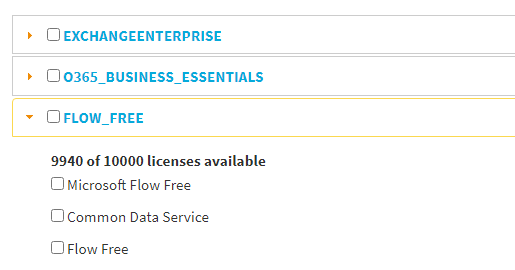
Select the Microsoft application resources licensed in your organization that you want to assign to the configured Azure guest user.
Figure 222: Azure Guest Users > Invite Guest > Licenses – Assigning application licenses to the Azure guest user
-
O365 Admin Roles
Select the O365 role(s) that you want to grant for the Azure guest user.
Figure 223: Azure Guest Users > Invite Guest > O365 Admin Roles – Assigning Office 365 administrator roles to the Azure guest user

NOTE: You can assign roles to the Azure guest user in Active Roles without any limitation. However, One Identity recommends that you assign Azure guest users only the admin roles that external contractors typically receive in your organization.
-
(Optional) Job Info
Enter the Job Title and the assigned Department of the guest user, if needed.
Figure 224: Azure Guest Users > Invite Guest > Job Info – Specifying organizational information for the Azure guest user

-
To save your changes and send the invite email to the guest user, click Finish.
NOTE: Consider the following when administering cloud-only Azure guest users:






