SSB continuously monitors a number of parameters of the SSB hardware and its environment. If a parameter reaches a critical level (set in its respective Maximum field), SSB sends e-mail and SNMP messages to alert the administrator.
SSB sends SNMP alerts using the management network interface by default, or using the external interface if the management interface is disabled. SSB supports the SNMPv2c and SNMPv3 protocols. The SNMP server set on the Management tab can query status information from SSB.
|
|
TIP:
To have your central monitoring system recognize the SNMP alerts sent by SSB, select Basic Settings > Alerting & Monitoring > Download MIBs to download the SSB-specific Management Information Base (MIB), then import it into your monitoring system. |
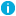
Figure 31: Basic Settings > Alerting & Monitoring — Configure SNMP and e-mail alerts
The following sections describe the parameters you can receive alerts on.
The following section describes how to configure monitoring.
To configure monitoring
-
Navigate to Basic Settings > Alerting & Monitoring.
Figure 32: Basic Settings > Alerting & Monitoring — Configure SNMP and e-mail alerts

-
The default threshold values of the parameters are suitable for most situations. Adjust the thresholds only if needed.
-
Select the type of alert (e-mail or SNMP) you want to receive for the different events. For details about the events that trigger an alert, see Health monitoring, System-related traps, and Alerts related to syslog-ng. See also Preventing disk space fill up and Configuring message rate alerting.
Note that for health-related alerts, SSB always sends at least e-mail alerts.
-
Click  .
.
-
Navigate to Basic Settings > Management and verify that the SNMP settings and Mail settings of SSB are correct. SSB sends alerts only to the alert e-mail address and to the SNMP server.
|
|
Caution:
Sending alerts fails if these settings are incorrect. |
Note that for health-related alerts, SSB always sends at least e-mail alerts.
-
Disk utilization maximum: Ratio of free space available on the hard disk. SSB sends an alert if the log files use more space than the set value. Archive the log files to a backup server to free disk space. For details, see Archiving and cleanup.
|

|
NOTE:
The alert message includes the actual disk usage, not the limit set on the web interface. For example, you set SSB to alert if the disk usage increases above 10 percent. If the disk usage of SSB increases above this limit (for example to 17 percent), you receive the following alert message: less than 90% free (= 17%). This means that the amount of used disk space increased above 10% (what you set as a limit, so it is less than 90%), namely to 17%. |
-
Load 1|5|15 maximum: The average load of SSB during the last one, five, or 15 minutes.
-
Swap utilization maximum: Ratio of the swap space used by SSB. SSB sends an alert if it uses more swap space than the set value.
This section describes how to prevent disk space from filling up.
To prevent disk space from filling up
-
Navigate to Basic Settings > Management > Disk space fill up prevention.
-
Set the limit of maximum disk utilization in percents in the respective field. When disk space is used above the set limit, SSB disconnects all clients. The default value is 90, and you can set values between 1-99.
-
Optional step: Enable the Automatically start archiving option to automatically start all configured archiving/cleanup jobs when disk usage goes over the limit.
|

|
NOTE:
If there is no archiving policy set, enabling this option will not trigger automatic archiving. |
-
Navigate to Basic Settings > Alerting & Monitoring > System related traps and enable alert Disk usage is above the defined ratio.
-
Click  .
.



 .
.