This section describes how to forward messages from syslog-ng Store Box (SSB) to Splunk.
From version 6.6.0, SSB uses the syslog-ng Premium Edition (syslog-ng PE) application's support to post messages to a Splunk deployment in JSON format, using the HTTP Event Collector (HEC) over HTTP and Secure HTTP (HTTPS).
For further details about how the application forwards messages to Splunk, see splunk-hec: Sending messages to Splunk HTTP Event Collector in the syslog-ng PE Administration Guide.

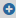 to create a new destination.
to create a new destination.