General considerations
To use this solution, you must have the necessary security permissions. It is sufficient to be a member of the Active Roles Admin account, in both the source and destination environments. The Active Roles Admin account is specified during installation of the Administration Service and defaults to the Administrators group on the computer running the Administration Service.
IMPORTANT: Before transferring the Active Roles configuration data, ensure that the Active Directory Organizational Unit (OU) structure in the destination environment is identical to the OU structure in the source environment.
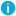
These are the general steps required to transfer Active Roles configuration data by using this solution:
- Collect configuration data from a source Active Roles environment In this step, you select the Active Roles configuration objects you want the configuration package to include, and then create a configuration package XML file. This step is performed in the source environment.
- Deploy the collected configuration data to a destination Active Roles environment In this step, the target Active Roles instance is populated with configuration objects from an earlier created package. This step is performed in the destination environment.
|
|
NOTE: If an object to deploy already exists in the target configuration, then the properties of the object are updated during the deployment process. |
To perform these steps, you can use either the Configuration Collection Wizard and Configuration Deployment Wizard, or the ARSconfig command-line tool. Both methods have the same effect and can be used interchangeably, depending on your requirements.
- You can use this solution to transfer Active Roles configuration objects of the following categories:
- Access Templates and containers that hold Access Templates
- Managed Units and containers that hold Managed Units
- Policy Objects and containers that hold Policy Objects
- Scheduled Task objects and containers that hold such objects
- Application objects and containers that hold such objects
- Script Modules and containers that hold Script Modules
- Virtual attributes
- Access Template Links (edsACE object type)
- Policy Object Links (edsPolicyObjectLink object type)
- Mail Configuration objects (edsMailConfiguration object type)
- Workflow definition objects (edsWorkflowDefinition object type)
- Automation Workflow definition objects (edsAutomationWorkflowDefinition object type)
- Policy Type objects (edsPolicyType object type)
- Entitlement Profile Specifier objects and containers (edsOneViewSpecifier or edsOneViewSpecifiersContainer object type) - requires Active Roles 6.7 or later
- Display specifiers and containers that hold display specifiers (displaySpecifier or edsDisplaySpecifierContainer object type)
The solution cannot be used to transfer configuration objects of the following categories:
- Built-in objects (the objects that have “built-in” as part of the name)
- Objects held in the Configuration/Application Configuration/Web Interface container (Web Interface configuration data)
If you need to roll back the changes made to the configuration of the target Active Roles instance, during the package deployment, you can do this by using the command-line tool included with the solution. For step-by-step instructions, see Scenario: Rolling back the configuration changes later in this document.
About dangling links
When collecting Access Templates and Policy Objects, the solution analyzes their links and writes the links to the destination package. Every link record includes information about the directory object and, if applicable, the trustee to which the respective Access Template or Policy Object is applied. In the configuration package file, this information normally takes the form of the distinguished name (DN), whereas in the Active Roles environment the links refer to the objects by security identifier (SID) or globally unique identifier (GUID). The solution needs DN rather than SID or GUID to identify an object as in a different environment, the object SID or GUID differs from that in the original environment. By identifying the link reference objects by DN, the solution enables the delegation and policy settings to be properly transferred from the source environment to the destination environment.
To have the link records identify the link reference objects by DN, the solution has to look up object SID or GUID to object DN. If this process fails for a given link, the link record is created that identifies the link reference object by SID or GUID. Such a record is referred to as dangling link.
If any dangling links have been recorded to the destination package, the solution informs of this condition. Deploying a package that contains dangling links may create links in the destination environment that refer to non-existent objects. As a result, some delegation and policy settings configured by deploying the package may not match the settings found in the source environment from which the package was collected.
The ARSconfig tool provides the danglingLinks parameter that allows you to specify how you want the deployment process to handle dangling links. For more information, see Using the ARSconfig command-line tool later in this document.
Using the Collection wizard and Deployment wizard
To transfer Active Roles configuration, you can collect configuration objects from one Active Roles environment and then deploy them to another environment in the following way:
- Create a configuration package file with the Configuration Collection Wizard.
- Deploy the package with the Configuration Deployment Wizard.
To create a configuration package with the Configuration Collection wizard
- Start the wizard by running the Configuration Collection Wizard application from the Start menu or Start page.
- On the Collect Active Roles Configuration Data page, do the following:
- Click Connect and using the Connect to Administration Service dialog that opens, select the Administration Service to which you want the wizard to connect.
- Under Select configuration objects to package, select the objects you want to include in the configuration package, and specify whether you want to collect the child objects of the selected objects.
- When finished, click Create Package.
- On the Specify a location for the configuration package page, do the following:
- Click Browse to specify a location and name for the configuration package file.
- Under Package description, enter the package description (optionally).
- To cause the wizard to collect Access Templates associated with selected objects, leave the Do not collect associated Access Templates check box cleared. Otherwise, select this check box.
- To cause the wizard to collect Policy Objects associated with selected objects, leave the Do not collect associated Policy Objects check box cleared. Otherwise, select this check box.
- On the Verify the information you specified page, click Start.
To deploy a configuration package with the Configuration Deployment wizard
- Start the wizard by running the Configuration Deployment Wizard application from the Start menu or Start page.
- On the Deploy Active Roles Configuration Data page, do the following:
- Click Browse to select the configuration package file.
- Optionally, select the Ignore errors check box for the wizard to ignore any errors during the configuration deployment.
- Click Deploy Package.
- On the Connect to Administration Service page, select the Administration Service to which you want the wizard to connect, and then click Next.
- On the Add Domain Name Mapping page, if names of the managed domains differ in the test and production environments, add domain name mapping entries, and then click Next.
- On the Verify the information you specified page, click Start.
Using the ARSconfig command-line tool
As an alternative to using the graphical user interface tools, you can use the ARSconfig command-line tool. The ARSconfig tool is the arsconfig.wsf Windows Script File (WSF) that defines the command line parameters and the required object references.
Using the ARSconfig tool requires two files to be pre-configured, before running the script. These are a file that lists the configuration objects that the package must include, and, if necessary, a file containing domain mapping entries.
To run the ARSconfig command-line tool
- From a command prompt, run the arsconfig.wsf script, specifying the required type of task and parameters. The script syntax is described in the section that follows.

