When processing a request to deprovision a user, Active Roles uses this policy to determine whether to schedule the deprovisioned user account for deletion. When scheduled for deletion, a user account is permanently deleted after a certain time period, referred to as a retention period.
A policy configured to delete user accounts specifies the number of days to retain deprovisioned user accounts. With such a policy, Active Roles permanently deletes a user account after the specified number of days has passed since the user was deprovisioned.
A policy can be configured not to delete user accounts. When applied at a certain level of the directory hierarchy, such a policy overrides any other policy of this category applied at a higher level of the directory hierarchy.
Let us consider an example to clarify this behavior. Suppose you configure a policy to delete accounts and apply that policy to a certain container. In general, the policy is passed down from parent to child containers, that is, the policy applies to all child containers beneath the parent container, causing Active Roles to delete deprovisioned user accounts in each container. However, if you configure a different policy not to delete accounts and apply that new policy to a child container, the child container policy overrides the policy inherited from the parent container. Active Roles does not delete deprovisioned user accounts in that child container or any container beneath that child container.
One more option of this policy is intended for domains where Active Directory Recycle Bin is enabled. The policy can be configured so that once a user account is deprovisioned, the account is moved to Recycle Bin (which effectively means that the account will be deleted immediately, without any retention period). Moving deprovisioned user accounts to the Recycle Bin may be required for security reasons, as an extra security precaution. The Active Directory Recycle Bin ensures that the account can be restored, if necessary, without any loss of data. Active Roles provides the ability to un-delete and then un-deprovision user accounts that were deprovisioned to the Recycle Bin.
You can configure a new User Account Permanent Deletion policy with the New Deprovisioning Policy Object Wizard of the Active Roles Console.
To configure a User Account Permanent Deletion policy
-
On the Policy to Configure page, select User Account Permanent Deletion, then click Next.
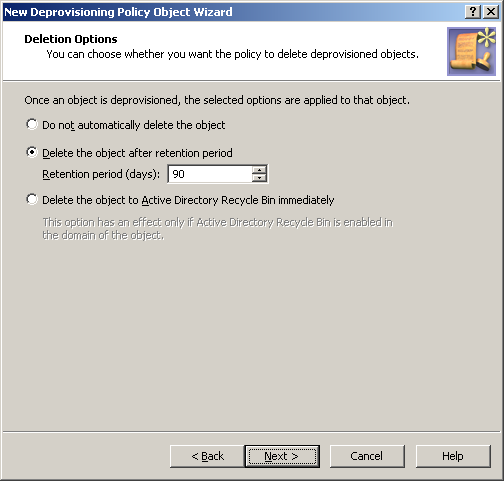
Figure 70: Deletion options
-
On the Deletion Options page, do one the following, then click Next:
-
Click Do not automatically delete the object if you want the policy not to delete deprovisioned user accounts.
-
Click Delete the object after retention period if you want the policy to schedule deprovisioned user accounts for deletion. Then, in Retention period (days), specify the number of days to retain the deprovisioned user account before it is deleted.
-
Click Delete the object to Active Directory Recycle Bin immediately if you want the policy to move deprovisioned user accounts to Recycle Bin.
NOTE: If you select this option, apply the policy to domains that have Active Directory Recycle Bin enabled, or the policy will have no effect.
With this option, once a user account is deprovisioned, the policy causes Active Roles to delete the user account immediately. In a domain where Active Directory Recycle Bin is enabled, this deletion means that the account is marked as deleted and moved to a specified container from which it can be restored later if necessary without any data loss.
Click Next.
-
On the Enforce Policy window, you can specify objects to which this Policy Object is to be applied:
-
Click Next, then click Finish.
This scenario describes how to configure a policy so that Active Roles permanently deletes deprovisioned user accounts after the 90-day retention period.
To implement this scenario, you must perform the following actions:
-
Create and configure the Policy Object that defines the appropriate policy.
-
Apply the Policy Object to a domain, OU, or Managed Unit.
As a result, after deprovisioning a user account in the container you selected in Step 2, Active Roles retains the deprovisioned account for 90 days and then it deletes that account.
You can create and configure the Policy Object you need by using the New Deprovisioning Policy Object Wizard. For more information about the wizard, see Creating a Policy Object.
To configure the policy, click User Account Permanent Deletion on the Select Policy Type page of the wizard. Then, click Next.
On the Deletion Options page, click Delete the object after retention period. Then, in the box beneath that option, type 90.
When you are done, click Next and follow the instructions in the wizard to create the Policy Object.

