One Identity Manager supports the implementation of Identity and Access Governance demands in IT environments, which are often a mix of traditional, on-premise applications and modern cloud applications. Users and entitlements from cloud applications can be mapped in One Identity Manager. This makes it possible to also use Identity and Access Governance processes such as attestation, identity audit, management of users and system entitlements, IT Shop, or report subscriptions for cloud applications.
Data protection policies, such as the General Data Protection Regulation, require agreement as to which employee data can be stored in cloud applications. If the system environment is configured appropriately, One Identity Manager guarantees that cloud applications and their administrators have no access to any employee main data or Identity and Access Governance processes respectively. For this reason, cloud applications are managed in two separate modules, which can be installed in separate databases if necessary.
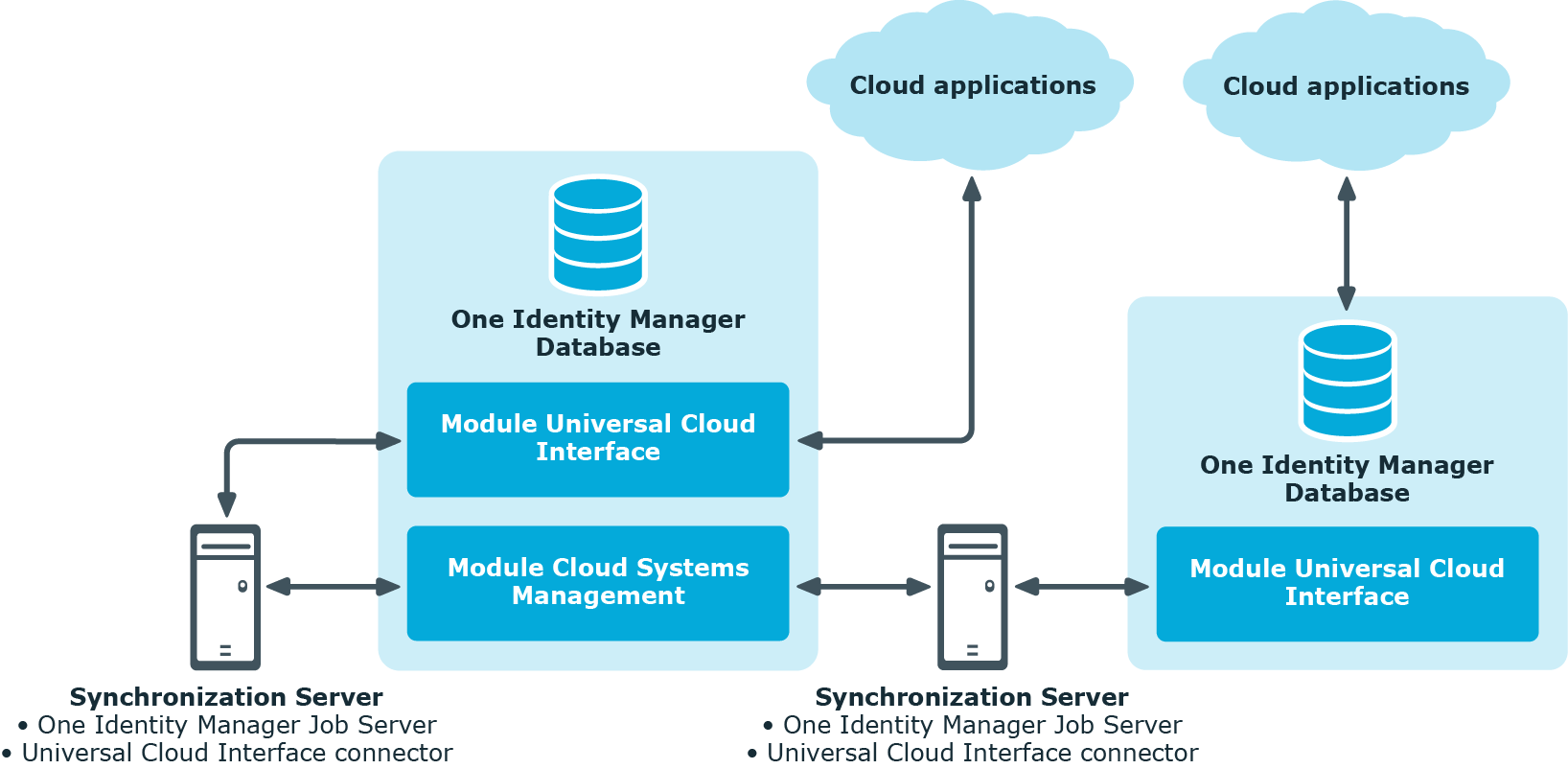
The Universal Cloud Interface Module provides the interface through which users and permissions can be transferred from cloud applications to a One Identity Manager database. Synchronization with the cloud applications is configured and run at this stage. Each cloud application is mapped as its own base object in One Identity Manager. The user data is saved as user accounts, groups, system entitlements, and permissions controls and can be organized into containers. They cannot be edited in One Identity Manager. There is no connection to identities (employees).
The connection to the identities is established in the Cloud Systems Management Module; user accounts, groups, system entitlements, and permissions controls can be created and edited. This allows Identity and Access Governance processes to be used for managing cloud user accounts and their permissions. Data is exchanged between the Universal Cloud Interface and Cloud System Management modules by synchronization. Provisioning processes ensure that object changes are transferred from the Cloud Systems Management Module to the Universal Cloud Interface Module.
Automated interfaces for provisioning changes from the Universal Cloud Interface Module to the cloud application can (on technical grounds) or should (due to too few changes) not be applied to certain cloud applications. In this case, changes can be manually provisioned.
Since only data that must be available in the cloud application is saved in the Universal Cloud Interface Module, the module can be installed in a separate database. This database may be outside the company's infrastructure.
The One Identity Starling Connect cloud solution provides a simple and comprehensive solution for integrating cloud applications and for meeting the requirements of hybrid solution scenarios.
A synchronization server installed with the Universal Cloud Interface Module connector is required for synchronizing cloud applications in the Universal Cloud Interface. The Universal Cloud Interface Module can exist in the same One Identity Manager database in which the Cloud Systems Management Module is installed. Synchronization can also be set up with another One Identity Manager database, which is provided on an external database server.
Figure 1: Architecture for synchronization
For more information about communicating between the Universal Cloud Interface and cloud application, see the One Identity Manager Administration Guide for Connecting to Cloud Applications.
The following users are used for setting up and administration of cloud target systems.
Table 1: Users
|
Target system administrators |
Target system administrators must be assigned to the Target systems | Administrators application role.
Users with this application role:
-
Administer application roles for individual target system types.
-
Specify the target system manager.
-
Set up other application roles for target system managers if required.
-
Specify which application roles for target system managers are mutually exclusive.
-
Authorize other employees to be target system administrators.
-
Do not assume any administrative tasks within the target system. |
|
Target system managers |
Target system managers must be assigned to the Target systems | Cloud target systems application role or a child application role.
Users with this application role:
-
Assume administrative tasks for the target system.
-
Create, change, or delete target system objects.
-
Edit password policies for the target system.
-
Prepare groups and system entitlements to add to the IT Shop.
-
Can add employees who have another identity than the Primary identity.
-
Configure synchronization in the Synchronization Editor and define the mapping for comparing target systems and One Identity Manager.
-
Edit the synchronization's target system types and outstanding objects.
-
Authorize other employees within their area of responsibility as target system managers and create child application roles if required. |
| One Identity Manager administrators |
administrator and administrative system users Administrative system users are not added to application roles.
administrators:
-
Create customized permissions groups for application roles for role-based login to administration tools in the Designer as required.
-
Create system users and permissions groups for non role-based login to administration tools in the Designer as required.
-
Enable or disable additional configuration parameters in the Designer as required.
-
Create custom processes in the Designer as required.
-
Create and configure schedules as required. |
| Administrators for the IT Shop |
Administrators must be assigned to the Request & Fulfillment | IT Shop | Administrators application role.
Users with this application role:
|
| Administrators for organizations |
Administrators must be assigned to the Identity Management | Organizations | Administrators application role.
Users with this application role:
-
Assign groups to departments, cost centers, and locations.
-
Assign system entitlements to departments, cost centers, and locations. |
| Business roles administrators |
Administrators must be assigned to the Identity Management | Business roles | Administrators application role.
Users with this application role:
|
Data is exchanged between the Universal Cloud Interface and Cloud System Management modules by synchronization. In order to apply Identity and Data Governance processes to cloud application objects, you must set up synchronization between the two modules.
NOTE: The terms target system and (One Identity Manager) database are used frequently in the following. The term target system always means a cloud application in the Universal Cloud Interface. One Identity Manager database or database refers to the objects in the Cloud Systems Management Module.
Table 2: Terms
| Connected system |
Cloud Systems Management Module |
Universal Cloud Interface Module |
| Base object |
Cloud target system |
Cloud application |
The mapping defines how schema types of the connection systems are mapped to each other. For more information, see Default project template for cloud applications in the Universal Cloud Interface.
This sections explains how to:
-
Set up synchronization between the Universal Cloud Interface and Cloud Systems Management modules.
-
Adapt a synchronization configuration, for example, to synchronize different target systems with the same synchronization project.
-
Start and deactivate the synchronization.
-
Evaluate the synchronization results.
TIP: Before you set up synchronization, familiarize yourself with the Synchronization Editor. For more information about this tool, see the One Identity Manager Target System Synchronization Reference Guide.
Detailed information about this topic

