Display template for displaying a list
You use a list display template to specify the form in which the table entries will be represented in the administration tool result list. You can define display templates for menu items, object definitions and table lists.
The display template is determined by the following in order:
-
List display template for the menu item
-
Object definition display template
-
Table display template
The display template for displaying a list can be described in the following syntax:
%columnname%
All the columns that belong to the table that will be displayed can be used in the display template. Variables may not be used in display templates for lists.
Replacing the display template supports the ?? operator. Thus you can formulate conditional display templates with the following syntax.
%columnname1??columnname2??columnname3%
%columnname1?? columnname2%
The first column that returns a value from the list of column names is used. Spaces are permitted before and after the ?? operator. Spaces are not allowed at the beginning and end of the conditional display template for performance reasons.
Example:
The Active Directory user account (ADSAccount table) should be shown as follows:
Common Name (fully qualified domain name)
The display template for the ADSAccount table to be specified for this purpose is:
%cn% (%CanonicalName%)
Related topics
Defining insert values
You can use insert values to initialize individual values when a new data set is added over the result list. You can apply insert values to interface forms, object definitions, menu item lists, and tables.
Enter insert values in VB.Net syntax. The Base. syntax Always accesses the object that is currently loaded. Insert values are described with the following syntax:
-
Value assignment with variable replacement (value must be a character string)
Base.PutValue("<column>", context.Replace(<value>))
All the columns of the table to be displayed may be applied. You can use variable for defining insert values.
Example:
Base.PutValue("IsITShopOnly", 1)
Base.PutValue("UID_ADSContainer", context.Replace("%cont%"))
NOTE: If you changed insert values, you must recompile the database.
Related topics
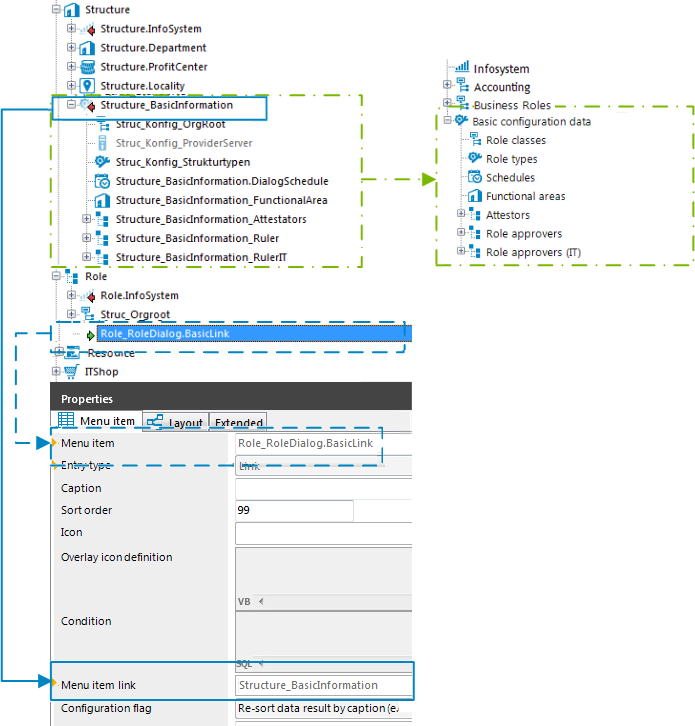
Using links in the navigation
Links support the navigation configuration. Links are implemented to reference frequently used menu items. Parts of the navigation interface that require an application several times, only need to be set up once. The links themselves do not appear in the navigation. Instead the referenced menu items and their child menu items are shown.
Figure 13: Structure of the navigation interface using links in the User Interface Editor (left) and display in the Manager (right).
Special features of using links
-
Links inherit some properties of the reference entry.
-
You can use variables in the reference entry, for example in conditions for lists or data-dependent menu entries. Value assignment to the variables only takes place in the link. You must define the variables in the link.
-
The caption and the icon of the reference entry are overwritten with the corresponding values from the link.
To use links
-
Create the menu item that you want to use as the reference entry.
-
If necessary, create other menu items below the reference entry.
-
Create the menu items that link to the reference entry. Enter at least the following information for the link.
-
Menu item: Enter the name of the menu item.
-
Entry type: Select the Link entry type.
-
Menu item link: Select the reference entry to be shown at runtime when the link is called.
-
Assign an application and the permissions groups.
-
Select the Database > Commit to database and click Save.
TIP:
-
If the menu item is of the Link type, you can use the Follow link node context menu to navigate to the reference entry.
-
For a reference entry, you can use the Referenced by context menu to display all links that refer to this reference entry and then navigate to these entries.
Related topics
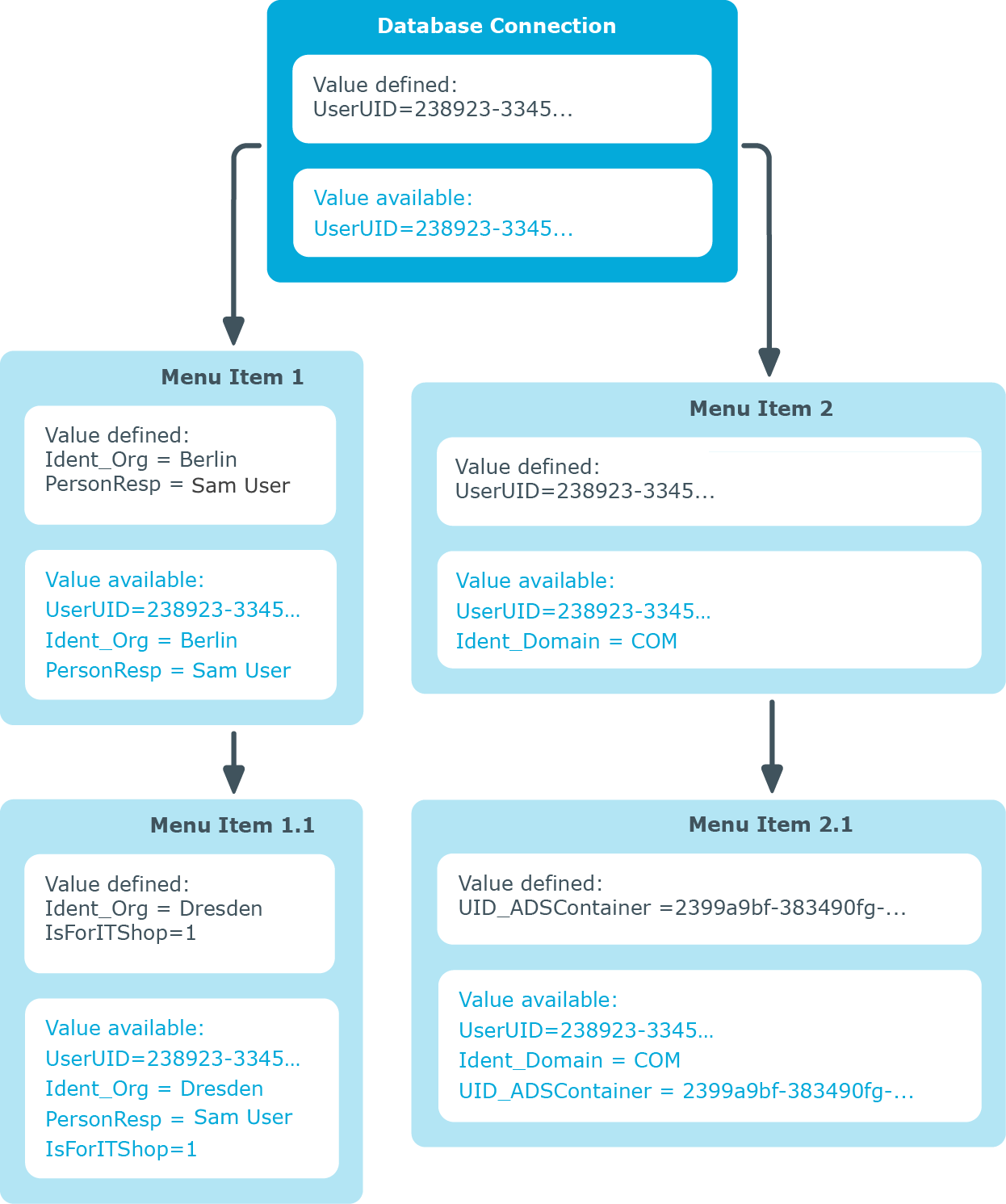
Using variables in the navigation
You may use variables to configure identifiers and menu item display templates for menu items in insert values and database queries. In some parts of the navigation interface you have to implement variables as, for example, in the case of formulating database queries for recursive data-dependent menu items.
Variables are inherited within a hierarchical navigation. This means that variables in deeper levels of a hierarchy can be reused or overwritten. The actual run-time value is passed to the variable.
Figure 14: Inheriting variables in a hierarchical navigation interface
The variables of the session object that are listed below are always available when the menu items are being set up.
Table 38: Global session object variables
|
EnvUserName |
Name of user to be authenticated in the environment, for example, Domain\User in Active Directory |
|
LogonUser |
DialogUser.Username of the currently logged in user. |
|
DialogUserUID |
DialogUser.UID_DialogUser of the logged in user. |
|
UserName |
Name displayed in XUserInserted or XUserUpdated. |
|
UserUID |
Logged in user’s UID_Person, if user related authentication is being used. |
|
ShowCommonData |
Specifies whether system data is shown (1) or not shown (0) The variable is evaluated in the Designer by the program settings. |
|
SessionType |
Specifies whether a direct database connection or a connection over an application server is supported.
Direct database connection only: '%SessionType%' = 'Direct'
Connect with the application server only: '%SessionType%' = 'AppServer' |
In addition to the variables belonging to the session object, you can also define other variables. The variable definition is made up of variable type, variable name and the value. Basically, any string is permitted in the variable definition. However, events have proved that it is a good idea to use a pattern that is unlikely to occur in the data but is accepted as a string by the database server in use.
Table 39: Permitted variable definitions
|
Column |
Any string |
Current object’s column name |
Only used in data-dependent menu items. |
|
Display value |
Any string |
Current object’s column name |
Only used in data-dependent menu items. The Multilingual and List of permitted values column properties are resolved when creating the display value for a column. |
|
Text |
Any string |
Freely defined value |
Can be used in all menu items.
NOTE: Format values that can potentially contain apostrophes (') using the DBString formatting function.
Example:
Variable: PersonWhereClause
Value: LastName = '%Name:DBString%' |
Use the following syntax when you edit the navigation to access the variables:
%Variable%
Related topics


