The following is a detailed description of all the available vascert commands, their usage and arguments.
vascert clean
Clears certificate enrollment state information.
vascert [common options] clean [-u <username>] [-x]
Arguments:
[-u <username>] is the name of the user to perform the operation.
[-x] removes all local state information.
Additional Information:
This command causes Certificate Autoenrollment to remove all previous configuration and downloaded policy. When run as root with the -x option, this command removes all local state information returning the system to the state it had just after package install.
vascert configure
Allows you to configure Certificate Autoenrollment settings.
vascert [common options] configure <sub-command> <command>
Sub-commands:
debug enables debug logging for all Certificate Autoenrollment components.
Debug command arguments:
vascert [common options] configure debug [-u <username>]
[-u <username>] is the name of the user to perform the operation.
vascert importca
Imports trusted root CA certificates based on policy.
vascert [common options] importca [-u <username>] [-p]
Arguments:
[-u <username>] is the name of the user to perform the operation.
[-p] simulates policy-based CA import.
vascert info
Dumps the contents of a policy template.
vascert [common options] info <policy template name>
vascert list
Lists all configured policy template names.
vascert [common options] list [-p]
Arguments:
[-p] lists pending enrollment requests.
vascert pulse
Performs Certificate Autoenrollment processing.
vascert [common options] pulse [-p]
Arguments:
[-p] simulates policy-based pulse.
vascert renew
Renews an existing certificate based on a policy template.
vascert [common options] renew -t <template name>
Arguments:
-t <template name> is the name of the policy template for which certificates are to be renewed.
vascert server
Manages local policy server configuration.
vascert [common options] server <sub-command>
Sub-commands:
remove removes a policy server configuration by URL.
list lists policy servers that are configured locally.
add adds a new local server configuration.
Remove command arguments:
vascert [common options] server remove [-u <username>] [-a] <URL>
[-u <username>] is the name of the user to perform the operation.
[-a] removes all server configurations.
List command arguments:
vascert [common options] server list [-u <username>]
[-u <username>] is the name of the user to perform the operation.
Add command arguments:
vascert [common options] server add [-u <username>] [-c <cost> ] -r <URL> [-n <name> ]
[-u <username>] is the name of the user to perform the operation.
[-c <cost>] specifies the cost associated with this server. Servers with lower cost are preferred when performing server selection.
-r <URL> specifies the service endpoint to contact to object enrollment policy.
[-n <name>] specifies the display name of this server.
vascert trigger
Triggers machine-based Certificate Autoenrollment policy processing.
vascert [common options] trigger
vascert unconfigure
Allows you to un-configure Certificate Autoenrollment settings.
vascert [common options] unconfigure <sub-command> <command>
Sub-commands:
debug disables debug logging for all Certificate Autoenrollment components.
Debug command arguments
vascert [common options] unconfigure debug [-u <username>]
[-u <username>] is the name of the user to perform the operation.
Integrating with other applications
Safeguard Authentication Services integrates with the following products.
-
InSync
-
One Identity™ Active Roles
-
One Identity™ Defender®
-
One Identity™ Privilege Manager for UNIX
-
Quest® Change Auditor
-
Quest® Enterprise Reporter
-
Quest® InTrust®
-
Quest® Recovery Manager for Active Directory
This section includes instructions for integrating Defender and Change Auditor with Safeguard Authentication Services.
NOTE: See the One Identity website for information related to the integration of Safeguard Authentication Services with other products.
Defender provides strong authentication capabilities.
Why is strong authentication an important part of an Active Directory bridge solution?
When Safeguard Authentication Services integrates UNIX with Active Directory, it provides centralized access control and password policy enforcement. However, there are situations where security policies dictate a stronger level of authentication. Safeguard Authentication Services addresses this need with optional strong authentication capabilities. Customers now can use the same solution for integrated Active Directory authentication and strong authentication. Organizations that have tight security requirements will no longer be forced to purchase and implement a third-party solution.
How is strong authentication used with an Active Directory bridge solution?
An organization may have many UNIX systems deployed in a traditional, highly secure perimeter network environment. As they are integrated with Active Directory, they will require an Active Directory credential to authenticate. Now, an additional layer of authentication can be added for administrators accessing these systems, using either a hardware or software token.
If an organization has integrated hundreds or thousands of UNIX systems with Active Directory, a system administrator can now use the same Active Directory credential to access all of them. An additional level of security can be easily added by requiring the system administrator to use one-time password (OTP) in additional to the Active Directory credential.
How do Safeguard Authentication Services’ strong authentication capabilities compare to other Active Directory bridge solutions?
Strong authentication combined with an Active Directory bridge is a unique and critical differentiator for One Identity. No other Active Directory bridge vendor offers strong authentication as an integrated part of its solution, and no strong authentication vendor offers UNIX coverage and Active Directory integration.
Is there an additional charge for strong authentication with Safeguard Authentication Services 4.x?
There is no additional cost for strong authentication with Safeguard Authentication Services 4.x; it is a new feature available to new and upgrading customers.
Safeguard Authentication Services provides strong authentication for up to 25 users at no additional cost through included licenses and tokens for Safeguard Authentication Services Defender. These licenses will cover and secure 25 of an organization‘s UNIX system administrators. Strong authentication support for additional end-users is available at an additional per-user cost.
How does strong authentication with Safeguard Authentication Services 4.x work?
Safeguard Authentication Services:
-
Includes strong authentication modules and native packages for all supported platforms (100+).
-
Remotely deploys and installs the strong authentication module.
-
Provides hardware and software tokens for one-time passwords.
-
Enables policy-based configuration of strong authentication through Active Directory Group Policy.
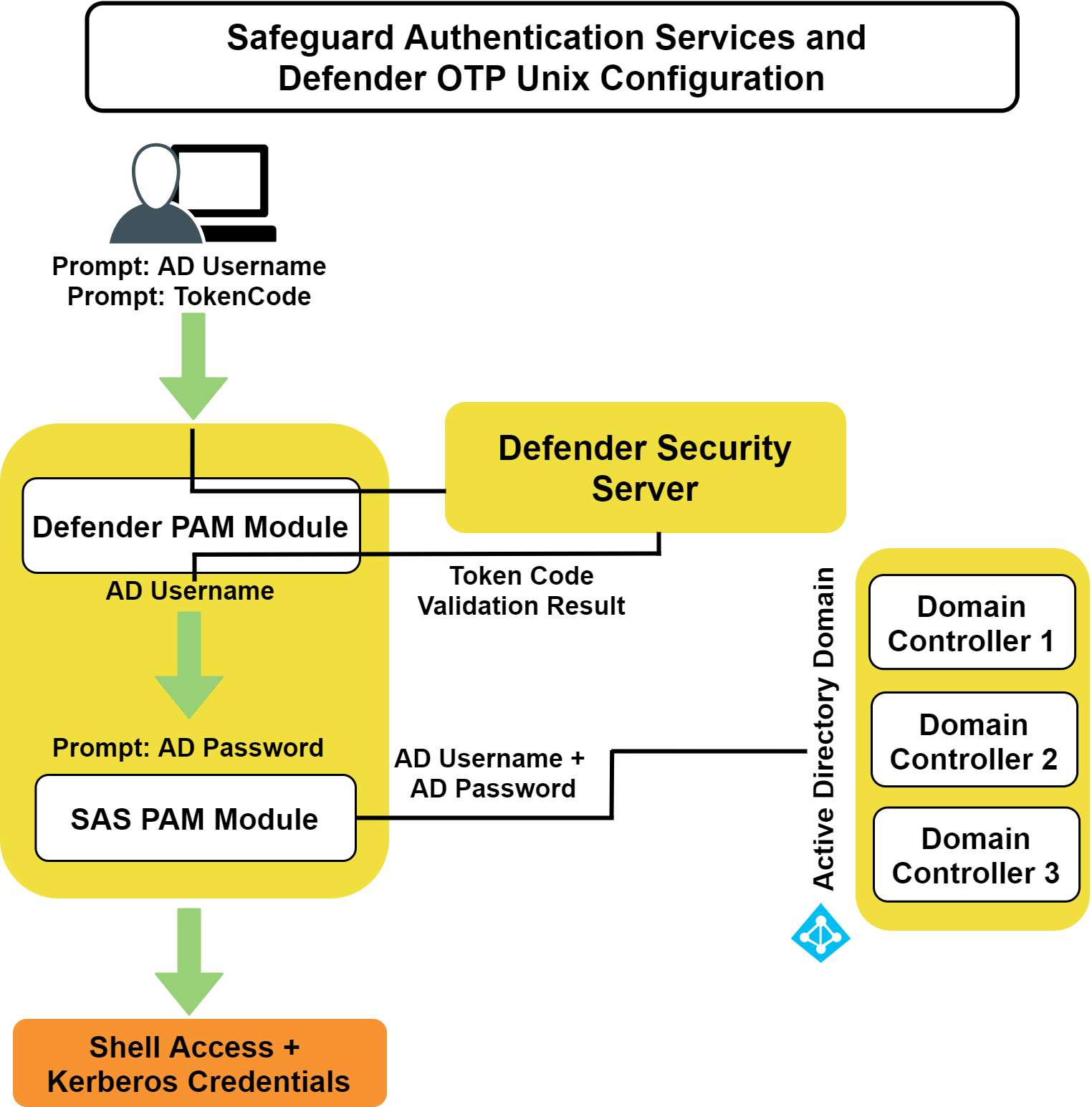
The following figure describes the flow of events that occur during a UNIX or Linux login after both Safeguard Authentication Services Defender and Safeguard Authentication Services are configured according to this guide.
Figure 2: Defender Integration
Before you install Safeguard Authentication Services Defender on your host, ensure that you have:
-
Installed a Defender security server in your Active Directory domain.
-
Installed the Defender Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in.
-
Installed Safeguard Authentication Services on your UNIX or Linux machine.

