Wildcards
You can also add wildcards and conditions to a search filter. The following examples show substrings that can be used to search the directory.
Get all entries:
(objectClass=*)
Get entries containing “bob” somewhere in the common name:
(cn=*bob*)
Get entries with a common name greater than or equal to “bob”:
(cn>='bob')
Get all users with an e-mail attribute:
(&(objectClass=user)(mail=*))
Get all user entries with an e-mail attribute and a surname equal to “smith”:
(&(sn=smith)(objectClass=user)(mail=*))
Get all user entries with a common name that starts with “andy”, “steve”, or “margaret”:
(&(objectClass=user) | (cn=andy*)(cn=steve)(cn=margaret))
Get all entries without an e-mail attribute:
(!(mail=*))
Special characters
If any of the following special characters must appear in the search filter as literals, they must be replaced by the listed escape sequence.
Table 7: Special characters in Search filter
|
* |
\2a |
|
( |
\28 |
|
) |
\29 |
|
\ |
\5c |
|
NUL |
\00 |
In addition, arbitrary binary data may be represented using the escape sequence syntax by encoding each byte of binary data with the backslash (\) followed by two hexadecimal digits. For example, the four-byte value 0x00000004 is encoded as \00\00\00\04 in a filter string.
Getting policy-related information
In object creation wizards and properties dialog boxes, some property labels may be displayed as hyperlinks. This indicates that Active Roles enforces policy restrictions on the property.
In the following figure, the User logon name and User logon name (pre-Windows 2000) labels are underlined, which means that these properties are under the control of a certain policy defined with Active Roles.
Figure 3: Policy related information
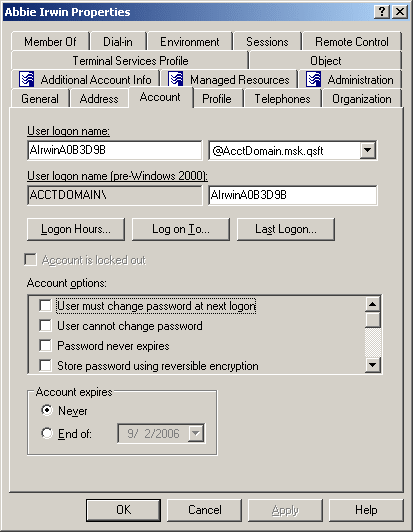
To examine the policy in detail, you can click the label. For example, if you click User logon name (pre-Windows 2000), the Active Roles console presents you with a window similar to the following figure.
Figure 4: Policy description

The window may display the following information:
- Policy Description Provides a brief description of the policy.
- Message Details the problem if the supplied property value violates the policy.
You can click arrows in the lower-left corner to display description of other policies enforced on the given property.
The Message section is displayed whenever the specified property value violates the policy. The following figure illustrates the situation where a value has not been supplied for a mandatory property.
Figure 5: Policy violation message
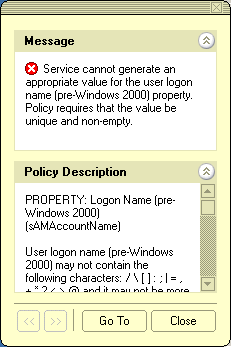
When you click Go To in this window, the console moves the pointer to the field that needs to be corrected. You can type or select an appropriate value to correct your input.
Performing Batch operations
In the Web Interface, you can select multiple objects (such as users, groups and computers), and then apply a certain command to your selection of objects. This allows you to perform a batch operation on all the selected objects at a time instead of executing the command on each object separately. The Web Interface supports the following batch operations:
- Delete Allows you to delete multiple objects at a time.
- Deprovision Allows you to deprovision multiple users or groups at a time.
- Move Allows you to move a batch of objects to a different organizational unit or container.
- Add to groups Allows you to add a batch of objects to one or more groups of your choice.
- Update object attributes Allows you to perform bulk attributes operations for multiple users at a time.
- Reset Password Allows you to reset the password for multiple users at a time.
Batch operations are available in the list of objects on the following Web Interface pages:
- Search This page lists the search results when you perform a search.
- View Contents This page displays the objects held in a given organizational unit, Managed Unit, or container.
To perform a batch operation, select the check box next to the name of each of the desired objects in the list, and then click a command in the top area of the Command pane. This executes the command on each object within your selection.
|
|
NOTE: Active Roles administrators can customize Web Interface by adding and removing commands, and modifying pages associated with commands. For more information, see “Customizing the Web Interface” in the Active Roles Web Interface Administration Guide. |




