Scenario 1: Disabling and renaming the user account upon deprovisioning
The policy described in this scenario performs the following functions during the user deprovisioning process:
- Disable the user account.
- Append this suffix to the user name: - Deprovisioned, followed by the date that the user account was deprovisioned.
For example, the policy changes the user name John Smith to John Smith - Deprovisioned 12/11/2010.
To implement this scenario, you must perform the following actions:
- Create and configure the Policy Object that defines the appropriate policy.
- Apply the Policy Object to a domain, OU, or Managed Unit.
As a result, when deprovisioning a user account in the container you selected in Step 2, Active Roles disables and renames the user account as prescribed by this policy.
The following two sections elaborate on the steps to implement this scenario.
Step 1: Creating and configuring the Policy Object
Step 1: Creating and configuring the Policy Object
You can create and configure the Policy Object you need by using the New Deprovisioning Policy Object wizard. For information about the wizard, see Creating a Policy Object in the Policy Object management tasks section earlier in this chapter.
To configure the policy, click User Account Deprovisioning on the Select Policy Type page of the wizard. Then, click Next.
On the Options to Prevent Logon page, select these check boxes:
- Disable the user account
- Rename the user account to
Then, click the Configure button, and use the following instructions to complete the Configure Value dialog box.
- Click Add.
- In the Add Entry window, click User Property under Entry type, and configure the entry as follows:
- Click Select and choose the Name property.
- Click All characters of the property value.
- Click OK.
- Click Add.
- In the Add Entry window, click Text under Entry type, and configure the entry as follows:
- In the Text value box, type - Deprovisioned.
- Click OK.
- Click Add.
- In the Add Entry window, click Date and Time under Entry type, and configure the entry as follows:
- From the list under Date and time format, select the format m/d/yyyy.
- Click OK.
After you complete these steps, the list of entries in the Configure Value dialog box should look like the following figure.
Figure 73: Configure Value
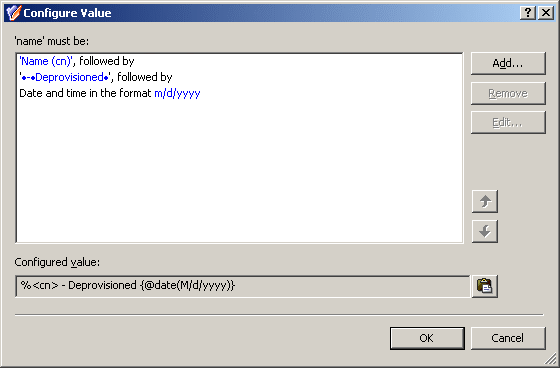
Click OK to close the Configure Value dialog box. Then, click Next and follow the instructions in the wizard to create the Policy Object.
Step 2: Applying the Policy Object
Step 2: Applying the Policy Object
You can apply the Policy Object by using the Enforce Policy page in the New Provisioning Policy Object wizard, or you can complete the wizard and then use the Enforce Policy command on the domain, OU, or Managed Unit where you want to apply the policy.
For more information on how to apply a Policy Object, see Applying Policy Objects and Managing policy scope earlier in this chapter.
Scenario 2: Managed Unit for deprovisioned user accounts
This scenario describes how to configure a Managed Unit and a User Account Deprovisioning policy so that the Managed Unit includes all the deprovisioned user accounts. The policy sets the Notes property to Deprovisioned upon the user deprovisioning, whereas the Managed Unit is configured to include user accounts that have the Notes property set to Deprovisioned.
To implement this scenario, you must perform the following actions:
- Create and configure the Managed Unit.
- Configure the Policy Object that defines the appropriate policy.
- Apply the Policy Object to a domain, OU, or Managed Unit.
As a result, after deprovisioning a user account in the container you selected in Step 3, Active Roles automatically adds that account to the Managed Unit you created in Step 1.
The following sections elaborate on the steps to implement this scenario.

