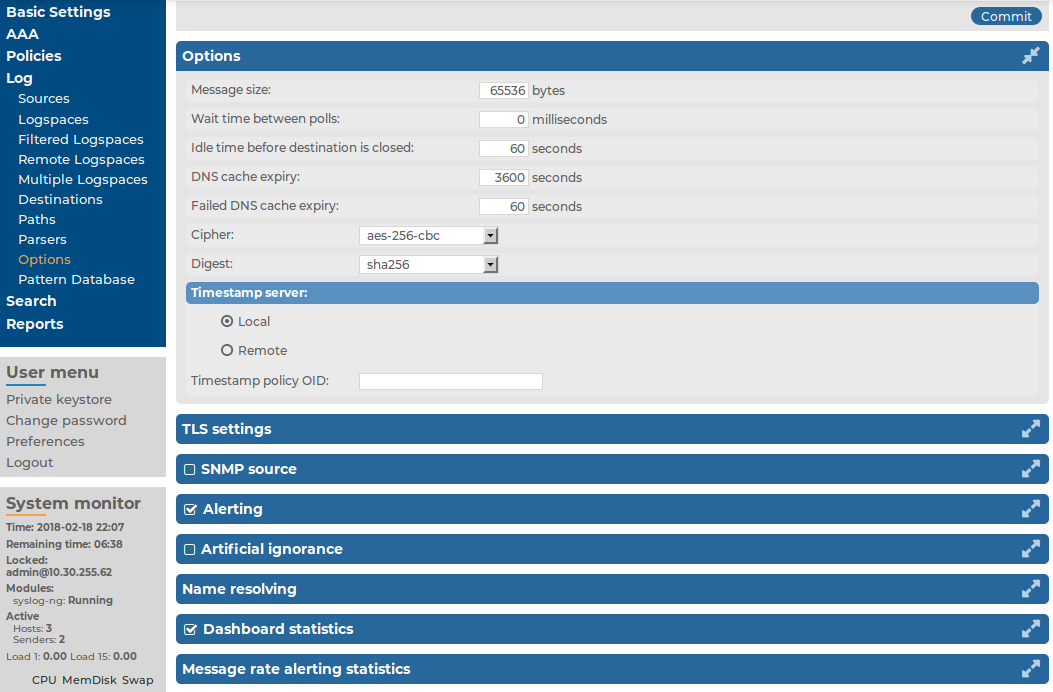
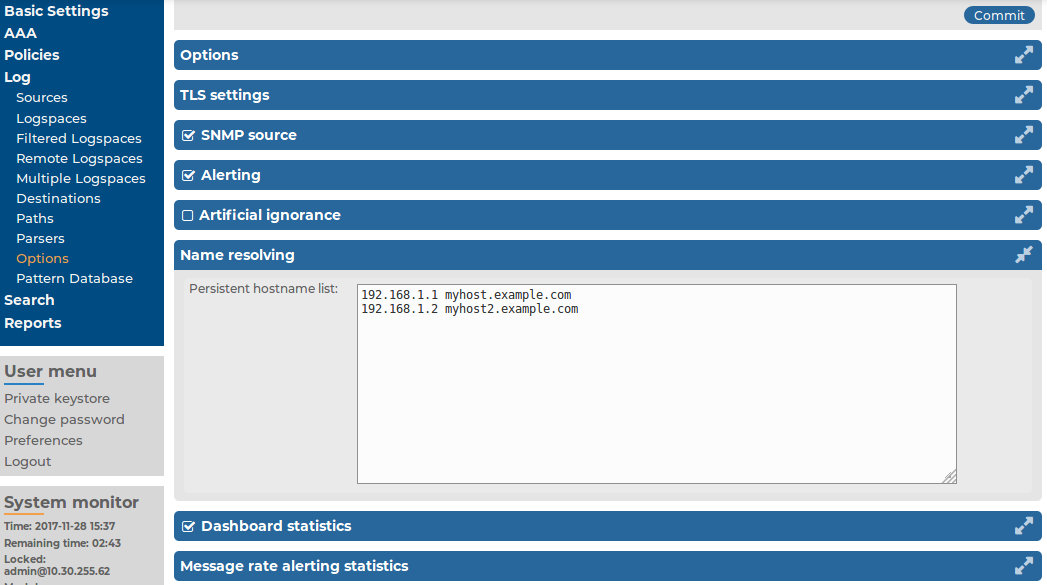
There are several options of the syslog-ng server running on syslog-ng Store Box(SSB) that can be configured. These include:
-
For details on general syslog-ng settings — see General syslog-ng settings.
-
For details on time stamping-related options — see Time stamping configuration on SSB.
-
For details on certificate management for receiving and sending log messages in TLS-encrypted channels —, see Setting the certificates used in TLS-encrypted log transport.
-
For details on managing domain name resolution for log messages — see Using name resolution on SSB.