The One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Passwords 4000 Appliance and 3000 Appliance are built specifically for use only with the Safeguard for Privileged Passwords privileged management software, which is pre-installed and ready for immediate use. The appliance is hardened to ensure the system is secured at the hardware, operating system, and software levels. The hardened appliance approach protects the privileged management software from attacks while simplifying deployment and ongoing management and shortening the time frame to value.
Safeguard for Privileged Passwords virtual appliances and cloud applications are also available. When setting up a virtual environment, carefully consider the configuration aspects such as CPU, memory availability, I/O subsystem, and network infrastructure to ensure the virtual layer has the necessary resources available. See One Identity's Product Support Policies for more information on environment virtualization.
Safeguard privileged management software suite
Safeguard privileged management software is used to control, monitor, and govern privileged user accounts and activities to identify possible malicious activities, detect entitlement risks, and provide tamper proof evidence. The Safeguard products also aid incident investigation, forensics work, and compliance efforts.
The Safeguard products' unique strengths are:
- One-stop solution for all privileged access management needs
- Easy to deploy and integrate
- Unparalleled depth of recording
- Comprehensive risk analysis of entitlements and activities
- Thorough Governance for privileged account
The suite includes the following modules:
- One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Passwords automates, controls, and secures the process of granting privileged credentials with role-based access management and automated workflows. Deployed on a hardened appliance, Safeguard for Privileged Passwords eliminates concerns about secured access to the solution itself, which helps to speed integration with your systems and IT strategies. Plus, its user-centered design means a small learning curve and the ability to manage passwords from anywhere and using nearly any device. The result is a solution that secures your enterprise and enables your privileged users with a new level of freedom and functionality.
-
One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS) is part of One Identity's Privileged Access Management portfolio. Addressing large enterprise needs, SPS is a privileged session management solution, which provides industry-leading access control, as well as session monitoring and recording to prevent privileged account misuse, facilitate compliance, and accelerate forensics investigations.
SPS is a quickly deployable enterprise appliance, completely independent from clients and servers to integrate seamlessly into existing networks. It captures the activity data necessary for user profiling and enables full user session drill-down for forensics investigations.
NOTE: Configuration options and details related to SPS will only be visible to customers that have purchased and joined the product to One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Passwords.
-
One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Analytics (SPA) integrates data from SPS to use as the basis of privileged user behavior analysis. Safeguard for SPA uses machine learning algorithms to scrutinize behavioral characteristics, and generates user behavior profiles for each individual privileged user. Safeguard for SPA compares actual user activity to user profiles in real time, and profiles are continually adjusted using machine learning. Safeguard for SPA detects anomalies and ranks them based on risk so you can prioritize and take appropriate action and ultimately prevent data breaches.
Figure 1: Privileged Sessions and Privileged Passwords
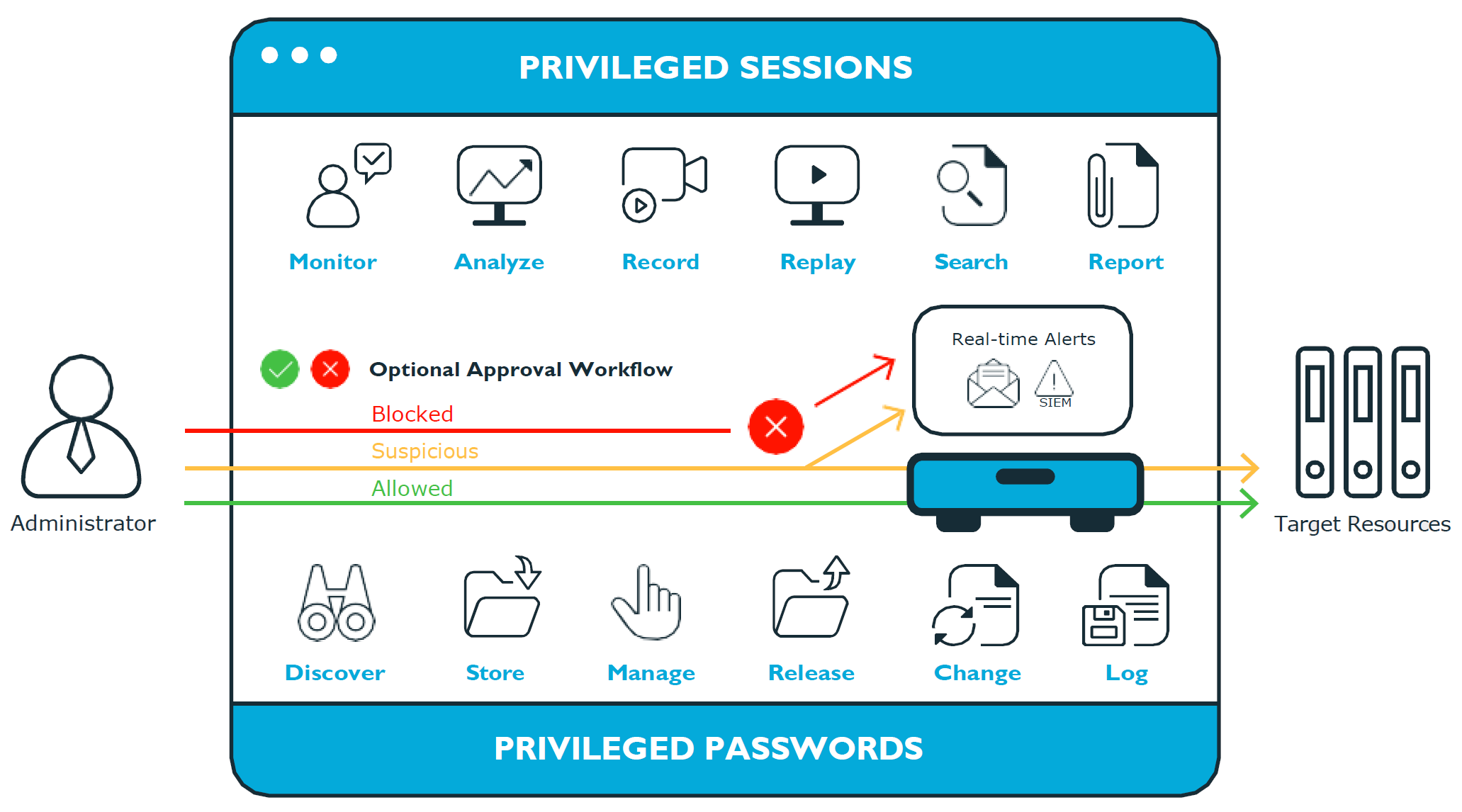
Safeguard for Privileged Passwords is a password, keys, and secrets vault to secure assets including computers, servers, network devices, directories, and applications.
A high-level introduction to the Safeguard for Privileged Passwords entities and how they relate follows.
Assets, partitions, and profiles
Assets include computers, servers, network devices, directories, or applications for Safeguard to manage. Assets have associated user accounts and service accounts. Assets and accounts may be imported (for example, from Active Directory). Assets may or may not be part of an asset group.
The partition is a container for delegated management for account passwords and SSH keys (including check and change). Partitions are also useful to segregate assets to various owners to achieve Separation of Duties (SoD). Partitions allow you to set up multiple asset managers, each with the ability to define password guidelines for the managed systems in their own workspace.
Typically you would partition assets by geographical location, owner, function, or by operating system. For example, you can group Unix assets in a partition and delegate the Unix administrator to manage it. Every partition should have a partition owner.
An asset can be assigned to only one partition at a time. When you assign an asset to a partition, all accounts associated with that asset are automatically reassigned to that partition, as well. Then, any new accounts you add for that asset are automatically assigned to that partition.
The profile includes the schedules and rules governing the partition’s assigned assets and the assets' accounts. For example, the profile defines how often a password check is required on an asset or account.
A partition can have multiple profiles, each assigned to different assets, if desired. An account is governed by only one profile. If an account is not explicitly assigned to a profile, the account is governed by the one assigned to the parent asset. If that asset does not have an assigned profile, the partition's default profile is assigned. When updating or restarting a service on a password change, the profile assigned to the asset is used for dependent account service modifications.
When you create a new partition, Safeguard for Privileged Passwords creates a corresponding default profile with default schedules and rules. You can create multiple profiles to govern the accounts assigned to a partition. Both assets and accounts are assigned to the scope of a profile.
For example, suppose you have an asset with 12 accounts and you configure the profile to check and change passwords every 60 days. If you want the password managed for one of those accounts every seven days, you can create another profile and add the individual account to the new profile. Now, Safeguard for Privileged Passwords will check and change all the passwords on this asset every 60 days except for this account, which will change every seven days.
In the example below, Partition A has three profiles (Profile A, B, and C) and a default profile. Profile A checks passwords every 30 days. Profile B checks passwords every three months, and Profile C has the highest level of security, checking passwords every seven days.
Note that the asset Server has two profiles each governing different accounts associated with the asset. Profiles A, B, and C are all explicitly assigned to the accounts and assets shown. Asset cloud service doesn't have an explicitly assigned profile so the default will be used to manage accounts on the asset.
Figure 2: Password control
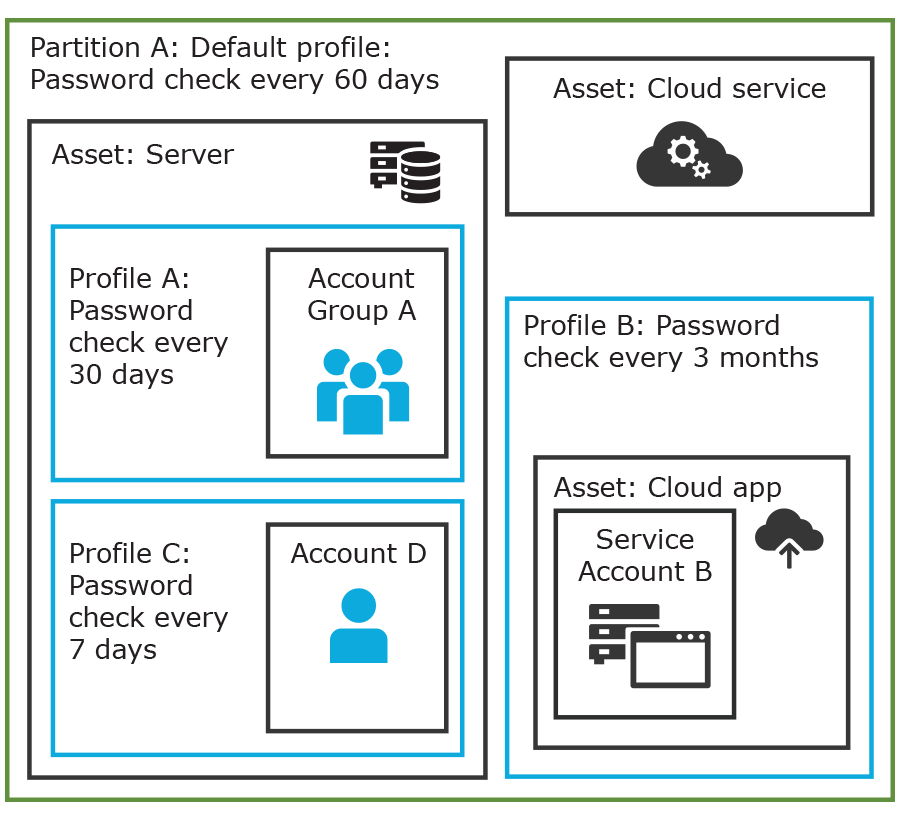
Details: Assets and asset groups
- An asset may be a computer, server, network device, directory, or application.
- You can log in to an asset with more than one account, but an account can only be associated with one asset.
-
If you select an asset for a profile, all accounts are included.
- An asset must be assigned to only one partition. An asset typically has a profile, but it is not mandatory.
-
You can create multiple assets for the same device or application then manage different accounts on each asset. For example, a directory asset can manage a subset of the forest.
- An asset group is a set of assets that can be added to the scope of an entitlement's access request policy.
Details: Partitions and profiles
- A partition is a group of assets (and the assets’ associated accounts) governed by a profile and used to delegate asset management. An asset can only be in one partition at a time. All accounts associated with that asset are automatically added to the partition.
- Profiles are the schedules and rules that govern a partition’s assets and the assets’ accounts. You can set a default profile to assign or you can manually assign a profile to an asset or account.
- When a partition is created, a default profile is created for that partition. This profile is implicitly associated with all assets and accounts added to the partition. Later, a different profile can be manually assigned to assets and accounts which is referred to as an explicit association. Explicit associations (manual assignments) override implicit associations (auto-assignments).
Accounts, account groups, entitlements, and entitlement access request policies
Assets have associated accounts, like a user account or an account for a Windows service. An account can only be associated with one asset.
Entitlements grant access to users, user groups, or both. An entitlement includes one or more access request policies and may be related to job functions like help desk support or Unix administrators.
An entitlement access request policy defines what is managed by the policy and is referred to as the "scope of the policy." Different types of access requests include password, SSH keys, and sessions.
- To define an access request policy for a password or SSH key request, the valid properties in scope are accounts and account groups.
- To define an access request policy for a sessions request, the valid properties in scope are accounts, account groups, assets, and asset groups. If only assets or asset groups are defined in the access request policy, the Asset Based Session Access must have an option other than None.
Entitlement access request policies may include:
- The access type:
- Credential access types include Password Release and SSH key
- Sessions access types include the protocols Secure SHell (SSH), Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), and Telnet
- The scope: Accounts, account groups, assets, and asset groups, as needed
- Requester settings: This includes a reason for the request, comment, ticket number (if applicable), and access duration
- Approver and Reviewer settings: If required, this includes the approvers and reviewers along with notifications
- Access configuration: Settings based on the type of access (Password, SSH key, SSH session, or RDP session set earlier)
- Session settings: Used for recording sessions, if you use SPS
- Time restrictions: Days and hours of access, if you choose to set these
- Emergency settings: Who to contact, if you choose to specify this information
In the example below, each account or account group is assigned to only one asset. The Server asset is associated with Account D and Account Group A which is made up of several accounts. Entitlement access request policy A is assigned to
Account Group A so that group can check out passwords from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. on Monday through Friday with no approval required.
Entitlement access request policy B, which is associated with Account D, allows for password check out for the same time frame, but the check outs require approvals.
Entitlement access request policy C allows for password check out from 12:59 a.m. to 11:01 p.m. to allow for the system maintenance window.
Figure 3: Entitlements and accounts
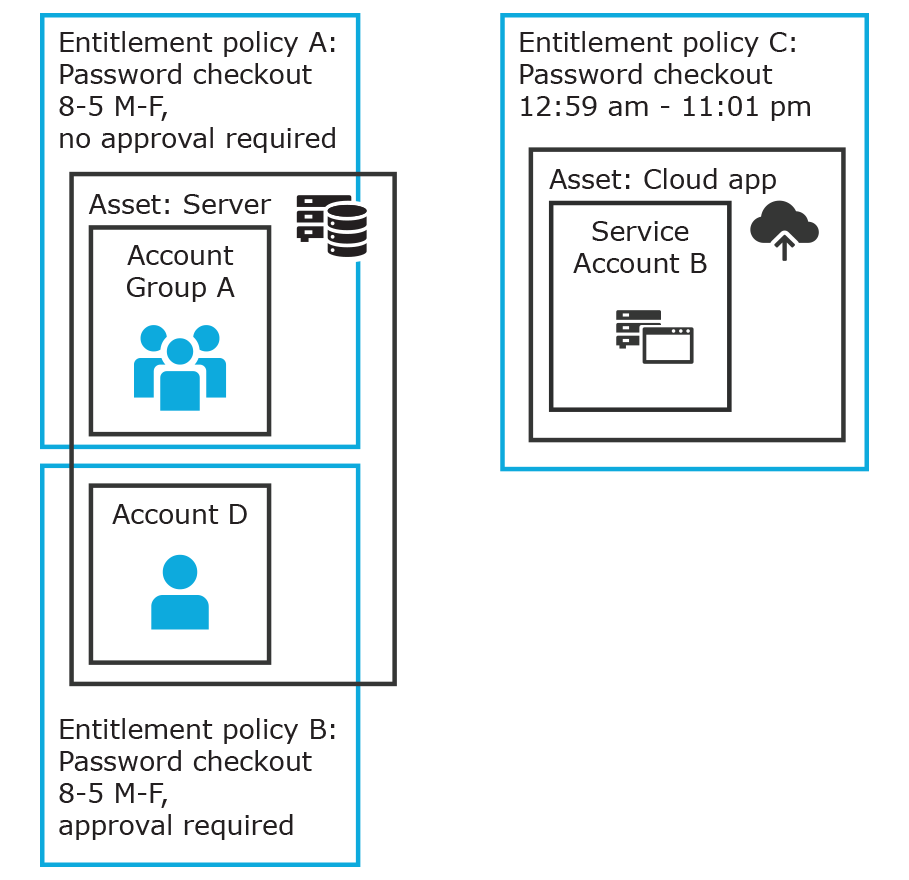
Details: Accounts and account groups
-
An account can only be associated with one asset.
- An account group is a set of accounts that can be added to the scope of an entitlement's access request policy. An account group can span multiple assets.
- Directory accounts are associated with assets that are directories.
-
Both directory accounts and directory assets can be visible or "shared" across partition boundaries, for specific purpose. Directory assets can be shared for Asset Discovery jobs. Directory accounts can be used as a service account or dependent account to a Windows service or task.
Details: Entitlements and access request policies
- An entitlement is a set of access request policies that restrict resources, typically by job role.
- Entitlements are used to authorize users or members of user groups to access accounts in the scope of the set of the entitlement's access request policies. One entitlement may have zero, one, or multiple access request policies. Users and user groups can be added to entitlements.
-
Access request policies contain the details of the type of access as well as conditions. For example, the type of access may include password versus session (RDP session, SSH client, other protocols), time limits, individual accountability (change after check-in), and other settings. Conditions may include number of approvers, time of day, ticketing system, reason codes, and so on. An access request policy can only be associated with one entitlement.
-
Access request policies are scoped to resources. Sometimes that scoping is done directly to accounts and the asset is implied. Or, the scoping is done to the asset and the access request policy identifies the account.
Users and user groups
Users are individuals. A user may be assigned administrative permissions to govern assets, partitions, accounts, and entitlement access request policies. A user may be assigned more than one set of permissions by the Authorizer Administrator. It is a best practice to follow the principles of separation of duties (SoD) in administration assignments. For example, the assignment of Asset Administrator, Security Policy Administrator, User Administrator, and Auditor should be different users.
Standard users do not have administrative permissions. They can request access, approve access requests, or review completed access requests.
Users can be configured for two-factor authentication.
Details: Users and user groups
-
A user is a person who can log into Safeguard for Privileged Passwords. A user can be associated with an identity provider that is local or a user can be a directory user from an external identity store such as Microsoft Active Directory. A user may be associated with user groups, partitions, entitlements, and linked accounts.
- A user group is a set of users that can be added to an entitlement, typically based on roles. The user group's access is governed by the entitlement’s access request policies. Both local user groups and directory user groups can be added to Safeguard for Privileged Passwords.
- A user can be assigned administrative permissions over assets, security, and so on. A standard user has no administrative permissions and performs other duties, for example, to approve access requests.
Discovery
You can discover assets and accounts that are not being managed so you can place them under management, if appropriate. Discovery jobs can be configured to discover assets and accounts.
Access request workflow
At a high-level, an end user or custom integration application may submit an access request for:
- A credential (password or SSH key) that is managed by Safeguard for Privileged Passwords
- A session (such as RDP, SSH, or Telnet) to an asset that is managed by Safeguard for Privileged Passwords with the addition of SPS
The access request may immediately be granted, or it may first have to go through an approval process.
Once approved, the credential or session can be checked out and used. For sessions, all connections are proxied through SPS and recorded.
After using the credentials or session, it can be checked in to signify that the user is done. The access request policy may then be configured such that a review of the request is required before it can be checked out again. For credential type requests, the access request policy may also be configured to change the credential.
The Safeguard for Privileged Passwords Appliance is built specifically for use only with the Safeguard for Privileged Passwords privileged management software that is already installed and ready for immediate use. It comes hardened to ensure the system is secure at the hardware, operating system, and software levels.
The following tables list the One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Passwords 4000 Appliance and 3000 Appliance specifications and power requirements.
For more information on the supported software versions for SPP hardware appliances, see Knowledge Base Article 4377774 (Compatibility Matrix for software version installs on SPP and SPS hardware appliances).
Table 1: 4000 Appliance: Feature specifications
| Processor |
Intel Xeon 4310T 2.3 GHz |
| # of Processors |
1 |
| # of Cores per Processor |
10 cores (20 threads) |
| L2/L3 Cache |
15 MB Cache |
| Chipset |
Intel C621A Chipset |
| DIMMs |
ECC DDR4-2667 |
| RAM |
64 GB |
| Internal HD Controller |
Supermicro AOC-S3908L-H8iR-16DD |
| Disk Hard Drive |
4 x Seagate Exos 7E10 2TB SAS 512e |
| Availability |
TPM 2.0, EEC Memory, Redundant PSU |
| I/O Slots |
2x PCIe 4.0 x16 FHHL 1x PCIe 4.0 x16 HHHL |
| RAID |
RAID10 |
| NIC/LOM |
Broadcom P210TP - 2 x 10G BASE-T Broadcom P210P - 2 x 10G SFP+ |
| Power Supplies |
Redundant, 500W/600W, Auto Ranging (100v~240V), RoHS and REACH compliant |
| Fans |
6 Supermicro FAN-0141L |
| Chassis |
1U Rack |
|
Dimensions (HxWxD) |
43 x 437.0 x 650.0 (mm)
1.7 x 17.2 x 25.6 (in) |
| Weight |
Max: 37 lbs (16.78 Kg) |
Table 2: 3000 Appliance: Feature specifications
| Processor |
Intel Xeon E3-1275v6 3.8 GHz |
| # of Processors |
1 |
| # of Cores per Processor |
4 cores (8 threads) |
| L2/L3 Cache |
8MB L3 Cache |
| Chipset |
Intel C236 Chipset |
| DIMMs |
Unbuffered ECC UDIMM DDR4 2400MHz |
| RAM |
32 GB |
| Internal HD Controller |
LSI MegaRAID SAS 9361-4i Single |
| Disk Hard Drive |
4 x Seagate 7E2000 2TB SAS 512E |
| Availability |
TPM 2.0, EEC Memory, Redundant PSU |
| I/O Slots |
x16 PCIe 3.0, x8 PCIe 3.0 |
| RAID |
RAID10 |
| NIC/LOM |
4 port - dual GbE LAN with Intel i210-AT |
| Power Supplies |
Redundant, 700W, Auto Ranging (100v~240V), ACPI compatible |
| Fans |
1 Supermicro SNK-P0046P and 2 Micron 16GB 2666MHz 2R ECC Unb Z01B Dual Label |
| Chassis |
1U Rack |
|
Dimensions (HxWxD) |
43 x 437.0 x 597.0 (mm)
1.7 x 17.2 x 23.5 (in) |
| Weight |
Max: 37 lbs (16.78 Kg) |
Table 3: One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Passwords 4000 Appliance and 3000 Appliance: Power requirements
| Input Voltage |
100-240 Vac |
| Frequency |
50-60Hz |
| Power Consumption (Watts) |
170.9 |
| BTU |
583 |
Safeguard for Privileged Passwords is also available as a virtual appliance and from the cloud. For details see:



