This section describes how to upgrade the indexer application on your external indexer hosts.
|
|
Caution:
After SPS 6.5, CentOS 6 operating systems will not be supported for external indexers. This means that after upgrading to SPS 6.5, or the LTS maintanance release in that cadence, you will not be able to use your external indexers that are running on CentOS 6. Make sure that you prepare your affected systems for this change and upgrade to CentOS 7 or later. |
NOTE: The version of the external indexer must be equal to or greater than the version of One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS). To make sure you meet this criterion, One Identity recommends that you always upgrade your external indexer when you upgrade SPS. You can check that SPS has established a connection to the external indexer on the Indexer > Worker status page of the SPS web interface.
Prerequisites
Before you start, create a backup copy of the /etc/indexer/indexerworker.cfg and /etc/indexer/indexer-certs.cfg indexer configuration files. After SPS 6.13, the /etc/indexer/indexer-certs.cfg indexer configuration file is automatically renamed to /etc/indexer/indexer-keys.cfg.
To upgrade the indexer application on your external indexer hosts
-
Download the latest indexer .rpm package from the Basic Settings > Local Services > Indexer service page of the SPS web interface.
NOTE: Due to legal reasons, installation packages of the external indexer application will be available only from the SPS web interface. After SPS versions 6.4 and 6.0.3 are released, the installation packages will be removed from our website.
-
Copy the downloaded .rpm package to your external indexer hosts.
-
Stop the indexer by using the following command.
-
On Red Hat or CentOS 6.5:
service external-indexer stop
-
On Red Hat or CentOS 7:
systemctl stop external-indexer.service
-
Execute the following command: yum upgrade -y indexer.rpm
-
Resolve any warnings displayed during the upgrade process.
-
Restart the indexer by using the following command.
-
On Red Hat or CentOS 6.5:
service external-indexer start
-
On Red Hat or CentOS 7:
systemctl start external-indexer.service
-
Repeat this procedure on every indexer host.
The indexers that run on an external host send log messages into the standard syslog of the external host. These log messages are not visible on One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS). If a problem occurs, check the logs of SPS and the external indexer to find out which component on which host causes the problem. If the problem is on the external indexer host, verify that the required decryption keys are available on the host, then restart the indexer service using the following command.
systemctl restart external-indexer.service
If the problem persists, contact our Support Team. You can increase the log level of the indexer processes from the configuration file.
You can monitor the status of your indexer services in a summarized view by navigating to the Indexer Status page of the Main Menu.
The Indexer Status page displays the overall health of your indexer services, summarizing the current state of your:
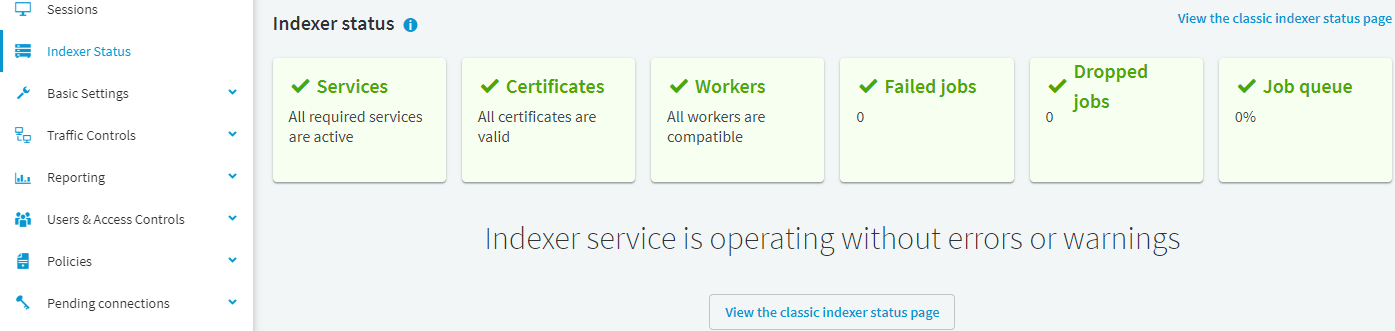
In an optimal state, or in case of a fairly new production environment, the page will display no errors or warnings:
Figure 254: Main Menu > Indexer Status — Indexer services working without errors or warnings
In a production environment that has been in use for some time, you will likely some have errors or warnings:
Figure 255: Main Menu > Indexer Status — Indexer services status with errors and warnings
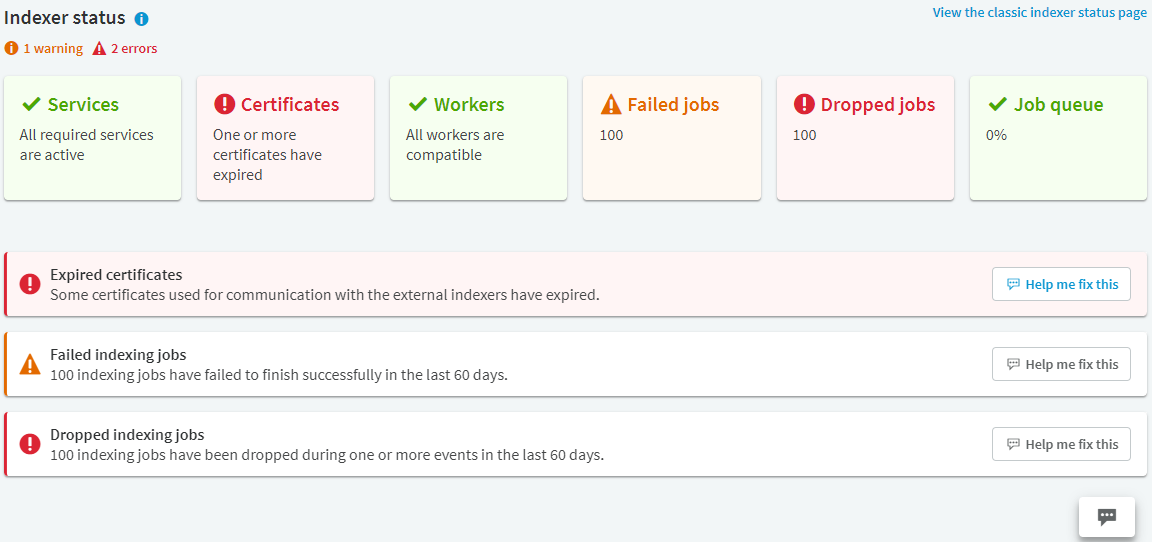
NOTE: If you have errors and warnings listed on the Indexer Status page, you can use the help chat function of the SPS web UI by clicking the Help me fix this button on the error or warning of your choice.
The help chat function gives you a summary of the issue, explain how the issue affects your production environment, and guide you through the process of fixing the issue.
When the help chat function is still in use (for example, if you have not yet fixed the issue, but have clicked away from the chat window to use a terminal window), the minimized chat window is still accessible by clicking on the help chat (  ) icon, located at the bottom right corner of the web UI.
) icon, located at the bottom right corner of the web UI.
Services
The general workflow of indexing requires a few internal services to be active and running. Inactive internal services interrupt your workflow, causing delays or data loss. You can monitor the state of these internal services and see if any of them are inactive.
Certificates
Certificates and keys used to encrypt the communication between the indexer service and the external indexer ensure the processing of audit trails. You can monitor the validity of these credentials and see if any of them have expired or is about to expire soon.
Workers
The indexer service and the indexer service you use on your workers should always be compatible, otherwise external indexers will not process audit trails, and the queue load of the indexer service may be affected. You can monitor the state of the compatibility of your indexer service and the external indexers.
Failed jobs
When some of your indexing jobs are not finished successfully (for example, as a result of audit trail files moved or deleted during indexing, unsupported protocol versions used during remote sessions, or misconfigured indexer worker key stores), some of your recorded audit trails are not processed completely. As a result, the search function to the affected audit trail files is limited. You can monitor which indexing jobs may be affected and find the reason for the failure.
Dropped jobs
When your indexing jobs are dropped during an unknown even (for example, a mismanaged upgrade, an internal service shutdown, or an ill-timed system reboot), the affected audit trails are not processed completely, and some of the recorded contents are not indexed. As a result, the search function to the affected audit trail files is limited. You can monitor which indexing jobs may be affected and find the reason for the failure.
Job queue
When there are no free indexer workers to process your audit trails, indexing jobs will wait in a priority queue. Long queues may cause delays in using detailed search, and if your queue gets full, your most recent indexing jobs get dropped. By monitoring the status of your job queue, you can see if you may encounter delays, or in case of a full queue, dropped indexing jobs.
You can monitor the status of audit trail processing in detail by navigating to the Indexer Status page of the Main Menu, and clicking the View the classic indexer status page link in the upper right corner, or the View the classic indexer status page button, if visible.
TIP: To automatically refresh the Indexer Status page every 5 seconds, select Auto refresh. To refresh the page immediately, click Refresh now.
TIP: To view the status of your indexer services in a summarized view, click the View the new indexer status page button in the top right corner of the web UI.
Elements of the Indexer Status page in classic view
The following list describes the elements of the Indexer page and their functions.
-
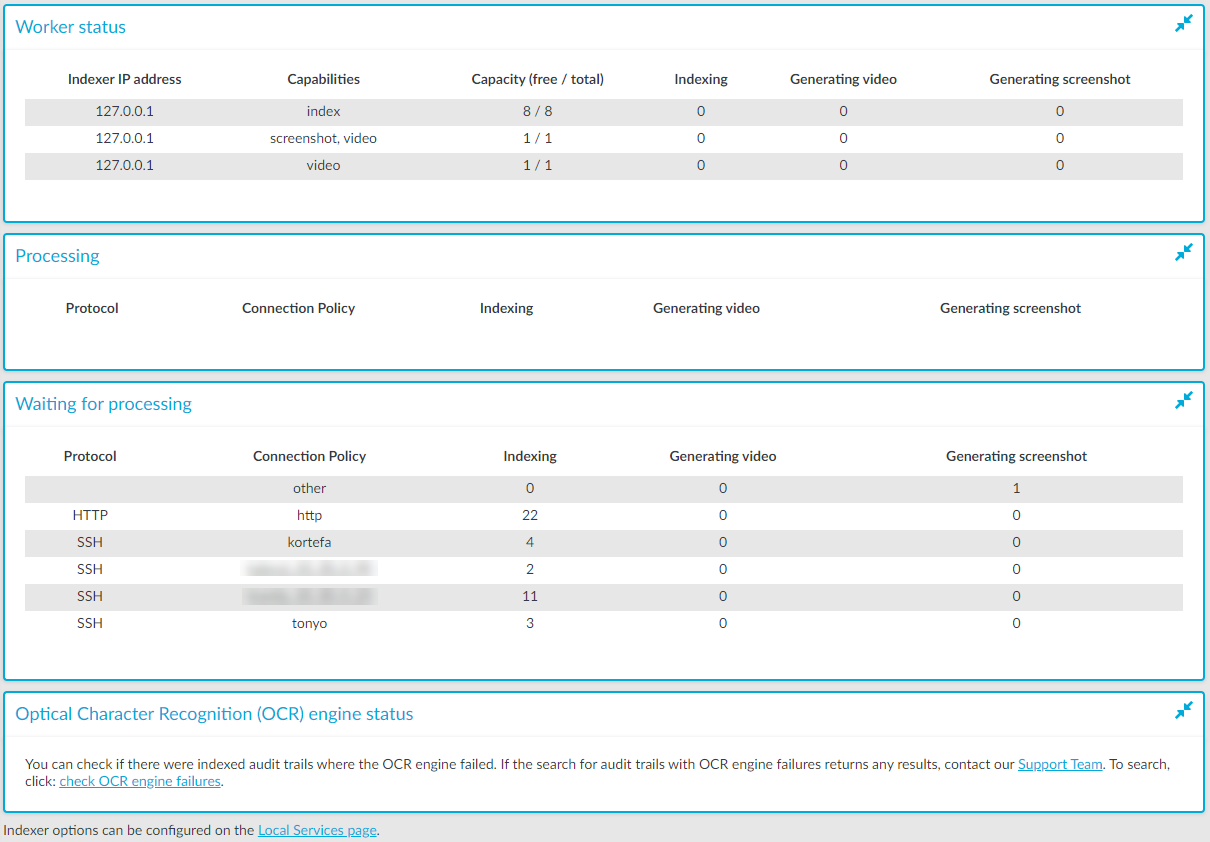
Worker status: displays information about the worker groups.
-
Indexer IP address: the IP address of the indexer running on One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS) or an external indexer.
NOTE:127.0.0.1 indicates the indexer running on SPS, while any IP address other than 127.0.0.1 indicates an external indexer.
-
Capabilities: the type of job(s) this worker can perform. Possible job types are index, near-realtime, screenshot, and video.
-
Capacity (free / total): the available and total Capacity of the indexer. The value of the total capacity indicates the number of maximum parallel audit trails that the indexer can process.
-
Indexing: the number of the active processes currently indexing an audit trail.
-
Generating video: the number of the active processes currently generating a video.
-
Generating screenshot: the number of the active processes currently generating a screenshot.
-
Processing: audit trails currently being processed.
-
Waiting for processing: audit trails waiting to be processed.
NOTE: Audit trails in the Indexing column may indicate any of the following:
-
The maximal queue size is 1000. If there are several trails waiting to be indexed, SPS will keep numerous trails in the queue.
-
The worker with the appropriate key for decryption is not available at the moment, and there are no other workers with the required key to take over indexing.
-
There are no workers with the required capacity available.
-
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) engine status: It allows you to check and report indexed audit trails where the OCR engine failed. You can perform a search on the Search interface using the provided link and if the search returns any results, you can contact our Support Team to submit a report.
Figure 256: Indexer > Indexer status — Monitoring the status of the indexers




 ) icon, located at the bottom right corner of the web UI.
) icon, located at the bottom right corner of the web UI. 