You can run all audit data cleanup policies immediately. This procedure deletes all data matching the queries and older than the retention period.
Prerequisites
Running cleanup policies immediately
-
Navigate to Policies > Audit Data Cleanup Policies.
-
Select Run all policies now.
-
Select Run policies to confirm running all policies immediately in the pop-up dialog.
After confirming the cleanup, you still have 10 seconds to undo the procedure in the pop-up dialog by selecting Undo. After 10 seconds or after selecting Okay, SPS completes the cleanup.
To download the official plugins for your product version, navigate to the product page on the Support Portal. The not officially supported plugins are also available on GitHub .
To write your own custom plugin, feel free to use our Plugin SDK.
Figure 75: Basic Settings > Plugins — Viewing the uploaded plugins
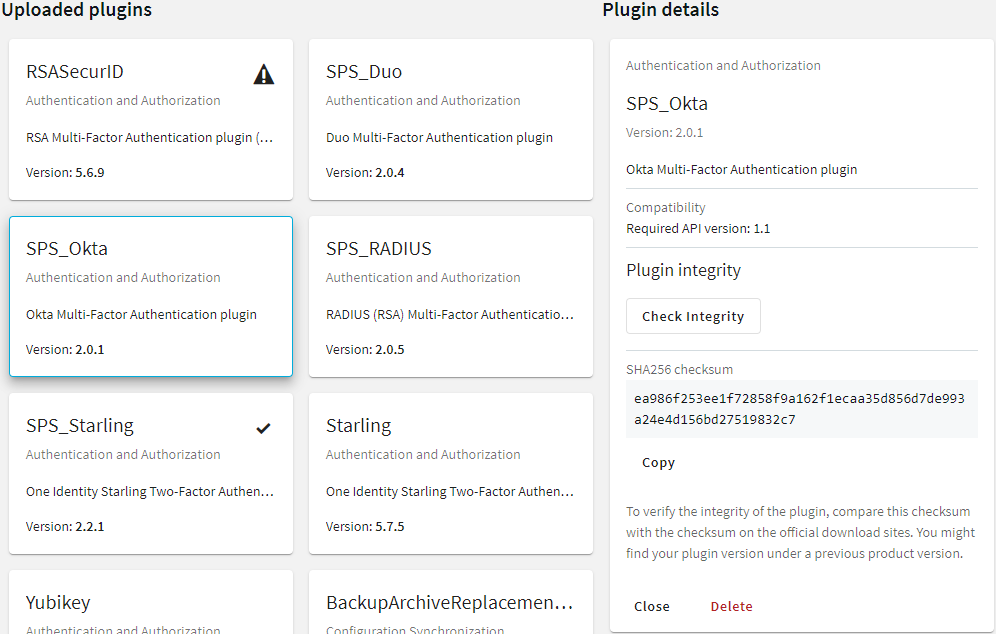
The following plugin types can be uploaded to SPS:
To upload a plugin to SPS
-
Navigate to Basic Settings > Plugins and click Upload plugin.
-
Browse for the plugin .zip file and click Open.
NOTE: It is not possible to upload or delete plugins if SPS is in sealed mode. For more information, see Sealed mode in the Administration Guide.
To verify the integrity of the plugin archive (that is, that the .zip file has officially been issued by One Identity and has not been tampered with before its extraction and uploading the plugin), complete the following steps. These also verify whether the plugin has been modified after upload or not.
This procedure only applies to plugins downloaded from the official repositories.
Prerequisites
-
Make sure that you have already uploaded a plugin.
For more information on uploading plugins, see Uploading plugins.
To verify the integrity of a plugin
-
Navigate to Basic Settings > Plugins.
-
Select the plugin that you want to verify.
-
Under Plugin details > Plugin integrity, click Check integrity.
Figure 76: Basic Settings > Plugins > Plugin details — Verifying plugin integrity
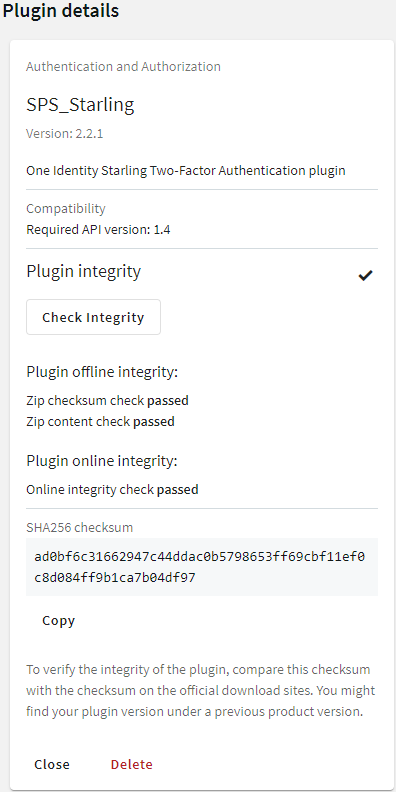
There are three integrity checks:
-
Plugin offline integrity > Zip checksum check
This check verifies whether the recalculated checksum is the same as the checksum that has been stored in the configuration after uploading plugin.
-
Plugin offline integrity > Zip content check
This check verifies whether the plugin runtime files are the same since you have uploaded the plugin .zip.
-
Online integrity check
This check verifies whether the plugin .zip checksums match with the .zip checksums stored online.
NOTE: The online integrity check works only if you have joined to Starling.
For more information, see Starling integration
To verify the integrity of a plugin manually
-
Under Plugin details > Plugin integrity > SHA256 checksum, click Copy.
-
To verify the integrity of the plugin, compare this checksum with the checksum on the official download sites. You might find your plugin version under a previous product version.
On the support portal:
-
Navigate to the product page on the Support Portal that you have downloaded the plugin from. Click on the name of the plugin.
-
Next to the sha256 section, you will see the checksum of the official One Identity plugin.
On GitHub:
-
Navigate to the GitHub plugin repository that you have downloaded the plugin from. Click on the name of the plugin.
-
Navigate to the releases tab.
-
Scroll to the specific release that you use.
-
Under the SHA256 checksum section, you will see the checksum of the official One Identity plugin.
-
Compare the checksum of the official One Identity plugin with the one you have copied from Plugin details > Plugin integrity > SHA256 checksum.


