Managing Microsoft 365 Groups
Active Roles supports CRUD (create, read, update and delete) operations for Microsoft 365 (M365) groups and also lets you specify owners and add/remove members to or from existing M365 groups in your organization.
M365 groups facilitate teamwork within an organization by providing the same set of permissions to (guest) users, allowing you to provide access efficiently to various shared resources (such as a common Microsoft Outlook inbox and calendar, a shared OneNote notebook, or other Microsoft 365 resources). For more information on M365 groups, see Overview of Microsoft 365 Groups for administrators in the Microsoft 365 documentation.
You can administer M365 groups either via the Active Roles Web Interface or through the Active Roles Management Shell.
Configuring M365 Groups with the Web Interface
You can use the Active Roles Web Interface to:
-
Create, view, modify or delete Microsoft 365 (M365) groups in your organization.
-
Assign or remove owners and members to or from existing M365 groups.
-
View the change history of existing M365 groups.
NOTE: You cannot use the Active Roles Web Interface to synchronize existing M365 groups. To synchronize M365 groups, configure an M365 synchronization schedule task with the Active Roles Console (also known as the MMC Interface). For more information, see Scheduling an Azure object synchronization task.
Creating an M365 Group with the Web Interface
You can use the Active Roles Web Interface to create and enable new Microsoft 365 (M365) groups.
For more information on M365 groups, see Overview of Microsoft 365 Groups for administrators in the Microsoft 365 documentation.
To create a new M365 group
-
Navigate to Directory Management > Tree > Azure > <azure-tenant-name> > Microsoft 365 Groups.
The list of existing M365 groups in the selected Azure tenant appears.
NOTE: When opening the list of Microsoft 365 Groups the first time, Active Roles checks and fetches all existing M365 groups that may exist in the Azure cloud. This action is performed automatically and may take a few minutes to complete.
-
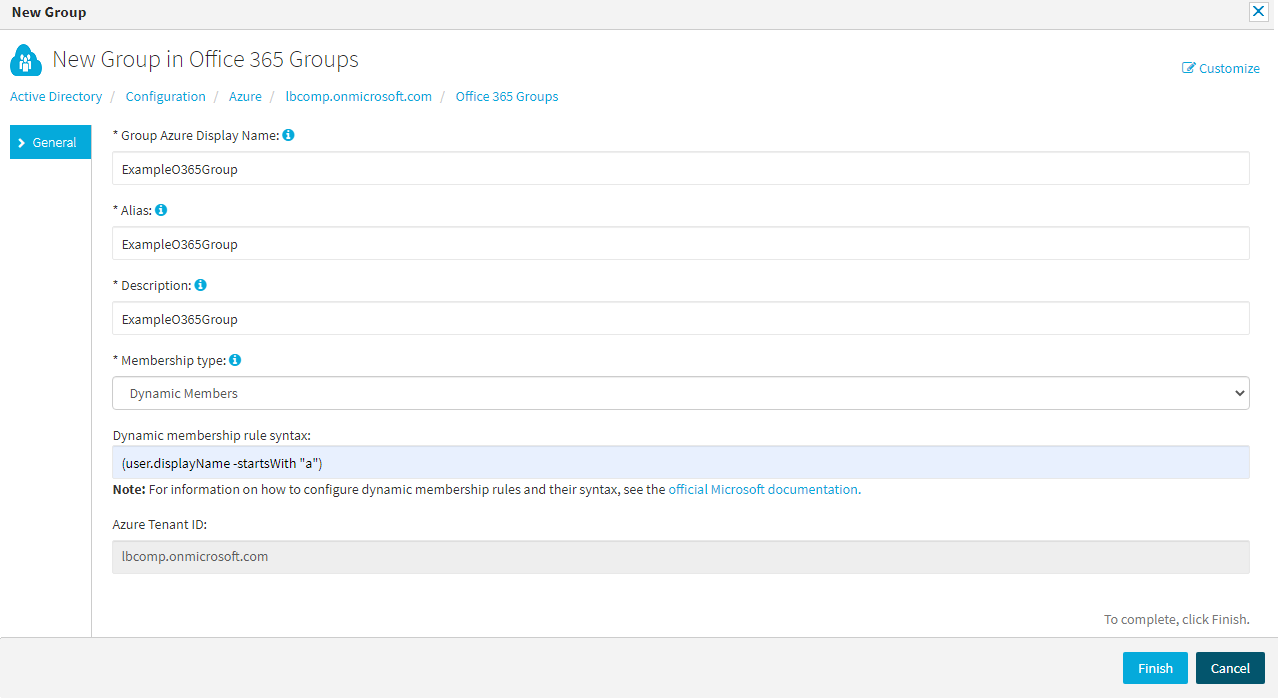
In the right-side pane, click New Group.
The New Group in Microsoft 365 Groups window appears.
-
Specify the Group Azure Display Name of the configured group.
TIP: You can configure multiple groups with the same Group Azure Display Name in the same Azure tenant.
-
Specify the Exchange Online Alias of the M365 group. This value is used for naming the SharePoint site URL of the M365 group, and will also name the primary email address of the shared mailbox associated with the M365 group.
TIP: The Alias of the M365 group must be unique within the Azure tenant.
-
Provide a short Description for the group.
-
Configure the Membership type of the group:
-
Assigned: When selected, you can add or remove members to or from the group manually later. For more information, see Adding or removing members from an M365 Group with the Web Interface.
-
Dynamic Members: When selected, Active Roles sets up the group as a dynamic membership group, and will automatically update group membership based on the configured Dynamic membership rule syntax.
TIP: Consider the following when configuring the Membership type:
-
Select Dynamic Members to quickly configure a group based on a certain membership logic. For example, if you need to set up a group for employees from the same geographical location, business unit, or functional area, One Identity recommends configuring the group with Dynamic Members.
-
If you select Dynamic Members, you will not be able to manually add or remove members to or from the M365 group, unless you change its Membership type to Assigned later. However, you can still manually configure the owner(s) for a dynamic M365 group, as described in Adding or removing owners from an M365 Group with the Web Interface.
-
You can always change the Membership type later by navigating to the following option of the Active Roles Web Interface:
Directory Management > Tree > Azure > <azure-tenant-name> > Microsoft 365 Groups > <m365-group-name> > Azure Properties > General.
-
Changing the Membership type from Dynamic Members to Assigned later will keep the last set of members that were dynamically assigned to the group.
-
If you set the Membership type to Dynamic Members, specify the Dynamic membership rule syntax. Active Roles will send the logic configured in this field to Azure to automatically assign or remove members to or from the group later.
NOTE: Consider the following when using the Dynamic membership rule syntax setting:
-
This setting is enabled only if Membership type is set to Dynamic Members. However, in that case, it is mandatory and cannot be empty.
-
The specified dynamic membership rule must meet all rule syntax requirements, otherwise the window will return an error. For more information on the available membership rule properties, operators and values, see Dynamic membership rules for groups in Azure Active Directory in the Microsoft 365 documentation.
-
Whenever you modify the dynamic membership rule of a dynamic M365 group, it can take several minutes for Azure to update the list of group members in the Directory Management > Tree > Azure > <azure-tenant-name> > Microsoft 365 Groups > <m365-group-name> > Dynamic Members window.
-
To complete the configuration of the new M365 group, click Finish.
The new M365 group will appear under the Directory Management > Tree > Azure > <azure-tenant-name> > Microsoft 365 Groups node.
Modifying an M365 Group with the Web Interface
You can use the Active Roles Web Interface to modify the Azure properties of existing Microsoft 365 (M365) groups in your Azure tenant. This is typically useful if you must:
-
Modify the display name of the M365 group, for example because of an organizational change.
-
Change the configured membership type (manually assigned or dynamic) of the M365 group.
NOTE: You cannot change the Exchange Online alias of an existing M365 group.
To modify the Azure properties of an M365 group
-
Navigate to Directory Management > Tree > Azure > <azure-tenant-name> > Microsoft 365 Groups.
The list of existing M365 groups in the selected Azure tenant appears.
NOTE: When opening the list of Microsoft 365 Groups the first time, Active Roles checks and fetches all existing M365 groups that may exist in the Azure cloud. This action is performed automatically and may take a few minutes to complete.
-
Select the group that you want to configure.
-
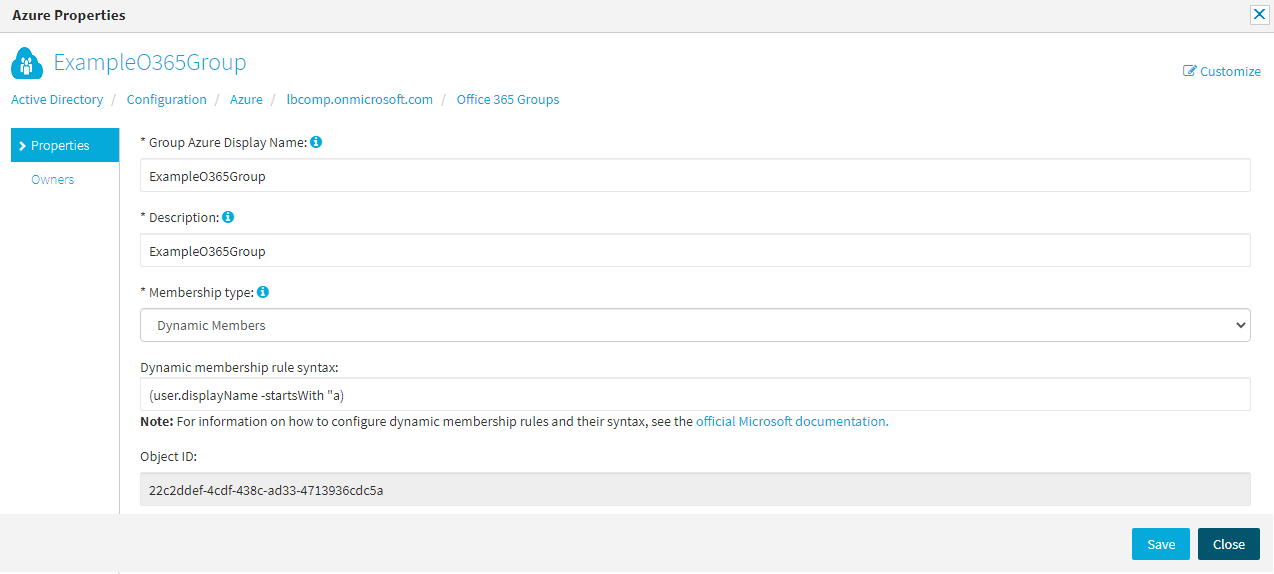
In the right-side pane, click Azure Properties.
-
In the left-side pane of the Azure Properties window, click Properties.
-
(Optional) Specify the Group Azure Display Name of the configured group.
TIP: You can configure multiple groups with the same Group Azure Display Name in the same Azure tenant.
-
(Optional) Provide a short Description for the group.
-
(Optional) Configure the Membership type of the group:
-
Assigned: When selected, you can add or remove members to or from the group manually later. For more information, see Adding or removing members from an M365 Group with the Web Interface.
-
Dynamic Members: When selected, Active Roles sets up the group as a dynamic membership group, and will automatically update group membership based on the configured Dynamic membership rule syntax.
TIP: Consider the following when configuring the Membership type:
-
Select Dynamic Members to quickly configure a group based on a certain membership logic. For example, if you need to set up a group for employees from the same geographical location, business unit, or functional area, One Identity recommends configuring the group with Dynamic Members.
-
If you select Dynamic Members, you will not be able to manually add or remove members to or from the M365 group, unless you change its Membership type to Assigned later. However, you can still manually configure the owner(s) for a dynamic M365 group, as described in Adding or removing owners from an M365 Group with the Web Interface.
-
Changing the Membership type from Dynamic Members to Assigned later will keep the last set of members that were dynamically assigned to the group.
-
(Optional) If you set the Membership type to Dynamic Members, specify the Dynamic membership rule syntax. Active Roles will send the logic configured in this field to Azure to automatically assign or remove members to or from the group later. For more information on how to specify a membership rule, see Dynamic membership rules for groups in Azure Active Directory in the Microsoft 365 documentation.
-
To apply your changes, click Save.


