Access to Active Roles Web Interface
To access the Active Roles Web Interface through a firewall, open the following ports:
The Web Interface normally runs over port 80, or over port 443 if SSL is enabled (off by default).
Active Roles and supported Azure environments
Active Roles and supported Azure environments
Active Roles supports 3 different Azure environment configurations: Non-federated, Synchronized Identity, and Federated.
Non-federated
In a non-federated environment, the on-premises domains are not registered in Azure AD, and neither Azure AD Connect nor any third-party synchronization tools are configured in the domain for synchronization. In non-federated environments, the changes made in Active Roles are immediately replicated to Azure or Microsoft 365 using Graph API calls or cmdlet calls. Azure users or guest users are typically created with the onmicrosoft.com UPN suffix.
Example: Non-federated environment configuration
A non-federated environment may have the following settings:
-
On-premises domain: test.local
-
Azure AD Domain: ARSAzure.onmicrosoft.com
-
Azure AD Connect is not configured for synchronization.
The on-premises domain is not registered in Azure. The Azure user is created in Active Roles with the ID of user001@test.local and in Azure as user001@ARSAzure.onmicrosoft.com. The user is created in Azure simultaneously when it is created in Active Roles using a Graph API call.
NOTE: One Identity recommends using Non-federated environments for testing purposes only, and does not recommend setting them up as a live production environment.
Synchronized identity
In a Synchronized identity environment, the on-premises domain is optionally registered in Azure AD, while Azure AD Connect is configured to synchronize the local AD objects to Azure. Azure users or guest users are typically created either with the selected on-premises domain or with the onmicrosoft.com UPN suffix.
Figure 266: Synchronized identity configuration
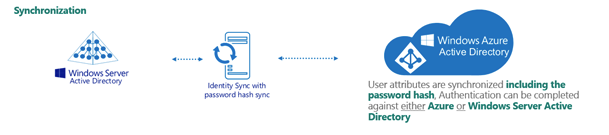
Example: Synchronized identity configuration
A synchronized identity environment may have the following settings:
-
On-premises domain: test.local
-
Azure AD Domain: rd4.qsftdemo.com
-
Azure AD Connect is configured for synchronization.
The on-premises domain is optionally registered in Azure. The Azure user is created in Active Roles with the ID of user001@test.local and in Azure as user001@rd4.qsftdemo.com.
Federated
In a federated environment, the on-premises domain is always registered in Azure AD, while Azure AD Connect and Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) are configured to facilitate synchronization. Azure users and guest users are typically created with the onmicrosoft.com UPN suffix of the selected on-premises domain.
Figure 267: Federated configuration
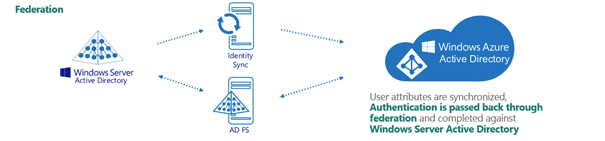
Example: Federated configuration
A federated configuration may have the following settings:
-
On-premises domain: rd4.qsftdemo.com
-
Azure AD Domain: rd4.qsftdemo.com
-
Azure AD Connect and ADFS are configured for synchronization.
The on-premises domain is registered and verified in Azure. The Azure user is created in Active Roles and Azure AD with the same ID of user001@rd4.qsftdemo.com.
Azure object management supported in various Azure environments
This section provides information about the supported Azure object operations and methods in various Azure environments using the Active Roles Web Interface. Active Roles supports Non-federated, Federated and Synchronized Identity environments.
You can select the Azure environment configuration type in the Active Roles Configuration Center when creating the Azure tenant, as described in Configuring a new Azure tenant and consenting Active Roles as an Azure application. You can modify the configuration type later by changing the Azure properties of the tenant.
Active Roles identifies the environment based on the Azure tenant type and applies the changes accordingly.
Azure object management in a Non-Federated environment
A Non-federated environment is typically used for testing purposes. In a Non-federated environment, most of the Azure properties can be modified, with the exception of attributes that uniquely identify the object (such as UserPrincipalName and ObjectId).
The following table provides information about the operations and methods of operation that can be performed on Azure objects in a Non-federated environment.
Table 143: Supported Azure configurations comparison chart
|
User |
Create |
Using Graph API |
| Read |
Using Graph API and Exchange Online cmdlets |
| Update |
Using Graph API and Exchange Online cmdlets |
| Delete |
Using Graph API |
|
Guest User |
Create |
Using Graph API |
| Read |
Using Graph API |
| Update |
Using Graph API |
| Delete |
Using Graph API |
|
Security Group |
Create |
Using Graph API |
| Read |
Using Graph API |
| Update |
Using Graph API |
| Delete |
Using Graph API |
|
Mail Enabled Security Group |
Create |
Using Exchange Online cmdlets |
| Read |
Using Graph API |
| Update |
Using Graph API |
| Delete |
Using Graph API |
|
Distribution Group |
Create |
Using Exchange Online cmdlets |
| Read |
Using Graph API |
| Update |
Using Graph API |
| Delete |
Using Graph API |
|
Native Microsoft 365 Group (Cloud-only) |
Create |
Using Graph API |
|
Read |
Using Graph API |
|
Update |
Using Graph API |
|
Delete |
Using Graph API |
|
Contacts |
Create |
Using Exchange Online cmdlets |
| Read |
Using Graph API |
| Update |
Using Exchange Online cmdlets |
| Delete |
Using Graph API |
NOTE: Active Roles provides cloud-only support only for Native Microsoft 365 Groups management.


