Managing Microsoft Exchange environments
The key aspects of managing a Microsoft Exchange environment with One Identity Manager include the mapping of mailboxes, mail users, mail contacts, and the mail-enabled distribution group.
The system information for the Microsoft Exchange structure is loaded into the One Identity Manager database during data synchronization. It is not possible to customize this system information in One Identity Manager due to the complex dependencies and far reaching effects of changes.
NOTE: The Microsoft Exchange Module must be installed as a prerequisite for managing Microsoft Exchange in One Identity Manager. For more information about installing, see the One Identity Manager Installation Guide.
Architecture overview
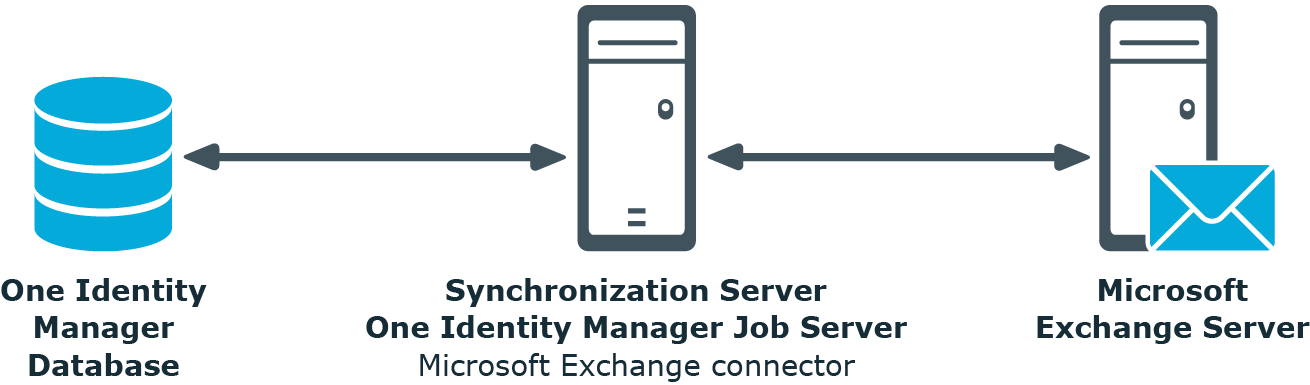
In One Identity Manager, the following servers play a role in managing Microsoft Exchange:
-
Microsoft Exchange server
The Microsoft Exchange server against which Microsoft Exchange objects are synchronized. The synchronization server connects to this server in order to access the Microsoft Exchange objects.
-
Synchronization server
Synchronization server for synchronizing One Identity Manager data with Microsoft Exchange. The One Identity Manager Service with the Microsoft Exchange connector is installed on this server. The synchronization server connects to the Microsoft Exchange server.
The One Identity Manager Microsoft Exchange connector uses Windows PowerShell to communicate with the Microsoft Exchange server.
Figure 1: Architecture for synchronization
One Identity Manager users for managing Microsoft Exchange
The following users are used for setting up and administration of Microsoft Exchange.
Table 1: Users
| Target system administrators |
Target system administrators must be assigned to the Target systems | Administrators application role.
Users with this application role:
-
Administer application roles for individual target system types.
-
Specify the target system manager.
-
Set up other application roles for target system managers if required.
-
Specify which application roles for target system managers are mutually exclusive.
-
Authorize other employees to be target system administrators.
-
Do not assume any administrative tasks within the target system. |
| Target system managers |
Target system managers must be assigned to the Target systems | Exchange application role or a child application role.
Users with this application role:
-
Assume administrative tasks for the target system.
-
Create, change, or delete target system objects.
-
Edit password policies for the target system.
-
Can add employees who have another identity than the Primary identity.
-
Configure synchronization in the Synchronization Editor and define the mapping for comparing target systems and One Identity Manager.
-
Edit the synchronization's target system types and outstanding objects.
-
Authorize other employees within their area of responsibility as target system managers and create child application roles if required. |
| One Identity Manager administrators |
administrator and administrative system users Administrative system users are not added to application roles.
administrators:
-
Create customized permissions groups for application roles for role-based login to administration tools in the Designer as required.
-
Create system users and permissions groups for non role-based login to administration tools in the Designer as required.
-
Enable or disable additional configuration parameters in the Designer as required.
-
Create custom processes in the Designer as required.
-
Create and configure schedules as required.
-
Create and configure password policies as required. |
Configuration parameters for managing Microsoft Exchange environments
Use configuration parameters to configure the behavior of the system's basic settings. One Identity Manager provides default settings for different configuration parameters. Check the configuration parameters and modify them as necessary to suit your requirements.
Configuration parameters are defined in the One Identity Manager modules. Each One Identity Manager module can also install configuration parameters. In the Designer, you can find an overview of all configuration parameters in the Base data > General > Configuration parameters category.
For more information, see Configuration parameters for managing a Microsoft Exchange environment.

