Scenario: Mailbox store load balancing
The policy described in this scenario allows multiple stores to be used for mailbox creation, and forces Active Roles to automatically select the store that holds the least amount of mailboxes.
To implement this scenario, you must perform the following actions:
- Create and configure a Policy Object that defines the appropriate policy.
- Apply the Policy Object to a domain, OU, or Managed Unit.
As a result, when creating a mailbox for a user account that resides in the container you selected in Step 2, Active Roles chooses the least loaded store among those where mailbox creation is allowed.
The following two sections elaborate on the steps to implement this scenario.
Step 1: Creating and configuring the Policy Object
Step 1: Creating and configuring the Policy Object
You can create and configure the Policy Object you need by using the New Provisioning Policy Object wizard. For information about the wizard, see Creating a Policy Object in the Policy Object management tasks section earlier in this chapter.
To configure the policy, click Exchange Mailbox AutoProvisioning on the Select Policy Type page of the wizard. Then, click Next.
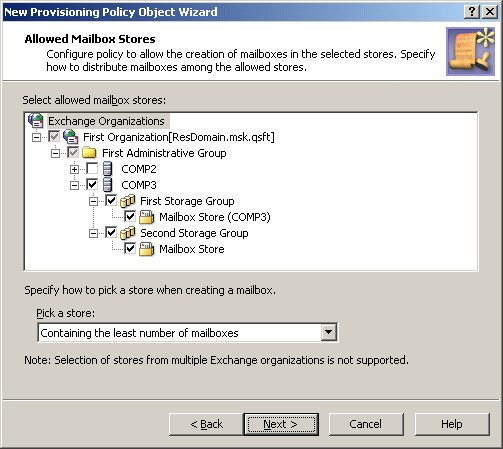
On the Allowed Mailbox Stores page, select the stores in which you want mailbox creation to be allowed. Then, under Pick a store, click Containing the least number of mailboxes, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 71: Allowed mailbox stores
Click Next, and follow the instructions in the wizard to create the Policy Object.
Step 2: Applying the Policy Object
Step 2: Applying the Policy Object
You can apply the Policy Object by using the Enforce Policy page in the New Provisioning Policy Object wizard, or you can complete the wizard and then use the Enforce Policy command on the domain, OU, or Managed Unit where you want to apply the policy.
For more information on how to apply a Policy Object, see Applying Policy Objects and Managing policy scope earlier in this chapter.
Default creation options for Exchange mailbox
In the wizard for creating user accounts, whether in the Active Roles console or Web Interface, the Create an Exchange mailbox option is selected by default, causing the user mailbox to be created upon creation of a user account. This behavior can be changed by applying an appropriately crafted policy of the Exchange Mailbox AutoProvisioning category.
A policy can be configured so that the Create an Exchange mailbox option is not selected by default but the administrator who uses the wizard to create a user account can select that option if necessary. It is also possible to configure a policy that forces the Create an Exchange mailbox option to be selected.
To set default creation options for Exchange mailbox
- Create a Policy Object containing an Exchange Mailbox AutoProvisioning policy.
- Open the Properties dialog box for the Policy Object you created.
- On the Policies tab in the Properties dialog box, double-click the Exchange Mailbox AutoProvisioning policy entry.
- On the Mailbox Creation tab in the Exchange Mailbox AutoProvisioning Policy Properties dialog box, set policy options as appropriate for your situation:
- Create the user mailbox by default. Determines whether the Create an Exchange mailbox option is selected by default in the wizard for creating user accounts. If you want user mailboxes not to be created by default, unselect this policy option.
- Enforce creation of the mailbox. Causes the Create an Exchange mailbox option to be selected and unavailable so that the administrator who creates a user account cannot unselect that option.
- Click OK to close the dialog boxes you opened.
- Apply the Policy Object to the scope (domains, containers, or Managed Units) where you want this policy to be in effect.

