Active Roles Web interface enables you to perform bulk attributes operation for multiple users at a time.
To perform bulk attribute operation
- On the Navigation bar, click Directory Management.
- On the Views tab in the Browse pane, click the required container.
- From the list of objects displayed for the selected container, select the required users for which you need to perform bulk attributes operation.
The batch operations that can be performed on users are displayed in the Command pane.
- In the Command pane, click Update object attributes.
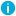
The Update object attributes window is displayed, which lists the user attributes that can be selected for bulk operation.
- From the Attribute List tab, select the required attribute on which you want to perform the bulk operation, and click the + symbol.
- On the Update object attributes dialog box that is displayed, in the New Value field, enter a value for the attribute, and click OK.
The selected attribute with the updated value is displayed in the Select attribute table.
- Repeat step 5 and step 6 to select and update more attributes, and then click Next.
The Preview tab | Operation Summary section displays the summary of the selected attributes with the new values to be updated after the bulk operation is performed. To export the details, click Export as CSV.
- Click Finish, to complete the bulk operation on the selected attributes for the multiple users.
|
|
NOTE:
|
Active Roles Web interface enables you to reset the password for multiple users at a time.
To perform bulk users password reset operation
- On the Navigation bar, click Directory Management.
- On the Views tab in the Browse pane, click the required container.
- From the list of objects displayed for the selected container, select the required users for which you need to perform password reset operation.
The batch operations that can be performed on users are displayed in the Command pane.
- In the Command pane, click Reset Password.
The Reset Password window is displayed.
- On the General tab dialog box, click Generate to generate a new password for the selected users.
- Under Account options, select the check box corresponding to the required rule to be applied for change of password, and then click Save.
The password reset gets completed and the changes can be viewed on the selected user's Change History tab.
As Active Roles performs operations on objects on behalf of delegated users, the Active Roles service account which is used to manage the Active Directory domain requires adequate permissions. One Identity recommends to manage the domain using an account which is a member of the Domain Admins role group. If this configuration is not used, then guidance and documentation provided by One Identity may not be relevant.
Specify separate accounts for service and for managing the domain to separate the tasks performed by the service account from domain management. In this configuration scenario, the service account can be configured to run with the minimum permissions specified below, but the proxy account should be a member of the Domain Admins role group to stay within the One Identity Active Roles support model.
The service account credential has five main roles:
-
Access to the Administration Service computer
-
Service publication in Active Directory
-
All script modules are executed under the security context of the Active Roles Service Account
-
Connecting to the Microsoft SQL database
-
Synchronizing native permissions to Active Directory, if Active Roles is configured
Access to the Administration Service computer
The service account must be a member of the Administrators group on the computer running the Administration Service.
Service publication in Active Directory
The Administration Service attempts to publish itself in the Active Directory. This enables Active Roles clients to automatically discover the Administration Service. This functionality is non-critical and if permissions are not granted, this will not prevent the service from functioning as expected, instead Active Roles clients won't automatically discover the Active Roles Administration Service. They will still be able to connect if the service name or IP address is available. Service publication requires that the service account have the following permissions on the Aelita sub-container of the System container in the domain of the computer running the Administration Service:
-
Create Container Objects
-
Create serviceConnectionPoint Objects
-
Delete the serviceConnectionPoint objects in the System container
-
Write permission for the keywords attribute of the serviceConnectionPoint objects in the System container
Along with these permissions, the service account (or the override account, if specified), must have these permissions on the Aelita sub-container of the System container in every managed domain. If an account has the domain administrator rights, then it has the required permissions by default. Otherwise, provide the permissions to the account by using the ADSI Edit console. The following instructions apply to the ADSI Edit console that ships with Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019, or Windows Server 2022.
To grant permissions for Administration Service publication in Active Directory
-
Open the ADSI Edit console and connect to the Domain naming context.
-
In the console tree, expand the System container, right-click the Aelita subcontainer, and then click Properties. If the Aelita container does not exist, create it: right-click System, point to New, click Object, and then, in the Create Object wizard, select the Container class and specify Aelita for the cn value.
-
On the Security tab in the Properties dialog box, click Advanced.
-
On the Permissions tab in the Advanced Security Settings dialog box, click Add.
-
On the Permission Entry page, configure the permission entry:
-
Click the Select a principal link, and select the desired account.
-
Verify that the Type box indicates Allow.
-
Verify that the Applies onto box indicates This object and all descendant objects.
-
In the Permissions area, select the Create container objects and Create serviceConnectionPoint objects check boxes.
- Click OK
-
Click OK to close the Advanced Security Settings dialog box, and then click OK to close the Properties dialog box.
All script modules are executed under the security context of the Active Roles Service Account
The permissions needed by custom scripts will vary according to the needs of the scripts, and ideally should be reviewed on a case-by-case basis as a Best Practise security model.
Connecting to the Microsoft SQL database
In some configurations, assigning these permissions to the service account are optional, as a SQL Authentication credential may also be specified and the necessary permissions then be assigned to that SQL Authentication credential. For more information on the necessary SQL Server permissions, see SQL Server Permissions topic in the Active Roles Quick Start Guide.
Synchronizing native permissions to Active Directory
The service account must have the Read Permissions and Modify Permissions rights on the Active Directory objects and containers where it is desired to use the Active Roles security synchronization feature.

