View or modify the message size restrictions
View the Mail Flow settings of an Office 365 User
For an existing Office 365 user, you can use the Mail Flow settings tab in the Exchange Online Properties wizard to view or set the message size restrictions and delivery options.
To view and modify the message size restrictions for an Office 365 user
- In the Exchange Online Properties wizard of an Office 365 user, click Mail Flow Settings.
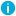
- Under Mail flow settings, click Message Size Restrictions and then Properties.
The Message Size Restrictions dialog box displays the sending and receiving message size restrictions.
- To set or modify sending and receiving message size restrictions, select one of the following in the Message Size Restrictions dialog box:
- Use default limit – Allows you to set the maximum size for the outgoing or incoming messages to the default value used in Exchange Online, which is applied through the built-in policy "Built-in Policy - Exchange Online - Default Message Size Restrictions" enforced on the container.
- Maximum (KB) – Allows you to specify the maximum value for the outgoing or incoming message size.
- Click Save.
- Close the dialog box and click Save.
|
|
NOTE: The changes made to message size restrictions settings for the Office 365 user can be verified in the Microsoft Office 365 portal. |
View or modify the message delivery options
To view or modify the message delivery options for an Office 365 user
- In the Exchange Online Properties wizard of an Office 365 user, click Mail Flow Settings.
- Under Mail flow settings, click Delivery Options and then Properties.
-
To allow one or more users to send messages on behalf of the Office 365 user, in the Delivery Options dialog box, click Add, select one or more users from the Select Object list, and then click OK.
-
To limit users from sending messages on behalf of the Office 365 user, select the users in the Name list and click Remove.
-
To specify a forwarding address for messages addressed to the Office 365 user, select Forward to, and click Modify.
Alternatively, to change the current forwarding address, click Modify.
-
From the Select Object wizard, select the users to whom the messages addressed to the mailbox can be forwarded and click OK.
- Click Save.
- Close the dialog box and click Save.
|

|
NOTE: The changes made to message delivery options for the Office 365 user can be verified in the Microsoft Office 365 portal. |
View or modify Mailbox delegation settings
For an existing Office 365 user, you can use the MailBox delegation settings tab in the Exchange Online Properties wizard to view or modify other users or groups who can send mails or be provided full access to the user's mailbox.
|

|
NOTE: The modify option is applicable for Office 365 users on all environments, such as, Federated, Synchronized and non-federated. |
To view or modify the MailBox delegation settings for an Office 365 user
- In the Exchange Online Properties wizard of an Office 365 user, click Delegation.
-
To specify or modify the list of users or groups who can send mail from the Office 365 user’s mailbox, under Send as, click Add.
- Select one or more users or groups from the Select Object list, and then click OK.
-
Alternatively, to limit users who can send emails from the Office 365 user’s mailbox, select the users in the Name list and click Remove.
-
Click Properties to view the general properties of the user added under the Send as option.
-
To specify Office 365 users or groups who can be provided full access to the user’s mailbox, under Full Access, click Add, select one or more users or groups from the Select Object list, and then click OK.
-
Alternatively, to limit users who can be provided full access to the user’s mailbox, select the users in the Name list and click Remove.
-
Click Properties to view the general properties of the user added under Full Access option.
- Click Save.
- Close the dialog box and click Save.
|

|
NOTE: The changes made to MailBox delegation settings for the Office 365 user can be verified in the Microsoft Office 365 portal. |
View or modify Email Address settings
For an existing Office 365 user, you can use the E-mail Address settings tab in the Exchange Online Properties wizard to view or set the email address settings.
|

|
IMPORTANT: The modify option is applicable for Office 365 users on a non-federated environment only. |
To view or modify the email address settings for an Azure AD user
- In the Exchange Online Properties wizard of an Office 365 user, click E-mail Settings.
-
To add email addresses, click Add.
-
In the E-mail Addresses dialog box, select the email address type, add the email address, and click OK.
-
To modify a selected email address, click Edit.
-
In the E-mail Addresses dialog box, edit the selected email address, and click OK.
-
To delete a selected email address, click Remove.
- Click Save.
- Close the dialog box and click Save.
|

|
NOTE: The changes made to email address settings for the Office 365 user can be verified in the Microsoft Office 365 portal. |

