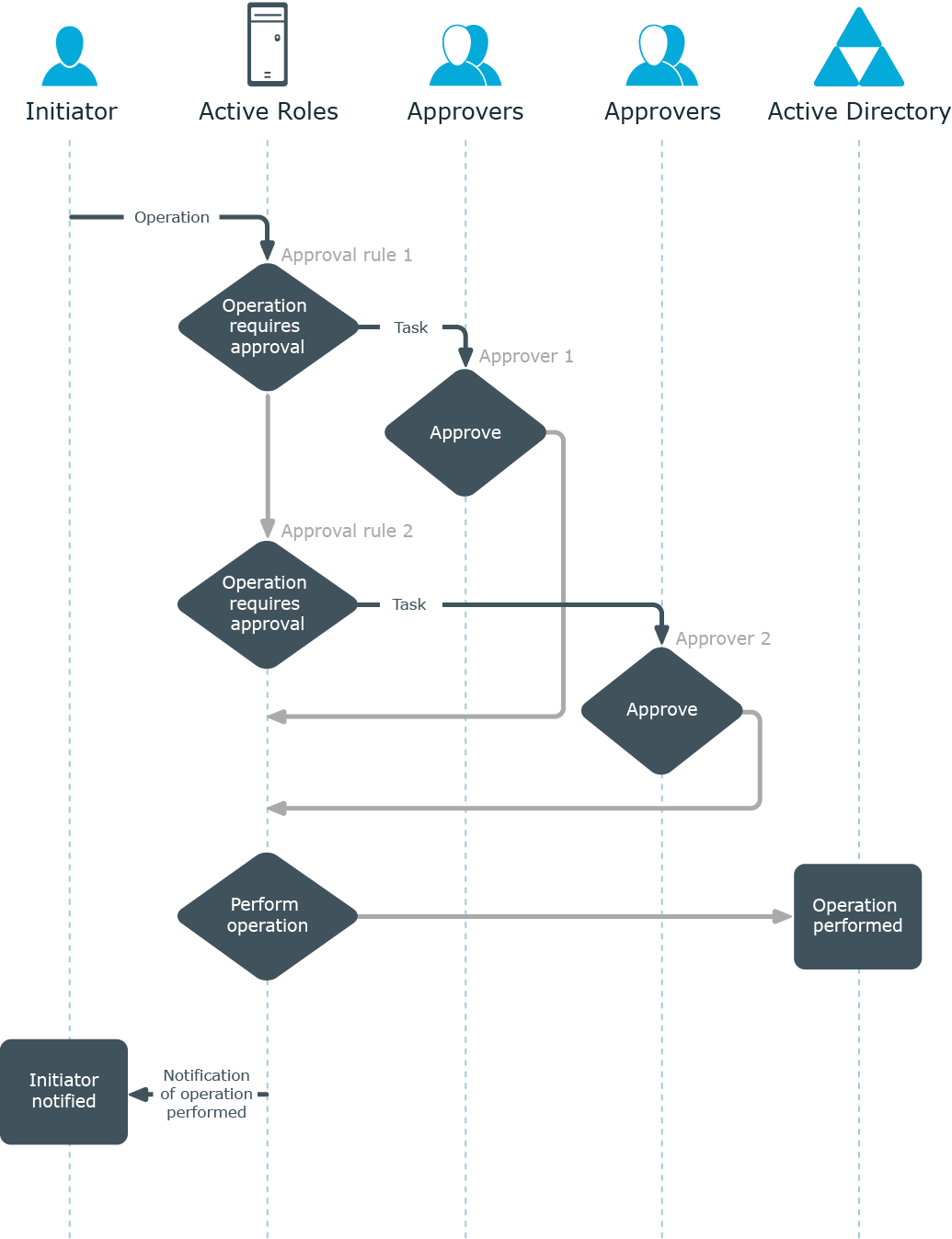
Multiple tasks
The number of approval tasks generated by a single workflow instance depends on how many approval rules are included in the workflow (one task per each rule). Therefore, if a workflow has multiple approval rules, multiple tasks will be created and assigned to the respective approvers.
Within a single workflow, approval rules are applied in a sequential manner. This means that a subsequent rule is applied only after the requested operation has passes the previous rule.
If each of the tasks receives the Approve action, Active Roles allows the operation to be performed.
Figure 104: Multiple tasks
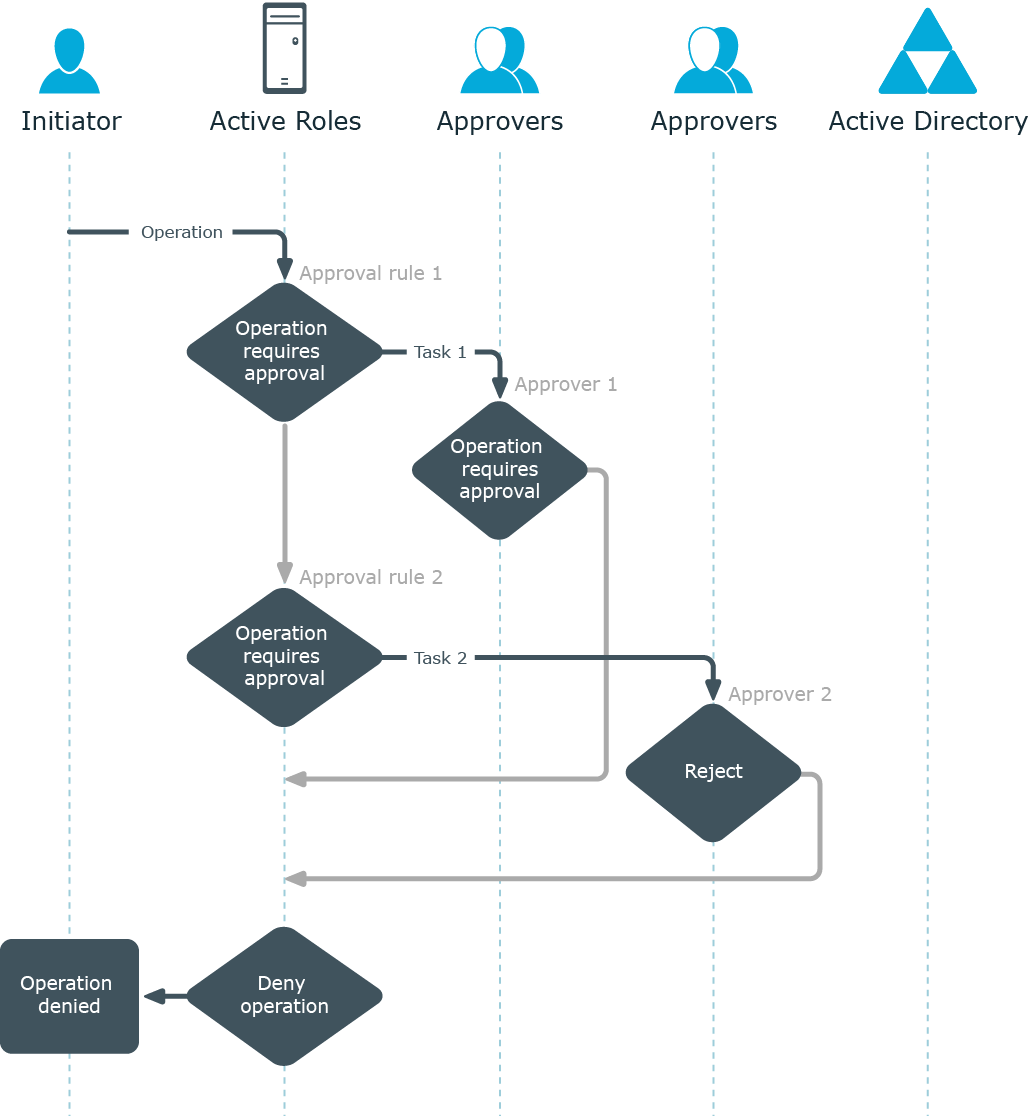
If at least one of the tasks receives the Reject action, Active Roles cancels the operation.
Figure 105: Cancellation of task
Creating and configuring an approval workflow
To implement an approval scenario where certain operations require approval in Active Roles, you create a workflow definition, configure the workflow start conditions, and add and configure approval activities (approval rules) as appropriate. All these tasks are performed using the Workflow Designer-a graphical tool included in the Active Roles Console.
When configuring workflow start conditions, you specify:
-
A type of operation, such as Create, Rename, Modify, or Delete. The workflow starts only if an operation of that type is requested.
-
A type of object, such as User, Group or Computer. The workflow starts only if the operation requests changes to an object of that type.
-
For the Modify operation type, a list of object properties. The workflow starts only if the operation requests changes to any of those properties of an object.
-
The identity of an operation requestor (initiator), such as a user, group, or service. The workflow starts only if the operation is requested on behalf of that identity.
-
A container, such as an Organizational Unit or Managed Unit. The workflow starts only if the operation requests changes to an object in that container or requests the creation of an object in that container.
-
(Optional) A filter that defines any additional conditions on entities involved in an operation. The workflow starts only if the operation satisfies those conditions. If no filter is set, then no additional conditions are in effect.
Any operation that meets all the start conditions specified on a workflow causes the workflow to start.
When configuring an approval rule within a workflow, you specify:
-
A list of approvers, such as users or groups: This setting identifies the persons who are authorized to allow or deny operations that start the workflow.
-
Notification settings: This includes workflow events to notify of, notification recipients, delivery options, and notification message template.
Creating a workflow definition for a workflow
The Active Roles Console provides the Workflow Designer for creating and configuring workflows. First, you create a workflow definition. Then, you use the Workflow Designer to construct a workflow, saving the workflow configuration data in the workflow definition.
To create a workflow definition
-
In the Active Roles Console tree, expand Configuration > Policies, right-click Workflow, and select New > Workflow.
-
Follow the steps in the wizard for creating the workflow definition.
-
On the Workflow Type page, accept the default setting.
By default, the wizard creates a change workflow that starts upon a request to change data in the directory. Another option is to create an automation workflow that can be run on a scheduled basis or on user demand. For more information, see Automation workflow.
Once you have created a workflow definition, you can open it in the Workflow Designer to add workflow activities and specify workflow start conditions.
You can create containers to store related workflows and other containers. To create a workflow container, right-click Workflow in the Console tree and select New > Container. To create a workflow definition in a given container, right-click the container in the console tree, and select New > Workflow.
You can delete a workflow definition as follows: In the Console tree under Configuration > Policies > Workflow, right-click the object representing the workflow definition, and click Delete.
Specifying workflow start conditions for an Approval workflow
You can specify the start conditions for a workflow by editing its definition in the Workflow Designer. The start conditions determine which operations cause the workflow to start.
For more information, see Configuring workflow start conditions.
For example, suppose you want the creation of user accounts in a certain Organizational Unit to require approval. You can implement this scenario by configuring the workflow start conditions as follows:
-
Set type of operation to 'Create'.
-
Set type of object to 'User'.
-
Set initiator to 'Any User'.
-
Set container by selecting the Organizational Unit you want.
As a result of these conditions, the workflow will start whenever Active Roles is used to create a user account in that Organizational Unit.


