Table relations
As you can see from the One Identity Manager data model, parent/child relations exist between objects. If an object is processed by the One Identity Manager's object layer, all ForeignKey (FK) objects that are related to this object can be accessed. Use VB.Net notation to access objects access using relations.
Figure 11: Parent/child relation using the example of a person ADSAccount
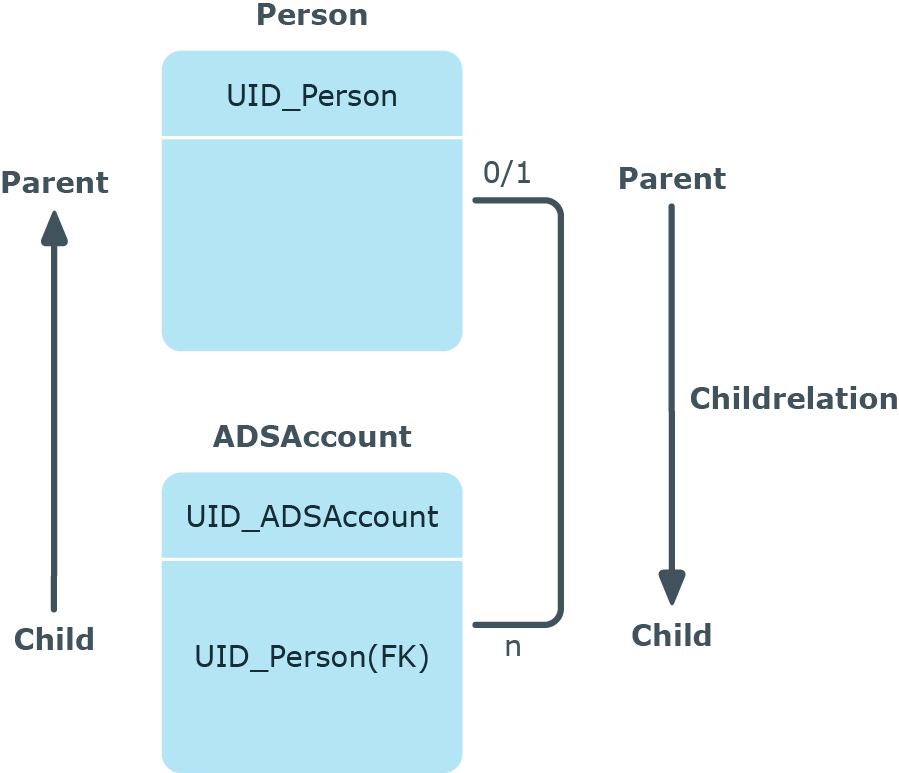
NOTE: You can always edit table relations of custom tables. The table relation supplied with the default tables can only be edited if the referential integrity has been tested using the object layer.
To edit table relations
-
In the Designer, select the One Identity Manager schema category.
-
Select the table and start the Schema Editor with the Show table definition task.
-
Under Table relations, select the table relation and edit the properties in the Relation properties view.
-
Select the Database > Save to database and click Save.
Table 27: Table relation properties
|
Display name |
Language-dependent relation for displaying in the administration tool’s user interface. |
|
Only transport as group |
Specifies if the contents of the table should be transferred together with the contents of the referenced table during data transports. You can combine the values. Permitted values are:
-
No value: Dependencies are not taken into account.
-
CR direction: The table relations are labeled with the values CR direction and FK direction. Superset handling is carried out.
-
FK direction: All objects referenced by a foreign key are also exported. Superset handling is carried out.
-
Ignore in superset handling: Referenced objects that are in the target system but not included in the transport package are not deleted.
Example:
When a process is transported (JobChain table), the process steps (Job table), events (JobEventGen and QBMEvent tables) and the process step parameters (JobRunParameter table) should also be transported. This should happen whether or not the process, a single process step or a process step parameter is transferred to a transport package. The table relations are labeled with the values CR direction and FK direction.
The parameter templates (JobParameter table) that are used in the (JobRunParameter table) process step parameters must not be transferred during the transport. The table relations are not labeled with a value. |
|
Update dependencies modification date |
When many-to-many entries are added, changed, or deleted, the value in the XDateSubItem column the associated parent entries is updated. Required for provisioning memberships in the target system. |
|
Export for SPML schema |
Specifies whether the table is to be exported for the SPML schema. |
|
Parent object in Job queue |
Specifies whether the parent object is added to the list of objects affected by a process. This can prevent the parent object from being processed simultaneously more than once. |
|
Parent column |
Unique parent column identifier. |
|
Configurable parent relation |
Specifies whether referential integrity can be configured. |
|
Parent relation test instance |
Specifies who will run these referential integrity tests. Permitted values are:
-
DLL: Checks through the object layer.
-
Trigger: Triggers and constraints are implemented to monitor the database. The triggers and constraints are created automatically and modified as necessary taking the preset restrictions of the DBQueue Processor into account. In the case of customized tables, specify the test instance and the limitations of the One Identity Manager schema extension.
-
Nothing: No test. |
|
Parent relation constraint |
Constraint on the relation. Permitted values are:
-
Delete: Dependencies are not taken into account on deletion.
-
Delete Cascade: All dependent objects are deleted when this object is deleted.
-
Delete Restrict: The object can only be deleted when no more references to other objects exist.
-
Delete Set NULL: When deleting the object, references to the object being deleted are removed from all dependent object (SetNULL). |
|
Generated restriction test for parent relation |
Identifier for triggers and constraints that are automatically generated by the DBQueue Processor. |
|
Connected column |
Unique connected column identifier. |
|
Configurable child relation |
Specifies whether referential integrity can be configured. |
|
Child relation test instance |
Specifies who will run these referential integrity tests. Permitted values are:
-
DLL: Checks through the object layer.
-
Trigger: Triggers and constraints are implemented to monitor the database. The triggers and constraints are created automatically and modified as necessary taking the preset restrictions of the DBQueue Processor into account. In the case of customized tables, specify the test instance and the limitations of the One Identity Manager schema extension.
-
Nothing: No test. |
|
Child relation constraint |
Constraint on the relation. Permitted values are:
|
|
Generated restriction test for child relation |
Identifier for triggers and constraints that are automatically generated by the DBQueue Processor. |
|
Relation ID |
Relation identifier. This is used for both directions. |
|
M:N relation |
Specifies whether the child relation can be reached by a many-to-many relation. |
|
table relation |
Unique identifier for table relation. |
|
Relation (base) |
Link to underlying base relation assuming a view is part of a the relation. |
|
Relation (M:N) |
Unique identifier for the M:N relation. |
Dynamic foreign key
Dynamic foreign keys are used if a reference can point to different tables. For example, the manager of a user account (<MMM>Account.ObjectKeyManagertable) can be another user account (<MMM>Account table) or a group (<MMM>Group table).
Dynamic foreign keys reference the object key (XObjectKey) of the permitted tables. Permitted tables can be limited. All tables are permitted, if there are no restrictions. Restrictions are stored in the DialogValidDynamicRef table.
If you are defining custom dynamic foreign keys, at least one of the participating partners (dynamic foreign key column or referenced table) must be a custom object. It is not possible to extend predefined dynamic foreign keys by adding references to predefined tables.
To display a dynamic foreign key
-
In the Designer, select the One Identity Manager schema category.
-
Select the table and start the Schema Editor with the Show table definition task.
Dynamic foreign keys are displayed under Dynamic table relations.
To define a dynamic foreign key
-
In the Designer, select One Identity Manager Schema.
-
Select the table and start the Schema Editor with the Show table definition task.
-
Select the column and then the Column properties view.
-
On the Miscellaneous tab, enter the following information.
-
Enable the Dynamic foreign key option.
-
If the dynamic key is part of a many-to-all table, enable the Part of key of many-to-all table option.
-
Enter the following information on the Valid reference tables tab by clicking  next to Dynamic referenced tables drop-down and enter the following information:
next to Dynamic referenced tables drop-down and enter the following information:
Table 28: Properties of dynamic foreign keys
|
Table |
Select the table to find the object key in. |
|
Parent relation constraint |
Constraint on the relation. Permitted values are:
-
Delete: Dependencies are not taken into account on deletion.
-
Delete Cascade: All dependent objects are deleted when this object is deleted.
-
Delete Restrict: The object can only be deleted when no more references to other objects exist.
-
Delete Set NULL: When deleting the object, references to the object being deleted are removed from all dependent object (SetNULL). |
|
Parent relation test instance |
Specifies who will run these referential integrity tests. Permitted values are:
|
|
Child relation constraint |
Constraint on the relation. Permitted values are:
|
|
Child relation test instance |
Specifies who will run these referential integrity tests. Permitted values are:
|
|
Only transport as group |
The column content is always transported together with the content of the referenced column. |
|
Parent object in Job queue |
Specifies whether the parent object is added to the list of objects affected by a process. This can prevent the parent object from being processed simultaneously more than once. |
-
Select the Database > Save to database and click Save.
Supporting file groups
One Identity Manager supports file groups to group tables together to help with administration, data assigning and data distribution. A distinction is made between logical disk stores and physical disk stores.
In the default installation, logical disk stores are predefined for the table in each module of One Identity Manager and the system tables. You cannot change the assignments. You can create your own logical disk storage for grouping custom tables.
To define logical storage for custom tables
-
In the Designer, select the One Identity Manager Schema > Logical disk stores category.
-
Select the Object > New menu item.
-
Enter a name and description for the logical storage.
-
Assign custom tables to the logical disk store.
-
Select the View > Select table relations menu item and enable the DialogTable table. This shows the Tables tab for assigning tables.
You can link logical storage with physical storage - the file groups - in the One Identity Manager schema.
If, for example, tables with identity data and tables with Active Directory content are created on different a data storage medium, performance can be improved by parallel access through your own E/A controller. Performance can also be improved if, for example, tables for processing DBQueue Processor tasks or table for handling processes in file groups are grouped together.
NOTE: You cannot move the following groups into other file groups. If you do so, proper functioning of the One Identity Manager database cannot be guaranteed.
-
DialogColumn
-
DialogTable
-
DialogValidDynamicRef
-
QBMDBQueueTask
-
QBMDBQueueTaskDepend
-
QBMModuleDef
-
QBMModuleDepend
-
QBMRelation
-
QBMViewAddOn
-
QBMDiskStoreLogical
-
QBMDiskStorePhysical
One Identity Manager supports the distribution of tables to file groups with a variety of database procedures that you run in a suitable program for running SQL queries in the database.
|
|
CAUTION: Only carry out the following steps for implementing file groups, together with an experienced database administrator.
Ensure that the database cannot be accessed while file groups are being set up, for example, by the Job server, application server, web server, user interfaces, or the Web Portal. After restarting the DBQueue Processor, wait for all DBQueue tasks to be processed before reconnecting the database. |
IMPORTANT: Select a user that you use for migrating the database to run the SQL queries.
To distribute tables to file groups under SQL Server
-
Create your file groups. For more information about this, see the documents for your currently installed version of SQL Server.
-
Synchronize the file groups to the One Identity Manager database. Run the query below using a suitable program for carrying out SQL queries in the database.
exec QBM_PDiskStorePhysicalSync
-
In the Designer, assign physical storage to logical storage.
-
In the Designer, select the One Identity Manager Schema > Logical disk stores category.
-
Select the logical disk store and in the Properties view, select the file group under Physical disk store.
-
Select the Database > Save to database and click Save.
-
Disable processing of DBQueue Processor tasks and process handling. Run the queries below using a suitable program for carrying out SQL queries in the database.
exec QBM_PWatchDogPrepare 1
exec QBM_PDBQueuePrepare 1
-
Move the tables into the configured file groups. Run the query below using a suitable program for carrying out SQL queries in the database.
exec QBM_PTableMove
-
Reactivate the DBQueue Processor. Run the queries below using a suitable program for carrying out SQL queries in the database.
exec QBM_PDBQueuePrepare 0,1
exec QBM_PWatchDogPrepare
The full-text search in One Identity Manager
Prerequisites for using full-text search is an application server installed with the search service. For more information about installing an application server for the full-text search, see the One Identity Manager Installation Guide.
The full-text search can be used in the Manager and in the Web Portal. For more information, see the One Identity Manager Web Portal User Guide and the One Identity Manager User Guide for One Identity Manager Tools User Interface.
The following applies for the configuration of the full-text search:
-
The columns XDateInserted, XDateUpdated, and XObjectKey must be available if you want to index a table or database view for full-text search.
-
Columns for full-text searching must be weighted. Increasing weighting results in a higher position in the full-text search result. The default installation provides columns for the full-text search with a weighting of 1.
Example: Weighting columns
The column Person.CentralAccount is weighted with the value 1. The column ADSAccount.SAMAccountName is weighted with the value 0.5. This results in the identity being listed before the user account in the full-text search.
NOTE: Weighting does not have any effect on how the results are sorted in the user interface. For example, if you limit the search in the Web Portal to the 100 best matches, weighting determines which 100 objects are returned. But these 100 objects are then sorted again by the user interface.
-
Only columns with the .Net data types String, Text, or Int can be included in the full-text search.
Exception: Columns that contain a list of permitted values, can always be included to the full-text search.
-
Columns of tables with the Work tables or Historical transaction data usage type cannot be included in the full-text search.
-
Columns of assignment tables (M:N tables, M:all tables) cannot be included to the full-text search.
The search service indexes the following:
-
Column content
-
Foreign key column display value
-
Display values for lists of permitted values
-
Translation for every active language
-
Object display value, if the table's primary key column is configured for full-text search
The object's display value comes from the display pattern defined for the table. The display value's weighting comes from the table's primary key column weighting
Example: Display value in the full-text search
The Person.UID_Person column is configured for full-text search. The display pattern of the Person table is defined as %InternalName% (%CentralAccount%).
So the display value of Alex Miller (AlexM) is indexed for the identity Alex Miller.
The searched index is updated when changes are made to a table with indexed columns, to referenced tables or translations.


 next to Dynamic referenced tables drop-down and enter the following information:
next to Dynamic referenced tables drop-down and enter the following information: