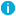
You can view the current total number of managed users on the root page in the Active Roles console. Select the console tree root to open the root page in the details pane, and then expand the Product Usage Statistics area on that page. The count of objects under Active Directory Domains, AD LDS Directory Partitions, Azure tenants, and SaaS application represents the current number of managed domain users , managed AD LDS users, Azure hybrid users, Azure cloud only users, Azure guest users, and SaaS users respectively.
|
|
NOTE: The count can be derived using the LDAP query “(&(objectCategory=person)(objectClass=user))”. |
It is possible to view the average or maximum number of managed users in each domain or instance for a certain reporting period. Click Product Usage Statistics to open a page allowing you to:
- Choose the reporting period.
The page displays options to export data in HTML format and as raw counters for the period you choose from the Reporting period options, such as past month, past half-year, past year, or a custom date range.
- Examine the managed user counts for the reporting period you’ve chosen.
The page displays the current number of managed users per Active Directory domain, AD LDS directory partition, Azure tenant, and SaaS application in the tables under Total accounts. The Average and the maximum values along with the total number of managed users can be viewed in the HTML file.
License type and Total estimated licenses, display the type of license in use and the number of estimated license required, respectively.
- View the information about the license.
Click License description to view a detailed information about the license.
- Save the contents of the page as an HTML file.
Click Save as HTML at the bottom of the page and specify the desired file name and location.
- Export the raw statistical data to a file.
Click Export raw counters at the bottom of the page and specify the desired file name and location. The data is exported in the comma-delimited (CSV) format, representing the daily counts of managed users over the reporting period.
By default, only Active Roles Admin role holders have permission to view managed object statistics. Active Roles provides the following Access Templates for delegating that task:
You can find these two Access Templates in the Configuration/Access Templates/Configuration container in the Active Roles console.
Active Roles uses a scheduled task to count the number of managed users in each Active Directory domain, AD LDS instance, Azure tenants, and SaaS applications registered with this product. Every Administration Service in your Active Roles environment runs that task on a daily basis, saving the obtained results in the Active Roles database. The statistical data collected by running that task over time is used to calculate managed object statistics, and can be exported by clicking Export raw counters.
The scheduled task in question is located in the Configuration/Server Configuration/Scheduled Tasks/Builtin container in the Active Roles console, and has the name Export raw counters. Changes to this task are not allowed, except for changing the start time. You can change the start time on the Schedule tab in the task’s Properties dialog box in the Active Roles console.
The area where Active Roles collects product usage statistics is referred to as managed scope. By default, managed scope comprises all Active Directory domains and AD LDS instances registered with Active Roles. This means that by default product usage statistics includes all enabled user accounts in all managed domains and instances. However, if you don’t use Active Roles to manage a particular domain or instance, or a part of a domain or instance (for example, individual Organizational Units), then you can exclude the entire domain or instance, or a part of a domain or instance, from managed scope.
Active Roles provides a built-in Policy Object allowing you to exclude entire AD domains, AD LDS directory partitions, individual Organizational Units (OUs), or even Managed Units (MUs) from managed scope. This Policy Object is located in the Configuration/Policies/Administration/Builtin container in the Active Roles console, and has the name Built-in Policy - Exclude from Managed Scope. When applied to a container such as an AD domain, AD LDS directory partition, OU or MU, this Policy Object:
- Stops product usage statistics from counting objects held in that container, and
- Prevents any changes to the objects held in that container, making the objects available for read access only.
Thus, you can exclude a certain domain from managed scope by applying a Policy Object: Choose the Enforce Policy command on the domain object under the Active Directory node in the Active Roles console, click Add, and select the Built-in Policy - Exclude from Managed Scope Policy Object. This stops product usage statistics from counting objects in that domain, and makes all objects in that domain available for read access only. You will not be able to create new objects (users, groups, computers, and so forth) or make changes to existing objects in that domain by using Active Roles.
After you have excluded a domain from managed scope, you may need to make a particular OU in that domain available for read/write access. You can accomplish this by blocking policy inheritance: In the Active Roles console, choose the Enforce Policy command on the OU and then select the Blocked option next to Built-in Policy - Exclude from Managed Scope. Doing so removes the read-only restriction from the OU and objects it contains, while causing product usage statistics to start counting objects held in that OU.
When you apply the Built-in Policy - Exclude from Managed Scope Policy Object to a Managed Unit, all objects that match the membership rules of that Managed Unit are excluded from managed scope. You can use this option to prevent product usage statistics from counting objects that satisfy certain conditions (for example, user accounts that have a particular country or department setting): Create a Managed Unit with the appropriate membership rules and then apply the Built-in Policy - Exclude from Managed Scope Policy Object to that Managed Unit. Doing so stops product usage statistics from counting objects that match the Managed Unit’s membership rules, while making those objects read-only.
You can determine whether a given object is excluded from managed scope by looking at the Managed field on the Object tab in the Properties dialog box for that object in the Active Roles console or on the General Properties page in the Active Roles Web Interface. If the object is excluded from managed scope, the Managed field reads No; otherwise, the field reads Yes.

