Scenario: Restricting group scope
This scenario describes how to configure a policy that prevents creation of universal groups. With this policy, the Active Roles console or Web Interface does not allow an administrator to create a new universal group or convert an existing group to a universal group.
To implement this scenario, you must perform the following actions:
- Prepare the script that implements this scenario.
- Create and configure the Policy Object to run that script.
- Apply the Policy Object to a domain, OU, or Managed Unit.
As a result, the Active Roles console or Web Interface cannot be used to set the universal group scope option when creating a new group or changing an existing group in the container you selected in Step 3. For example, if you choose the Universal option under Group scope and then click Next in the New Object - Group wizard, the Active Roles console presents you with an error message stating that creation of universal groups is not allowed.
The following sections elaborate on the steps to implement this scenario.
Step 1: Preparing the script module
Step 1: Preparing the script module
The script used in this scenario is installed with the Active Roles SDK. By default, the path and name of the script file is as follows:
%ProgramFiles%\One Identity\Active Roles\Active Roles\SDK\Samples\RestrictGroupScope\RestrictGroupScope.ps1.
The script receives control upon a request to check the property values submitted to the Administration Service, and analyzes the value of the groupType attribute to determine if the universal group scope option is attempted. If the script detects that the assumed groupType value would cause a group to be configured as a universal group, it raises a policy violation event in the Administration Service. As a result, the application that initiated the request (such as the Active Roles console or Web Interface) displays an error message provided by the script. For more information, see the “Restricting the Scope of Groups” topic in the Active Roles SDK documentation.
To import the script, right-click the Script Modules container in the Active Roles console, and click Import. Then, select and open the RestrictGroupScope.ps1 file.
Step 2: Creating and configuring the Policy Object
Step 2: Creating and configuring the Policy Object
You can create and configure the Policy Object you need by using the New Provisioning Policy Object wizard. For information about the wizard, see Creating a Policy Object in the Policy Object management tasks section earlier in this chapter.
To configure the policy, click Script Execution on the Policy to Configure page of the wizard. Then, click Next.
On the Script Module page, click Select a script module, and select RestrictGroupScope from the list of script modules, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 66: Script Module: Creating/configuring policy object
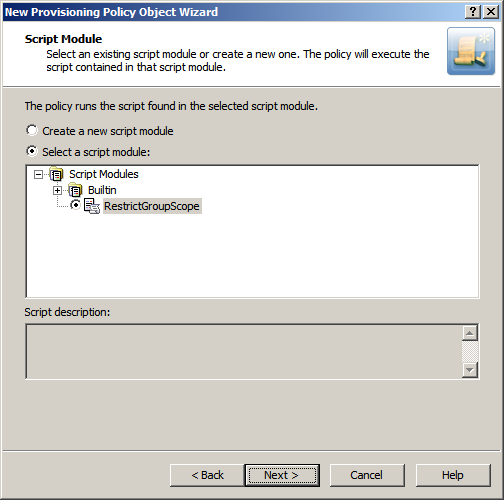
Click Next and follow the instructions in the wizard to create the Policy Object.
Step 3: Applying the Policy Object
Step 3: Applying the Policy Object
You can apply the Policy Object by using the Enforce Policy page in the New Provisioning Policy Object wizard, or you can complete the wizard and then use the Enforce Policy command on the domain, OU, or Managed Unit where you want to apply the policy.
For more information on how to apply a Policy Object, see Applying Policy Objects and Managing policy scope earlier in this chapter.

