When you select Group-by Property under Entry type in the Add Entry window, the Entry properties area looks similar to the following figure.
Figure 112: Group-by property
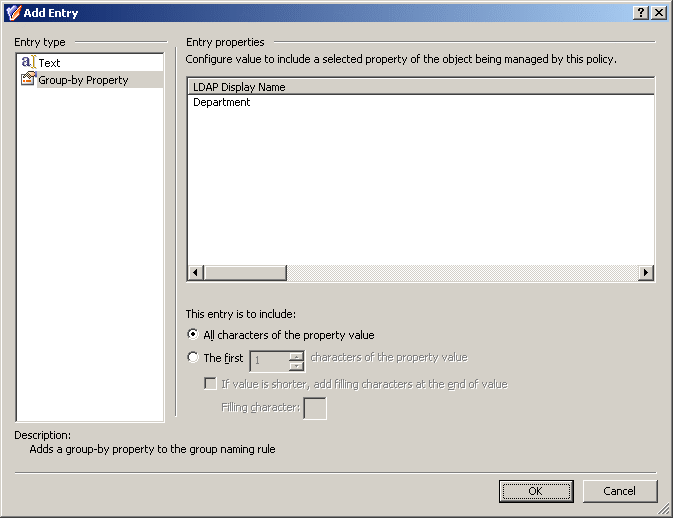
Using the Group-by Property entry type, you can add an entry representing a value (or a part of a value) of a group-by property. Select a group-by property from the list, and then do one of the following:
- If you want the entry to include the entire value of the property, click All characters of the property value.
- If you want the entry to include a part of the property value, click The first, and specify the number of characters to include in the entry.
If you choose the second option, you can select the If value is shorter, add filling characters at the end of value check box, and type a character in the Filling character box. This character will fill the missing characters in the value of the property if the value is shorter than specified in the box next to The first. For example, if you specify The first 12 characters and enter 0 as the filling character, the Accounting property value results in the Accounting00 entry.
When you are done configuring an entry, click OK to close the Add Entry window. The entry is added to the Configure Value dialog. When you have completed the list of entries, click OK to close that dialog.
NOTE: The naming rule must include an entry for each of the group-by properties.
By default, the same rule applies to these naming properties:
-
Group name
-
Group name (pre-Windows 2000)
-
Group display name
-
E-mail alias (If the Group Family is configured to create mail-enabled groups. For more information, see Exchange-related settings.)
You have the option to configure an individual rule for each of these naming properties. To do so, click Fine-tune on the Group Naming Rule page. This displays a window where you can select a naming property and configure a rule for that property the same way as you do for Group name. The window looks similar to the following figure.
Figure 113: Fine-tune naming rule
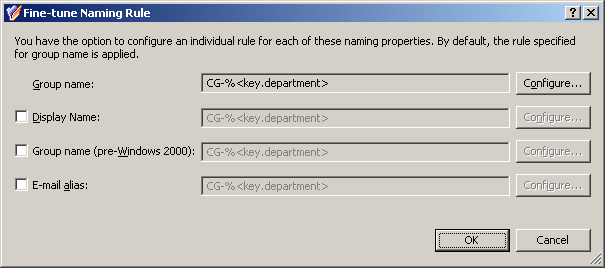
You may need to configure a separate rule for a certain property, considering restrictions imposed on that property. For example, Group name (pre-Windows 2000) must be less than 20 characters. In order to meet this requirement, select the Group name (pre-Windows 2000) check box and click Configure to set up an appropriate rule. When configuring entries to include group-by properties, limit the number of characters in each entry by using the option The first in the Add Entry window.
On the next page, you can specify the group scope and group type you want to be assigned to the groups generated by the Group Family.
Figure 114: Group type and scope
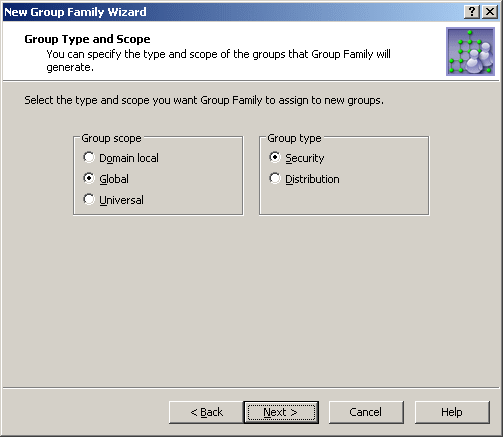
Available are the standard options for the group scope and group type. The Group Family creates groups of the scope and type you select.
On the next page, you can specify the container you want to hold the groups generated by the Group Family.
Figure 115: Location of groups
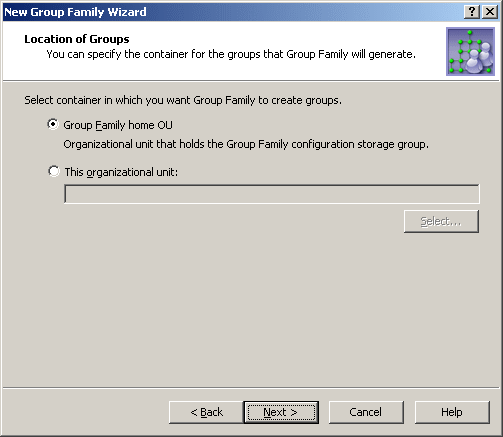
You can choose one of these options:
-
Group Family home OU: The Group Family creates groups in the container that holds the configuration storage group for that Group Family. For more information, see Starting the New Group Family Wizard.
-
This Organizational Unit: The Group Family creates groups in the specified container. This must be an Organizational Unit or container from the domain of the Group Family configuration storage group. Click Select to choose the desired Organizational Unit or container.




