Number of processes
Figure 294: Basic Settings > Dashboard > Number of processes
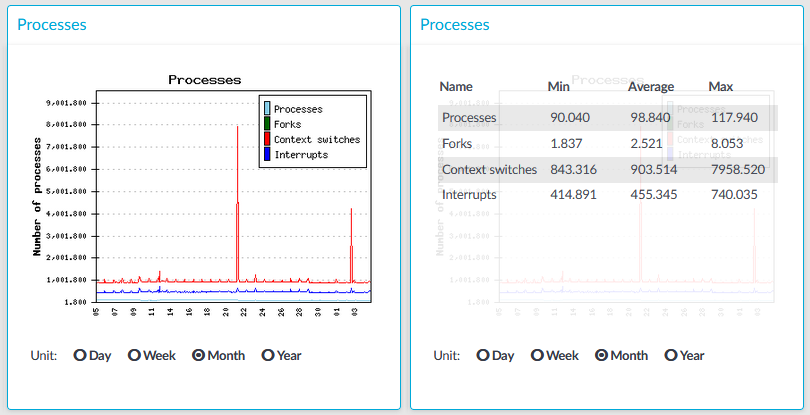
The Number of processes module on the Dashboard is based on the output of the ps command.
Statistics
The process types displayed are the following:
-
Processes: Number of running processes.
-
Forks: Number of forks (system calls). It is an operation where a process creates a copy of itself.
-
Context switches: Number of context switches. It is the switching of the CPU from one processor thread to another.
-
Interrupts: Number of interrupts.
Displaying custom connection statistics
The following describes how to display statistics of a specific connection policy.
To display statistics of a specific connection policy
-
Navigate to Basic Settings > Dashboard > Connection statistics.
-
To display the statistics of a connection policy, enter the name of the policy into the Connection.
-
Select the time period to display from the Select resolution field.
-
Click View graph.
Troubleshooting a One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS) cluster
The following sections help you to solve problems related to high availability clusters.
-
For a description of the possible statuses of the One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS) cluster and its nodes, the DRBD data storage system, and the heartbeat interfaces (if configured), see Understanding One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS) cluster statuses.
-
To recover a cluster that has broken down, see Recovering One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS) if both nodes broke down.
-
To resolve a split-bran situation when the nodes of the cluster were simultaneously active for a time, see Recovering from a split brain situation.
-
To replace a broken node with a new appliance, see Replacing a HA node in a One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS) cluster.
Understanding One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS) cluster statuses
This section explains the possible statuses of the One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS) cluster and its nodes, the DRBD data storage system, and the heartbeat interfaces (if configured). SPS displays this information on the Basic Settings > High Availability page.
The Status field indicates whether the SPS nodes recognize each other properly and whether those are configured to operate in high availability mode. The status of the individual SPS nodes is indicated in the Node HA state field of the each node. The following statuses can occur:
-
Standalone: There is only one SPS unit running in standalone mode, or the units have not been converted to a cluster (the Node HA state of both nodes is standalone). Click Convert to Cluster to enable High Availability mode.
-
HA: The two SPS nodes are running in High Availability mode. Node HA state is HA on both nodes, and the Node HA UUID is the same on both nodes.
-
Half: High Availability mode is not configured properly, one node is in standalone, the other one in HA mode. Connect to the node in HA mode, and click Join HA to enable High Availability mode.
-
Broken: The two SPS nodes are running in High Availability mode. Node HA state is HA on both nodes, but the Node HA UUID is different. For assistance, contact our Support Team.
-
Degraded: SPS was running in high availability mode, but one of the nodes has disappeared (for example broken down, or removed from the network). Power on, reconnect, or repair the missing node.
-
Degraded (Disk Failure): A hard disk of the secondary node is not functioning properly and must be replaced. To request a replacement hard disk and for details on replacing the hard disk, contact our Support Team.
-
Degraded Sync: Two SPS units were joined to High Availability mode, and the first-time synchronization of the disks is currently in progress. Wait for the synchronization to complete. Note that in case of large disks with lots of stored data, synchronizing the disks can take several hours.
-
Split brain: The two nodes lost the connection to each other, with the possibility of both nodes being active nodes (that is, primary nodes) for a time.
Caution: Hazard of data loss In this case, valuable audit trails might be available on both SPS nodes, so special care must be taken to avoid data loss. For details on solving this problem, see Recovering from a split brain situation.
Do NOT reboot or shut down the nodes.
-
Invalidated: The data on one of the nodes is considered out-of-sync and should be updated with data from the other node. This state usually occurs during the recovery of a split-brain situation when the DRBD is manually invalidated.
-
Converted: After converting nodes to a cluster (clicking Convert to Cluster) or enabling High Availability mode (clicking Join HA) and before rebooting the node(s).
|
|
NOTE:
If you experience problems because the nodes of the HA cluster do not find each other during system startup, navigate to Basic Settings > High Availability and select HA (Fix current). That way the IP address of the HA interfaces of the nodes will be fix, which helps if the HA connection between the nodes is slow. |
The DRBD status field indicates whether the latest data (including SPS configuration,
The DRBD status field also indicates the connection between the disk system of the SPS nodes. The following statuses are possible:
-
Connected: Both nodes are functioning properly.
-
Connected (Disk Failure): A hard disk of the secondary node is not functioning properly and must be replaced. To request a replacement hard disk and for details on replacing the hard disk, contact our Support Team.
-
Invalidated: The data on one of the nodes is considered out-of-sync and should be updated with data from the other node. This state usually occurs during the recovery of a split-brain situation when the DRBD is manually invalidated.
-
Sync source or Sync target: One node (Sync target) is downloading data from the other node (Sync source).
When synchronizing data, the progress and the remaining time is displayed in the System monitor.
Caution: When the two nodes are synchronizing data, do not reboot or shutdown the primary node. If you absolutely must shutdown the primary node during synchronization, shutdown the secondary node first, and then the primary node.
-
Split brain: The two nodes lost the connection to each other, with the possibility of both nodes being active nodes (that is, primary nodes) for a time.
Caution: Hazard of data loss In this case, valuable audit trails might be available on both SPS nodes, so special care must be taken to avoid data loss. For details on solving this problem, see Recovering from a split brain situation.
-
WFConnection: One node is waiting for the other node, the connection between the nodes has not been established yet.
If a redundant heartbeat interface is configured, its status is also displayed in the Redundant Heartbeat status field, and also in the HA > Redundant field of the System monitor. For a description of redundant heartbeat interfaces, see Redundant heartbeat interfaces.
The possible status messages are explained below.
-
NOT USED: There are no redundant heartbeat interfaces configured.
-
OK: Normal operation, every redundant heartbeat interface is working properly.
-
DEGRADED-WORKING: Two or more redundant heartbeat interfaces are configured, and at least one of them is functioning properly. This status is displayed also when a new redundant heartbeat interface has been configured, but the nodes of the SPS cluster has not been restarted yet.
-
DEGRADED: The connection between the redundant heartbeat interfaces has been lost. Investigate the problem to restore the connection.
-
INVALID: An error occurred with the redundant heartbeat interfaces. Contact the One Identity Support Team for help. For assistance, contact our Support Team.