Use the Active Roles Configuration Center to view or modify the tenant type of an existing Azure tenant. This is useful if you need to change the default domain settings of an Azure tenant due to an IT or organizational change.
NOTE: Consider the following limitations when modifying the properties of the selected Azure tenant:
-
If you set the tenant type of your Azure tenant to Federated Domain or Synchronized Identity Domain, then the Azure properties fields of the objects (Azure users, Azure guest users, groups and contacts) in the Azure tenant will be disabled and cannot be edited in the Active Roles Web Interface.
-
You cannot modify the Tenant name, Tenant ID, Tenant Environment Type and authentication settings of the Azure tenant.
To view or modify the Azure tenant properties
-
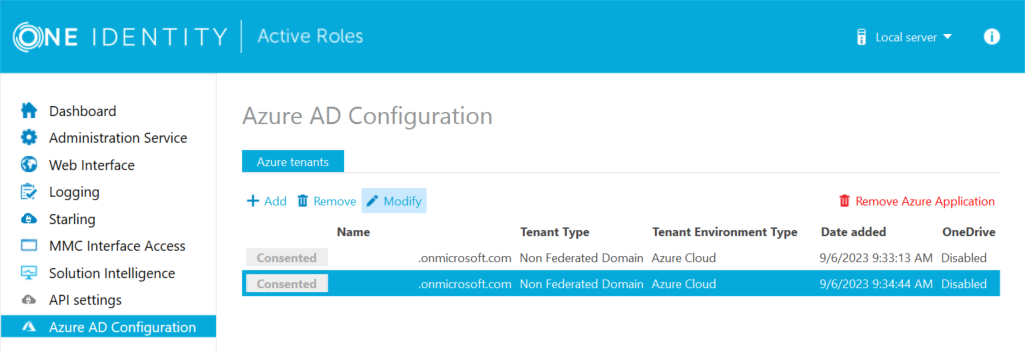
In the Active Roles Configuration Center, on the left pane, click Azure AD Configuration.
The list of existing Azure tenants appears.
-
Select the Azure tenant you want to view or modify, then click Modify.
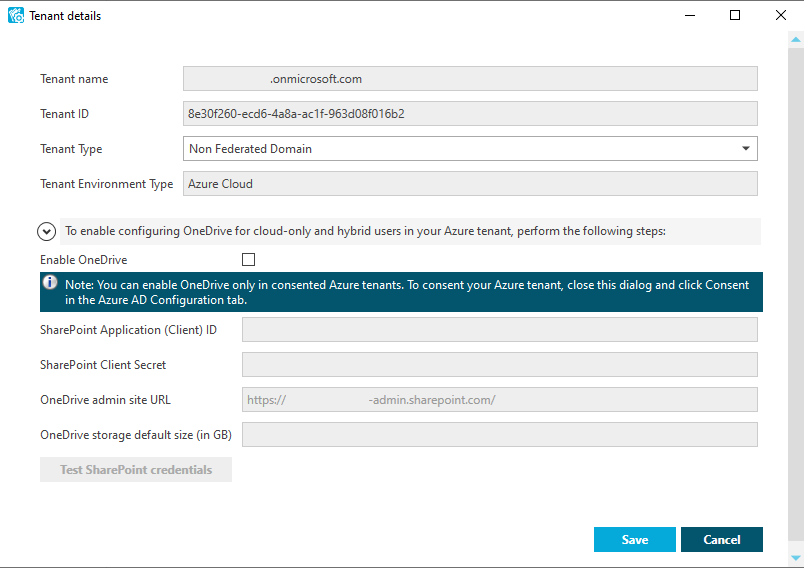
The Tenant details window appears.
-
(Optional) To change the Tenant type of the Azure tenant, select the applicable type from the drop-down list.
-
Non-Federated Domain: When selected, on-premises domains are not registered in Azure AD , and Azure AD Connect is not configured. Azure users and Azure guest users are typically created with the onmicrosoft.com UPN suffix.
-
Federated Domain: On-premises domains are registered in Azure AD and Azure AD Connect. Also, Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) is configured. Azure users and Azure guest users are typically created with the UPN suffix of the selected on-premises domain.
-
Synchronized Identity Domain: On-premises domains may or may not be registered in Azure AD. Azure AD Connect is configured. Azure users and Azure guest users can be created either with the selected on-premises domain, or with the onmicrosoft.com UPN suffix.
-
-
(Optional) To enable, disable or modify the provisioned OneDrive storage of the Azure tenant, select or clear Enable OneDrive, and (when selected), configure the SharePoint and OneDrive settings listed in the Tenant details window. For more information on configuring OneDrive storage in an Azure tenant, see Enabling OneDrive in an Azure tenant.
-
To close the Tenant details window without any changes, click Cancel. To apply your changes, click Save.