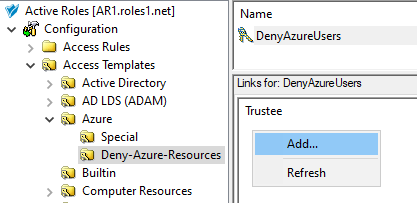
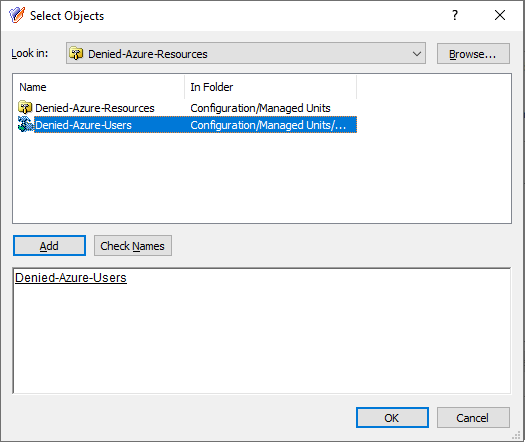
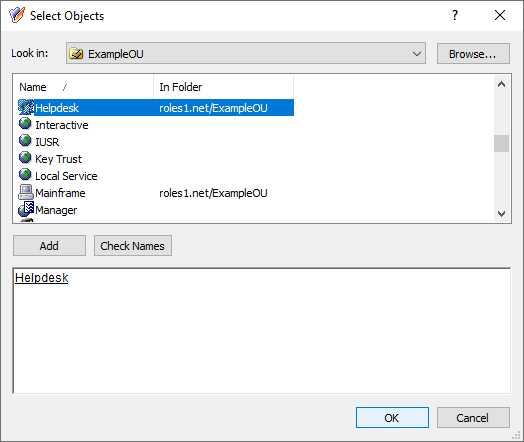
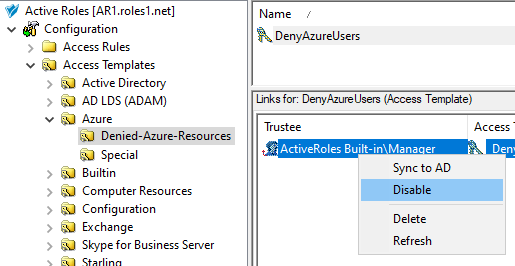
This scenario describes how to use the Managed Units (MUs) and Access Templates (ATs) of the Active Roles Console together to configure Azure user administration permissions with high granularity. In this example, the MUs and ATs are used to deny the read access of a group of helpdesk users to Azure users reporting to a specific manager. You can achieve this by:
-
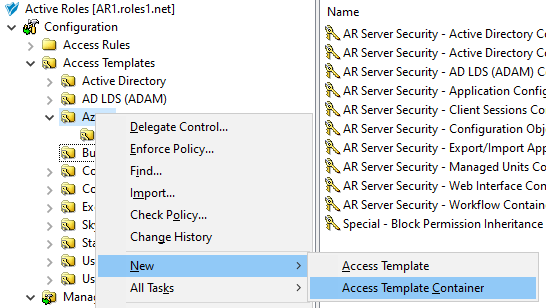
Configuring an MU containing all the Azure users that the helpdesk users should not access. For more information on this procedure, see Configuring a Managed Unit to hide specific Azure users.
-
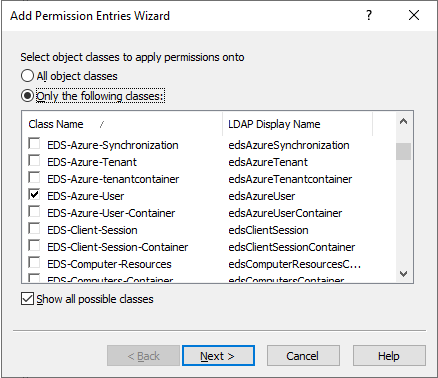
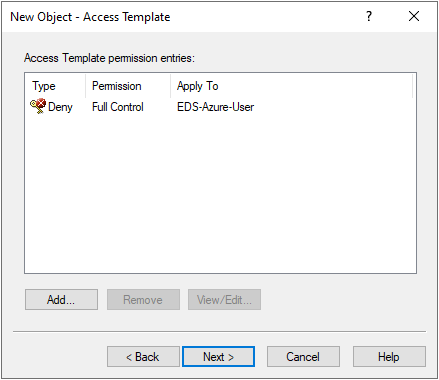
Configuring an AT to deny access to those Azure users for the helpdesk users. For more information on this procedure, see Configuring an Access Template to hide Azure users.
Prerequisites
To configure this example scenario, your organization must meet the following requirements:
-
To create MUs and ATs in the Active Roles Console, you must use an Active Roles Administration Service account. For more information, see Configuring the Administration Service account in the Active Roles Quick Start Guide.
-
The organization must already have one or more Azure tenants configured and consented for use with Active Roles. For more information, see Configuring a new Azure tenant and consenting Active Roles as an Azure application.
-
To ensure that the Helpdesk group receiving the granular read permission can still read other Azure users, the group must have the built-in Azure Cloud User - Read All Attributes AT (or a custom AT based on this built-in AT) applied to them, with the affected Object being the Azure tenant of the managed Azure AD resources. For more information on how to apply an AT, see Applying Access Templates.
-
The users receiving the configured permissions must be on-premises or hybrid Active Directory users. You cannot delegate the configured granular permission to cloud-only Azure users.

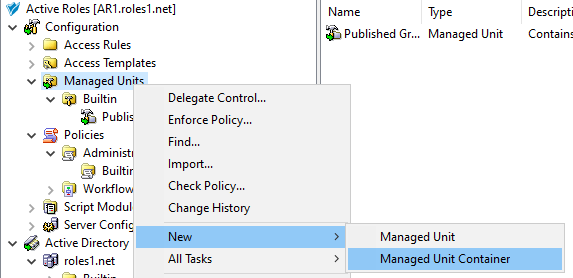
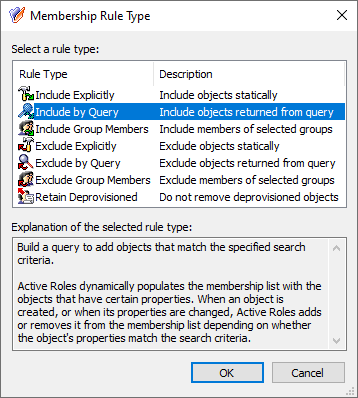
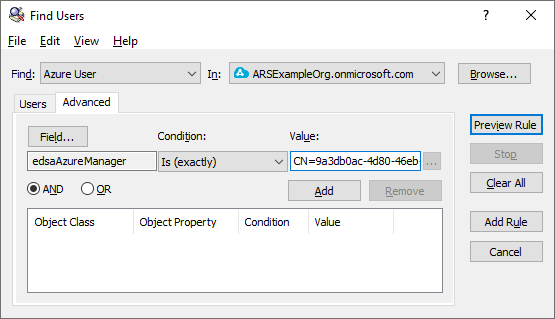
 (Browse) button and selecting it from the Azure Users container. Once selected, the distinguished name of the Azure user appears in the Value text box.
(Browse) button and selecting it from the Azure Users container. Once selected, the distinguished name of the Azure user appears in the Value text box.