Configuring an unmanaged domain
You can configure an unmanaged domain by applying the Built-in Policy - Exclude from Managed Scope Policy Object in the Active Roles console.
To configure an unmanaged domain
- In the console tree, under the Active Directory node, right-click the domain you want to configure, and click Enforce Policy.
- Click Add in the dialog box that appears, and then select the Built-in Policy - Exclude from Managed Scope Policy Object.
- Click OK to close the dialog boxes.
Once applied to a domain, the Built-in Policy - Exclude from Managed Scope Policy Object stops product usage statistics from counting objects in the domain and prevents any changes to the objects held in that domain, making the objects available for read access only. For more information, see Managed scope to control product usage.
Evaluating product usage
Active Roles provides a predefined collection of statistics that helps you understand how many Active Directory domain users, AD LDS, Azure, and SaaS users are managed by this product over time. By analyzing this statistical data, you can establish a baseline of product usage, verify your current Active Roles licensing compliance, and plan for future licensing needs. Since Active Roles’ license fee is calculated based on the number of managed users, product usage statistics enables you to justify and predict your Active Roles licensing expenditures. For instructions on how to examine product usage, see Viewing product usage statistics.
For each Active Directory domain, AD LDS instance, Azure tenants, and SaaS applications registered with Active Roles, product usage data is collected on a scheduled basis by counting the number of enabled users in that domain, instance, registered Azure tenants, and connected SaaS applications with the resulting counts stored in the Active Roles database. For further details, see Scheduled task to count managed objects.
By default, Active Roles counts users in the entire domain or instance. It is possible to have Active Roles count users within a part of a domain or instance by changing managed scope—a tunable collection of containers assumed to hold the managed users. For further details, see Managed scope to control product usage.
Active Roles counts the managed objects on a scheduled basis, and provides a report of managed object statistics. This does not impose any restrictions on the number of objects managed by Active Roles. However, as the number of the managed objects is a key factor in determining the license fee, you may need to ensure that your managed object count does not exceed a certain limit. For this purpose, you can configure Active Roles to check the number of managed objects and send an e-mail notification if the total number of managed objects exceeds a given threshold value. For further details, see Voluntary thresholds for the managed object count.
Viewing product usage statistics
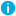
You can view the current total number of managed users on the root page in the Active Roles console. Select the console tree root to open the root page in the details pane, and then expand the Product Usage Statistics area on that page. The count of objects under Active Directory Domains, AD LDS Directory Partitions, Azure tenants, and SaaS application represents the current number of managed domain users , managed AD LDS users, Azure hybrid users, Azure cloud only users, Azure guest users, and SaaS users respectively.
|
|
NOTE: The count can be derived using the LDAP query “(&(objectCategory=person)(objectClass=user))”. |
It is possible to view the average or maximum number of managed users in each domain or instance for a certain reporting period. Click Product Usage Statistics to open a page allowing you to:
- Choose the reporting period.
The page displays options to export data in HTML format and as raw counters for the period you choose from the Reporting period options, such as past month, past half-year, past year, or a custom date range.
- Examine the managed user counts for the reporting period you’ve chosen.
The page displays the current number of managed users per Active Directory domain, AD LDS directory partition, Azure tenant, and SaaS application in the tables under Total accounts. The Average and the maximum values along with the total number of managed users can be viewed in the HTML file.
License type and Total estimated licenses, display the type of license in use and the number of estimated license required, respectively.
- View the information about the license.
Click License description to view a detailed information about the license.
- Save the contents of the page as an HTML file.
Click Save as HTML at the bottom of the page and specify the desired file name and location.
- Export the raw statistical data to a file.
Click Export raw counters at the bottom of the page and specify the desired file name and location. The data is exported in the comma-delimited (CSV) format, representing the daily counts of managed users over the reporting period.
Delegating access to the managed object statistics
By default, only Active Roles Admin role holders have permission to view managed object statistics. Active Roles provides the following Access Templates for delegating that task:
You can find these two Access Templates in the Configuration/Access Templates/Configuration container in the Active Roles console.

