View or modify Email Address settings
For an existing Office 365 user, you can use the E-mail Address settings tab in the Exchange Online Properties wizard to view or set the email address settings.
|
|
IMPORTANT: The modify option is applicable for Office 365 users on a non-federated environment only. |
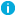
To view or modify the email address settings for an Azure AD user
- In the Exchange Online Properties wizard of an Office 365 user, click E-mail Settings.
-
To add email addresses, click Add.
-
In the E-mail Addresses dialog box, select the email address type, add the email address, and click OK.
-
To modify a selected email address, click Edit.
-
In the E-mail Addresses dialog box, edit the selected email address, and click OK.
-
To delete a selected email address, click Remove.
- Click Save.
- Close the dialog box and click Save.
|

|
NOTE: The changes made to email address settings for the Office 365 user can be verified in the Microsoft Office 365 portal. |
View or modify Mailbox features
You can use the Exchange Features tab to manage a variety of mailbox features for the Office 365 mailbox user.
To view or modify the Mailbox features for an Office 365 user
-
In the Exchange Online Properties wizard of an Office 365 user, click Mailbox Features.
The following mailbox features are displayed and can be managed for the Office 365 mailbox user:
- Exchange ActiveSync: Allows the user to access the mailbox from a mobile device.
- Outlook Web App: Allows the user to browse the mailbox with a cell phone or other wireless devices.
- MAPI: Allows the user to access the mailbox from a MAPI client such as Microsoft Outlook.
- IMAP4: Allows the user to access the mailbox from an IMAP4 client such as Outlook Express.
- POP3: Allows the user to access the mailbox from a POP3 client such as Outlook Express.
- Archive: If the mailbox is archive-enabled, you can view or change the archive properties.
-
Under Mailbox Features, select the required feature you want to enable or disable for the Office 365 mailbox user, and then click Enable or Disable respectively.
-
Click Save.
-
Close the dialog box and click Save.
|

|
NOTE: The changes made to MailBox Features for the Office 365 mailbox user can be verified in the Microsoft Office 365 portal. |
Specify Archive Mailbox name
You can use the Exchange Features tab to view, modify, or specify the archive mailbox name of an archive-enabled Office 365 mailbox user.
To view, modify, or specify the archive mailbox name of an archive-enabled Office 365 mailbox user
-
In the Exchange Online Properties wizard of an Office 365 user, click Mailbox Features.
-
Under Mailbox Features, select Archive, click Enable, and then click Save.
- Click Properties.
The Exchange Online Archive Mailbox wizard is displayed, which allows you to view or modify the archive name derived from the Microsoft Office 365 portal and displayed in the Specify a name for this archive field.
- Click OK, close the dialog box, and then click Save.
-
To specify a new name to the archive, select Archive, click Enable, and then click Properties.
- On the Exchange Online Archive Mailbox wizard, in the Specify a name for this archive field, provide a name for the archive.
- Click OK, close the dialog box, and then click Save.
|

|
NOTE: The changes made to MailBox Features for the Office 365 mailbox user can be verified in the Microsoft Office 365 portal. |
View or modify Mailbox settings
View or modify the Mailbox settings for an Office 365 User
For an existing Office 365 user, you can use the Mailbox settings tab in the Exchange Online Properties wizard to view or modify the messaging records management settings.
|

|
NOTE: The modify option is applicable for Office 365 users on all environments, such as, Federated, Synchronized and non-federated. |
To view or modify the messaging records management settings for an Office 365 user
- In the Exchange Online Properties wizard of an Office 365 user, click Mailbox Settings.
-
To place the user mailbox on litigation hold, make sure that the Exchange Online Plan 2 license is enabled for the Office 365 user.
For information on enabling Office 365 licenses for a user, see Create a new Azure AD user.
- Under Messaging Records Management, click Properties, and then select the Enable litigation hold check box.
An error is displayed if the Exchange Online Plan 2 license is not enabled for the user.
-
In the Messaging records management description URL text box, enter URL of the location where the deleted mailbox items are preserved and changes made to mailbox items are recorded.
-
In the Comments text box, enter the mailbox comments, and click Save.
A message is displayed confirming the success of the operation.
- Close the dialog box and click Save.
|

|
NOTE: The changes made to Mailbox settings for the Office 365 user can be verified in the Microsoft Office 365 portal. |

